Tentoxin
| Tentoxin | |
|---|---|
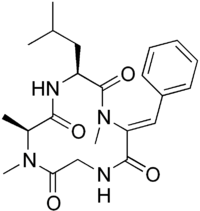 | |
| IUPAC name Cyclo(N-methyl-L-alanyl-L-leucyl-alpha,beta- | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 28540-82-1 |
| PubChem | 5281143 |
| ChemSpider | 4444584 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O=C1N[C@H](C(=O)N(/C(C(=O)NCC(=O)N(C)[C@H]1C)=C\c2ccccc2)C)CC(C)C|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C22H30N4O4 |
| Molar mass | 414.498 g/mol |
| Melting point | 172–175 °C |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Tentoxin is a natural cyclic tetrapeptide produced by phytopathogenic fungus Alternaria alternata. It selectively induces chlorosis in several germinating seedling plants. Therefore, tentoxin may be used as a potential natural herbicide.
Tentoxin was first isolated from Alternaria alternata (syn. tenuis) and characterized by George Templeton et al. in 1967.[1]
Tentoxin has also been used in recent research to eliminate the polyphenol oxidase (PPO) activity from seedlings of higher plants.[2]
References
- ↑ Templeton, G. E., C. 1. Grable, N. D. Fulton, W. L. Meyer. 1967. Tentoxin from Alternaria tenuis: its isolation and characterization. Proceedings of the Mycotoxin Research Seminar, Washington, D. C., June 8–9, 1967. United States Department of Agriculture. pp. 27-29
- ↑ Duke, S.O. & Vaughn, K.C. 1982. Lack of involvement of polyphenol oxidase in ortho-hydroxylation of phenolic compounds in mung bean seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 54: 381-385.
External MSDS
- Tentoxin MSDS from Fermentek