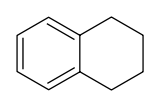
Tetralin
| Tetralin | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| IUPAC name 1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene | |
| Other names naphthalene 1,2,3,4-tetrahydride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 119-64-2 |
| PubChem | 8404 |
| ChemSpider | 8097 |
| UNII | FT6XMI58YQ |
| KEGG | C14114 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:35008 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C10H12 |
| Molar mass | 132.20 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.970 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | −35.8 °C; −32.4 °F; 237.3 K |
| Boiling point | 206 to 208 °C; 403 to 406 °F; 479 to 481 K |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| Viscosity | 2.02 cP at 25 °C[1] |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | JT Baker MSDS |
| Flash point | 77 °C; 171 °F; 350 K |
| Autoignition temperature | 385 °C; 725 °F; 658 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Tetralin (1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene) is a hydrocarbon having the chemical formula C10H12. This molecule is similar to the naphthalene chemical structure except that one ring is saturated.
The compound can be synthesized in a Bergman cyclization. In a classic named reaction called the Darzens tetralin synthesis (Auguste George Darzens (1867–1954), 1926) derivatives can be prepared by intramolecular ring-closing reaction of an 1-aryl-4-pentene with concentrated sulfuric acid,[2] or simply through the hydrogenation of naphthalene in the presence of a platinum catalyst.

Production
Tetralin is produced by the catalytic hydrogenation of naphthalene.

A large amount of work has been devoted to the hydrogenation of naphthalene into tetralin. Mixtures containing different proportions of naphthalene, tetralin, and decalin can be produced depending on the pressure and temperature of the process. Tetralin has been obtained from pressed naphthalene isolated from coke tar by hydrogenating it over commercial catalyst WS2 + NiS + Al2O3 and CoO + MoO3 + Al2O3 under pressure of 50–300 atm. The extent to which naphthalene is hydrogenated at pressures up to 60–70 atm is determined by catalyst activity; it is maximum if CoO + MoO3 + Al2O3 or WS2 + NiS + Al2O3 catalyst are used at 300–370 °C.[3]
Uses
Tetralin is used as a solvent.
See also
References
- ↑ Gonçalves, F. A.; Hamano, K.; Sengers, J. V. (1989). "Density and viscosity of tetralin and trans-decalin". International Journal of Thermophysics 10 (4): 845. doi:10.1007/BF00514480.
- ↑ Darzens Synthesis of Tetralin Derivatives. chempensoftware.com
- ↑ Krichko, A. A.; Skvortsov, D. V.; Titova, T. A.; Filippov, B. S.; Dogadkina, N. E. (1969). "Production of tetralin by the hydrogenation of naphthalene-containing fractions". Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils 5: 18. doi:10.1007/BF00727949.