Tetraazidomethane
| Tetraazidomethane | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| IUPAC name Tetraazidomethane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 869384-16-7 |
| PubChem | 16059578 |
| ChemSpider | 17219283 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[N-]=[N+]=N\C(\N=[N+]=[N-])(\N=[N+]=[N-])\N=[N+]=[N-]|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | CN12 |
| Molar mass | 180.09 g/mol |
| Boiling point | ~165 °C (estimate) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Tetraazidomethane is a colorless, highly explosive liquid. Its chemical structure consists of a carbon atom substituted with four azide functional groups.
Synthesis
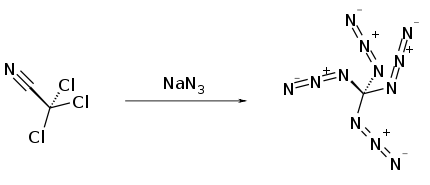
It was first prepared by Klaus Banert in 2006 by reaction of trichloroacetonitrile with sodium azide.[1]
Uses
As with other polyazides, tetraazidomethane has interest as a high-energy-density material with potential uses in explosives, propellants, or fireworks.[2] Silicon tetraazide is also a known compound.
Reactions
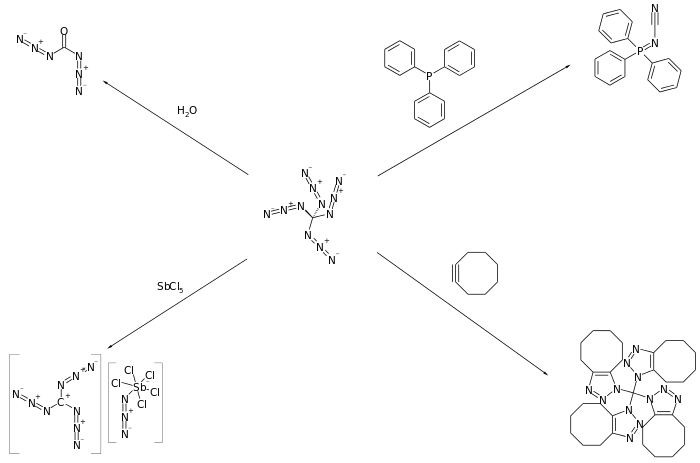
Banert has reported that tetraazidomethane participates in a number of surprising reactions including hydrolysis, cycloaddition reactions with alkenes and alkynes, and reaction with phosphines to form phosphazenes.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "The Exciting Chemistry of Tetraazidomethane", Klaus Banert, Young-Hyuk Joo, Tobias Ruffer, Bernhard Walfort, and Heinrich Lang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1168–1171. doi:10.1002/anie.200603960
- ↑ "Tetraazidomethane: Chemistry with a Bang", Chemical & Engineering News, Dec. 18, 2006, 46.