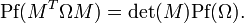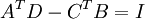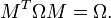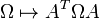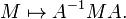Symplectic matrix
In mathematics, a symplectic matrix is a 2n×2n matrix M with real entries that satisfies the condition
-
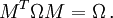
(1)
where MT denotes the transpose of M and Ω is a fixed 2n×2n nonsingular, skew-symmetric matrix. This definition can be extended to 2n×2n matrices with entries in other fields, e.g. the complex numbers.
Typically Ω is chosen to be the block matrix
where In is the n×n identity matrix. The matrix Ω has determinant +1 and has an inverse given by Ω−1 = ΩT = −Ω.
Every symplectic matrix has unit determinant, and the 2n×2n symplectic matrices with real entries form a subgroup of the special linear group SL(2n, R) under matrix multiplication, specifically a connected noncompact real Lie group of real dimension n(2n + 1), the symplectic group Sp(2n, R). The symplectic group can be defined as the set of linear transformations that preserve the symplectic form of a real symplectic vector space.
Properties
Every symplectic matrix is invertible with the inverse matrix given by
Furthermore, the product of two symplectic matrices is, again, a symplectic matrix. This gives the set of all symplectic matrices the structure of a group. There exists a natural manifold structure on this group which makes it into a (real or complex) Lie group called the symplectic group. The symplectic group has dimension n(2n + 1).
It follows easily from the definition that the determinant of any symplectic matrix is ±1. Actually, it turns out that the determinant is always +1. One way to see this is through the use of the Pfaffian and the identity
Since 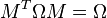 and
and 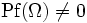 we have that det(M) = 1.
we have that det(M) = 1.
Suppose Ω is given in the standard form and let M be a 2n×2n block matrix given by
where A, B, C, D are n×n matrices. The condition for M to be symplectic is equivalent to the conditions
When n = 1 these conditions reduce to the single condition det(M) = 1. Thus a 2×2 matrix is symplectic iff it has unit determinant.
With Ω in standard form, the inverse of M is given by
Symplectic transformations
In the abstract formulation of linear algebra, matrices are replaced with linear transformations of finite-dimensional vector spaces. The abstract analog of a symplectic matrix is a symplectic transformation of a symplectic vector space. Briefly, a symplectic vector space is a 2n-dimensional vector space V equipped with a nondegenerate, skew-symmetric bilinear form ω called the symplectic form.
A symplectic transformation is then a linear transformation L : V → V which preserves ω, i.e.
Fixing a basis for V, ω can be written as a matrix Ω and L as a matrix M. The condition that L be a symplectic transformation is precisely the condition that M be a symplectic matrix:
Under a change of basis, represented by a matrix A, we have
One can always bring Ω to either the standard form given in the introduction or the block diagonal form described below by a suitable choice of A.
The matrix Ω
Symplectic matrices are defined relative to a fixed nonsingular, skew-symmetric matrix Ω. As explained in the previous section, Ω can be thought of as the coordinate representation of a nondegenerate skew-symmetric bilinear form. It is a basic result in linear algebra that any two such matrices differ from each other by a change of basis.
The most common alternative to the standard Ω given above is the block diagonal form
This choice differs from the previous one by a permutation of basis vectors.
Sometimes the notation J is used instead of Ω for the skew-symmetric matrix. This is a particularly unfortunate choice as it leads to confusion with the notion of a complex structure, which often has the same coordinate expression as Ω but represents a very different structure. A complex structure J is the coordinate representation of a linear transformation that squares to −1, whereas Ω is the coordinate representation of a nondegenerate skew-symmetric bilinear form. One could easily choose bases in which J is not skew-symmetric or Ω does not square to −1.
Given a hermitian structure on a vector space, J and Ω are related via
where 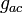 is the metric. That J and Ω usually have the same coordinate expression (up to an overall sign) is simply a consequence of the fact that the metric g is usually the identity matrix.
is the metric. That J and Ω usually have the same coordinate expression (up to an overall sign) is simply a consequence of the fact that the metric g is usually the identity matrix.
Complex matrices
If instead M is a 2n×2n matrix with complex entries, the definition is not standard throughout the literature. Many authors [1] adjust the definition above to
-

(2)
where M* denotes the conjugate transpose of M. In this case, the determinant may not be 1, but will have absolute value 1. In the 2×2 case (n=1), M will be the product of a real symplectic matrix and a complex number of absolute value 1.
Other authors [2] retain the definition (1) for complex matrices and call matrices satisfying (2) conjugate symplectic.
See also
- symplectic vector space
- symplectic group
- symplectic representation
- orthogonal matrix
- unitary matrix
- Hamiltonian mechanics
References
- ↑ Xu, H. G. (July 15, 2003). "An SVD-like matrix decomposition and its applications". Linear Algebra and its Applications 368: 1–24. doi:10.1016/S0024-3795(03)00370-7.
- ↑ Mackey, D. S.; Mackey, N. (2003). On the Determinant of Symplectic Matrices. Numerical Analysis Report 422. Manchester, England: Manchester Centre for Computational Mathematics.
External links
- Symplectic matrix, PlanetMath.org.
- The characteristic polynomial of a symplectic matrix is a reciprocal polynomial, PlanetMath.org.