Taiga shrew
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Taiga shrew[1] | |
|---|---|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Soricomorpha |
| Family: | Soricidae |
| Genus: | Sorex |
| Species: | S. isodon |
| Binomial name | |
| Sorex isodon Turov, 1924 | |
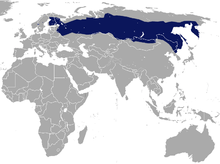 | |
| Taiga shrew range | |
The taiga shrew (Sorex isodon), also known as the even-toothed shrew can achieve a body length of about 67 millimeters, with a tail of about 43 millimeters. This shrew is very similar to the long-clawed shrew. This species inhabits forested mountain valleys, and is found across northern Eurasia. It ranges from the Baltic Sea area through the Lake Baikal region of Siberia into the Russian Far East and along the Baekdudaegan mountains of the Korean Peninsula.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Hutterer, R. (2005). Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M, eds. Mammal Species of the World (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 289–290. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ↑ Amori, G., Henttonen, H., Stubbe, M., Samiya, R., Ariunbold, J., Buuveibaatar, V., Dorjderem, S., Monkhzul, Ts., Otgonbaatar, M., Tsogbadrakh, M. & Gankhuyag, P. (2008). "Sorex isodon". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2010.4. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- ↑ Won, Byeong-o (원병오) (2004). 한국의 포유동물 (Hangugui poyudongmul, Mammals of Korea). Seoul: Dongbang Media. ISBN 89-8457-310-8.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.
