Tetraethylmethane
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Tetraethylmethane | |
|---|---|
 | |
 |
 |
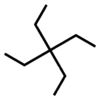
| IUPAC name 3,3-Diethylpentane[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 1067-20-5 |
| PubChem | 14020 |
| ChemSpider | 13402 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C9H20 |
| Molar mass | 128.26 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colourless liquid |
| Odor | Odourless |
| Density | 724 mg mL−1 |
| Melting point | −34 to −30 °C; −29 to −22 °F; 239 to 243 K |
| Boiling point | 145.8 to 146.6 °C; 294.3 to 295.8 °F; 418.9 to 419.7 K |
| kH | 1.5 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of combustion ΔcH |
−6.1261–−6.1229 MJ mol−1 |
| Standard molar entropy S |
333.4 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Specific heat capacity, C | 278.2 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 |
 3
0
0
|
| Related compounds | |
| Related alkanes | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Tetraethylmethane is a branched alkane with 9 carbon atoms. It is a highly flammable and volatile liquid at room temperature.
References
- ↑ "Tetraethylmethane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
See also
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.