Technetium hexafluoride
| Technetium(VI) fluoride | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 13842-93-8 | |
| Properties | ||
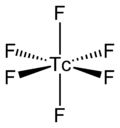
| Molecular formula | TcF6 | |
| Molar mass | 212 g/mol (98Tc) | |
| Appearance | golden-yellow crystals[1] | |
| Density | 3,58 g/cm³ (−140 °C), solid[2] | |
| Melting point | 37.4 °C[1] | |
| Boiling point | 55.3 °C[1] | |
| Structure | ||
| Crystal structure | cubic | |
| Hazards | ||
| EU classification | not listed | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Technetium hexafluoride or technetium(VI) fluoride (TcF6) is a yellow inorganic compound with a low melting point. It was first identified in 1961.[3] In this compound, technetium has an oxidation state of +6, the highest oxidation state found in the technetium halides. The other such compound is technetium(VI) chloride, TcCl6. In this respect, technetium differs from rhenium, which forms a heptafluoride, ReF7.[4] Technetium hexafluoride occurs as an impurity in uranium hexafluoride, as technetium is a fission product of uranium.
Preparation
Technetium hexafluoride is prepared by heating technetium metal with an excess of F2 at 400 °C.[3]
- Tc + 3 F
2 → TcF
6
Description
Technetium hexafluoride is a golden-yellow solid at room temperature. Its melting point is 37.4 °C and its boiling point is 55.3 °C.[1]
Technetium hexafluoride undergoes a solid phase transition at −4.54 °C. Above this temperature (measured at 10 °C), the solid structure is cubic. Lattice parameters are a = 6.16 Å. There are two formula units (in this case, discrete molecules) per unit cell, giving a density of 3.02 g·cm−3. Below this temperature (measured at −19 °C), the solid structure is orthorhombic space group Pnma. Lattice parameters are a = 9.55 Å, b = 8.74 Å, and c = 5.02 Å. There are four formula units (in this case, discrete molecules) per unit cell, giving a density of 3.38 g·cm−3. At −140 °C, the solid structure is still orthothombic, but the lattice parameters are now a = 9.360 Å, b = 8.517 Å, and c = 4.934 Å, giving a density of 3.58 g·cm−3.[2]
The TcF6 molecule itself (the form important for the liquid or gas phase) has octahedral molecular geometry, which has point group (Oh). The Tc–F bond length is 1.812 Å.[2] Its magnetic moment has been measured to be 0.45 μB.[5]
Properties
Physical
TcF6 is octahedral, as shown by infrared and Raman spectra.[6][7] Its low-temperature orthorhombic form converts to the higher symmetry body-centred cubic form at room temperature, like other metal hexafluorides such as RhF6 and OsF6.[8] Preliminary measurements of magnetic moment yield a value of 0.45 µB, which is lower than expected for a d1 octahedral compound.[9]
Chemical
TcF6 reacts with alkaline chlorides in iodine pentafluoride (IF5) solution to form hexafluorotechnetates.[10][11] TcF6 disproportionates on hydrolysis with aqueous NaOH to form a black precipitate of TcO2.[3] In hydrogen fluoride solution, TcF6 reacts with hydrazinium fluoride to yield N2H6TcF6 or N2H6(TcF6)2.[12]
References
- This article incorporates information from the German Wikipedia.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 90th Edition, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2009, ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0, Section 4, Physical Constants of Inorganic Compounds, p. 4-93.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 T. Drews, J. Supeł, A. Hagenbach, K. Seppelt: "Solid State Molecular Structures of Transition Metal Hexafluorides", Inorganic Chemistry, 2006, 45 (9), S. 3782–3788; doi:10.1021/ic052029f; PMID 16634614.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Selig, H.; Chernick, C.L.; Malm, J.G. (1961). "The Preparation and Properties of TcF6". J. Inorg. & Nuclear Chem. 19 (3–4): 377–381.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0080379419.
- ↑ Henry Selig, Fred A. Cafasso, Dieter M. Gruen, John G. Malm: "Magnetic Susceptibility of ReF6", in: Journal of Chemical Physics, 1962, 36 (12), S. 3440–3444; doi:10.1063/1.1732477.
- ↑ Howard H. Claassen, Henry Selig, and John G. Malm (1962). "Vibrational Spectra of MoF6 and TcF6". J. Chem. Phys. 36 (11): 2888–2890. doi:10.1063/1.1732396.
- ↑ Howard H. Claassen, Gordon L. Goodman, John H. Holloway, and Henry Selig (1970). "Raman Spectra of MoF6, TcF6, ReF6, UF6, SF6, SeF6, and TeF6 in the Vapor State". J. Chem. Phys. 53 (1): 341–348. doi:10.1063/1.1673786.
- ↑ Siegel S and Northrop D A (1966). "X-Ray Diffraction Studies of Some Transition Metal Hexafluorides". Inorg. Chem. 5 (12): 2187–2188. doi:10.1021/ic50046a025.
- ↑ Selig, H; Cafasso, F A.; Gruen, D M.; Malm, J G. (1962). "Magnetic Susceptibility of ReF6". Journal of Chemical Physics 36 (12): 3440–3444. doi:10.1063/1.1732477.
- ↑ Edwards, A. J.; Hugill, D.; Peacock, R. D. (1963). "New Fluorine Compounds of Technetium". A. J. Edwards, D. Hugill & R. D. Peacock 200 (4907): 672. doi:10.1038/200672a0.
- ↑ D. Hugill and R. D. Peacock (1966). "Some quinquevalent fluorotechnetates". J. Chem. Soc. A: 1339–1341. doi:10.1039/J19660001339.
- ↑ Frlec B, Selig H, and Hyman H.H (1967). "Hydrazinium(+2) Hexafluorometalates(IV) and -(V) in the 4d and 5d Transition Series". Inorg Chem 6 (10): 1775–1783. doi:10.1021/ic50056a004.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||