T-HCA
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
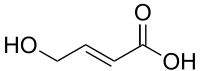
| (2E)-4-hydroxybut-2-enoic acid | |
| Clinical data | |
| Legal status | ? |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 24587-49-3 |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | CID 6155526 |
| ChemSpider | 4825947 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL507046 |
| Synonyms | trans-4-hydroxycrotonic acid |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C4H6O3 |
| Mol. mass | 102.09 g/mol |
| SMILES
| |
| |
| | |
T-HCA, or trans-4-hydroxycrotonic acid, is a drug used in scientific research. It is structurally related to GHB and binds to the GHB receptor with 4-fold higher affinity than GHB itself,[1] but is not an agonist for the primary sedative target of GHB, the GABAB receptor, and so does not produce sedative effects, instead causing convulsions thought to be mediated through increased glutamate release.[2] It may also be naturally produced in the mammalian CNS and is suspected to be an endogenous ligand for the GHB receptor.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Wellendorph P, Høg S, Greenwood JR, de Lichtenberg A, Nielsen B, Frølund B, Brehm L, Clausen RP, Bräuner-Osborne H (2005). "Novel Cyclic γ-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) Analogs with High Affinity and Stereoselectivity of Binding to GHB Sites in Rat Brain" (pdf). The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 315 (1): 346–351. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.090472. PMID 16014570.
- ↑ Castelli MP, Ferraro L, Mocci I, et al. (2003). "Selective γ-hydroxybutyric acid receptor ligands increase extracellular glutamate in the hippocampus, but fail to activate G protein and to produce the sedative/hypnotic effect of γ-hydroxybutyric acid". Journal of Neurochemistry 87 (3): 722–732. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02037.x. PMID 14535954.
- ↑ Vayer P, Dessort D, Bourguignon JJ, Wermuth CG, Mandel P, Maitre M (1985). "Natural occurrence of trans-γ hydroxycrotonic acid in rat brain". Biochemical Pharmacology 34 (13): 2401–2404. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(85)90804-4. PMID 4015683.
| ||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.