TROX-1
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
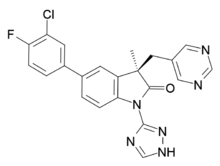 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (3R)-5-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-3-methyl-3-(pyrimidin-5-ylmethyl)-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-one | |
| Clinical data | |
| Legal status | ? |
| Identifiers | |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | CID 25256198 |
| ChemSpider | 24750794 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C22H16ClFN6O |
| Mol. mass | 434.853 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
TROX-1 is a drug which acts as a potent blocker of the Cav2 type calcium channels. It was developed as a potential analgesic after the discovery that the selective Cav2.2 blocker ziconotide is an active analgesic with similar efficacy to strong opioid drugs but comparatively milder side effects. Unlike ziconotide, TROX-1 is not so selective, and also blocks the Cav2.1 and Cav2.3 calcium channel subtypes, but it has the great advantage of being orally active, whereas ziconotide must be administered intrathecally, by injection into the spinal fluid. In animal studies of TROX-1, analgesic effects were observed with similar efficacy to NSAIDs such as naproxen or diclofenac, and anti-allodynia effects equivalent to pregabalin or duloxetine.[1]
References
- ↑ Abbadie C, McManus OB, Sun SY, Bugianesi RM, Dai G, Haedo RJ, Herrington JB, Kaczorowski GJ, Smith MM, Swensen AM, Warren VA, Williams B, Arneric SP, Eduljee C, Snutch TP, Tringham EW, Jochnowitz N, Liang A, Euan MacIntyre D, McGowan E, Mistry S, White VV, Hoyt SB, London C, Lyons KA, Bunting PB, Volksdorf S, Duffy JL (August 2010). "Analgesic effects of a substituted N-triazole oxindole (TROX-1), a state-dependent, voltage-gated calcium channel 2 blocker". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 334 (2): 545–55. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.166363. PMID 20439438.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.