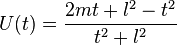Taub–NUT space
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| General relativity |
|---|
  |
|
Introduction Mathematical formulation Resources · Tests |
|
Fundamental concepts |
|
Phenomena |
|
Equations |
|
Advanced theories |
|
Scientists Einstein · Lorentz · Hilbert · Poincaré · Schwarzschild · Sitter · Reissner · Nordström · Weyl · Eddington · Friedman · Milne · Zwicky · Lemaître · Gödel · Wheeler · Robertson · Bardeen · Walker · Kerr · Chandrasekhar · Ehlers · Penrose · Hawking · Taylor · Hulse · Stockum · Taub · Newman · Yau · Thorne others |
The Taub–NUT space (/tɑːb nʌt/[1] or /tɑːb ɛnjuːˈtiː/) is an exact solution to Einstein's equations, a model universe formulated in the framework of general relativity.
The Taub–NUT metric was found by Abraham Haskel Taub (1951), and extended to a larger manifold by E. Newman, L. Tamburino, and T. Unti (1963), whose initials form the "NUT" of "Taub–NUT".
Taub's solution is an empty space solution of Einstein's equations with topology R×S3 and metric
where
and m and l are positive constants.
Taub's metric has coordinate singularities at U=0, t=m+(m2+l2)1/2, and Newman, Tamburino and Unti showed how to extend the metric across these surfaces.
References
- ↑ McGraw-Hill Science & Technology Dictionary: "Taub NUT space"
- Newman, E.; Tamburino, L.; Unti, T. (1963), "Empty-space generalization of the Schwarzschild metric", Journal of Mathematical Physics 4: 915–923, Bibcode:1963JMP.....4..915N, doi:10.1063/1.1704018, ISSN 0022-2488, MR 0152345
- Taub, A. H. (1951), "Empty space-times admitting a three parameter group of motions", Annals of Mathematics. Second Series 53: 472–490, ISSN 0003-486X, MR 0041565JSTOR 1969567
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.