Military of Switzerland
| Military of Switzerland | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| Service branches | Land Forces, Air Force |
| Leadership | |
| General | Vacant in peacetime |
| Minister of Defense | Swiss Federal Councilor Ueli Maurer |
| Chief of the Armed Forces | Lt Gen André Blattmann |
| Manpower | |
| Military age | 19 years of age for male compulsory military service; 18 years of age for voluntary male and female military service; |
| Conscription |
19–34 years of age obligatorily 36 for subaltern officers, 52 for staff officers and higher |
| Available for military service |
1,852,580 males, age 16–49 (2009 est.), 1,807,667 females, age 16–49 (2009 est.) |
| Fit for military service |
1,510,259 males, age 16–49 (2009 est.), 1,475,993 females, age 16–49 (2009 est.) |
| Reaching military age annually |
48,076 males (2009 est.), 44,049 females (2009 est.) |
| Active personnel | 134,886[1] |
| Reserve personnel | 77,000[1] |
| Expenditures | |
| Budget | CHF3.9 billion (~US$3.6 billion FY08)[1] |
| Percent of GDP | 0.9% (2006)[2] |
The Swiss Armed Forces operate on land and in the air, and also along international waters. They comprise the well-known militia element and a small professional element, or regular army. Under the country's militia system, professional soldiers constitute about 5 percent[citation needed] of military personnel; the rest are male citizen conscripts 19 to 34 (in some cases up to 50) years old. Because of the long history of neutrality, the army does not take part in armed conflicts in other countries, but does take part in peacekeeping missions around the world.
The structure of the Swiss militia system stipulates that the soldiers keep their own personal equipment, including all personally assigned weapons, at home (until 2007 this also included ammunition[3]). Compulsory military service concerns all male Swiss citizens, with women serving voluntarily. Males usually receive initial orders at the age of 18 for military conscription eligibility screening. About two-thirds of young Swiss men are found suitable for service, while alternative service exists for those found unsuitable.[4] Annually, approximately 20,000 persons are trained in basic training for a duration from 18 to 21 weeks (increased from 15 weeks, in 2003).
Since 1989, there have been several attempts to curb military activity or even abolish the armed forces altogether. A notable referendum on the subject was held on 26 November 1989 and, although defeated, did see a significant percentage of the voters in favour of such an initiative.[5] However, a similar referendum, called for before, but held shortly after the September 11 attacks in 2001 in the US, was defeated by over 77% of voters.[6]
The reform "Army XXI" was adopted by popular vote in 2003. It replaced the previous model "Army 95", reducing manpower from 400,000 to about 200,000 personnel, 120,000 receiving periodic military training and 80,000 reservists who have completed their total military training requirements.[7]
History

The Swiss army originated from the cantonal troops of the Old Swiss Confederacy, called upon in cases of external threats by the Tagsatzung or by the canton in distress. In the federal treaty of 1815, the Tagsatzung prescribed cantonal troops to put a contingent of 2% of the population of each canton at the federation's disposition, amounting to a force of some 33,000 men. The cantonal armies were converted into the federal army (Bundesheer) with the constitution of 1848. From this time, it was illegal for the individual cantons to declare war or to sign capitulations or peace agreements. Paragraph 13 explicitly prohibited the federation from sustaining a standing army, and the cantons were allowed a maximum standing force of 300 each (not including the Landjäger corps, a kind of police force). Paragraph 18 declared the "obligation" of every Swiss citizen to serve in the federal army if conscripted (Wehrpflicht), setting its size at 3% of the population plus a reserve of one and one half that number, amounting to a total force of some 80,000.

The first complete mobilization, under the command of Hans Herzog, was triggered by the Franco-Prussian War in 1871. In 1875, the army was called in to crush a strike of workers at the Gotthard tunnel. Four workers were killed and 13 were severely wounded.
Paragraph 19 of the revised constitution of 1874 extended the definition of the federal army to every able-bodied male citizen, swelling the size of the army (at least in theory) from under 150,000 to more than 700,000, with population growth during the 20th century rising further to some 1.5 million, the second largest armed force per capita after the Israeli Defence Forces.
A major manoeuvre commanded in 1912 by Ulrich Wille, a reputed Germanophile, convinced visiting European heads of state, in particular Kaiser Wilhelm II, of the efficacy and determination of Swiss defences.[8] Wille was subsequently put in command of the second complete mobilization in 1914, and Switzerland escaped invasion in the course of World War I. Wille also ordered the suppression of the 1918 general strike (Landesstreik) with military force. Three workers were killed, and a rather larger number of soldiers died of the Spanish flu during mobilization. In 1932, the army was called to suppress an anti-fascist demonstration in Geneva. The troops shot dead 13 demonstrators, wounding another 65. This incident long damaged the army's reputation, leading to persistent calls for its abolition among left-wing politicians. In both the 1918 and the 1932 incidents, the troops deployed were consciously selected from rural regions such as the Berner Oberland, fanning the enmity between the traditionally conservative rural population and the urban working class. The third complete mobilization of the army took place during World War II under the command of Henri Guisan (see also Switzerland during the World Wars). The Patrouille des Glaciers race, created to test the abilities of soldiers, was created during the war.

In the 1960s and 1970s, the armed forces were organised according to the "Armee 61" structure.
In 1989, the status of the army as a national icon was shaken by a popular initiative aiming at its complete dissolution (see: Group for a Switzerland without an Army) receiving 35.6% support. This triggered a series of reforms and, in 1995, the number of troops was reduced to 400,000 ("Armee 95"). Article 58.1 of the 1999 constitution repeats that the army is "in principle" organized as a militia, implicitly allowing a small number of professional soldiers. A second initiative aimed at the army's dissolution in late 2001 received a mere 21.9% support.[6] Nevertheless, the army was shrunk again in 2004, to 220,000 men ("Armee XXI"), including the reserves.
Structure
The armed forces consist of 134,886 people on active duty (in Switzerland called Angehöriger der Armee, shortly AdA, engl.: Member of the Army), of which 4,230 are professionals, with the rest being conscripts or volunteers.[1] Women, for whom military service is voluntary, numbered 1,050: less than 1% of the total, but 25% of career soldiers.[1] Once decided to serve, they have the same rights and duties as their male colleagues, and they can join all services, including combat units. Recruits are generally instructed in their native language; however, the small number of Romansh-speaking recruits are instructed in German.
In contrast to most other comparable armies, officer candidates are usually not career regulars: after seven weeks of basic training, selected recruits are offered the possibility of a cadre function. Officer candidate schools take place separately from NCOs training, but NCOs have the possibility of becoming officers later on.[9] There are currently 17,506 officers and 22,650 NCOs in the Swiss Armed Forces.[1] Those of higher rank serve for more time each year; an ordinary soldier may serve 365 days over 30 years, while a high-ranking officer may serve 2,000 before retiring. Each promotion requires more time, which is known as "paying your grade". Companies subsidize military training by continuing to pay their employees, who list their ranks and responsibilities on their résumés.[ 1]
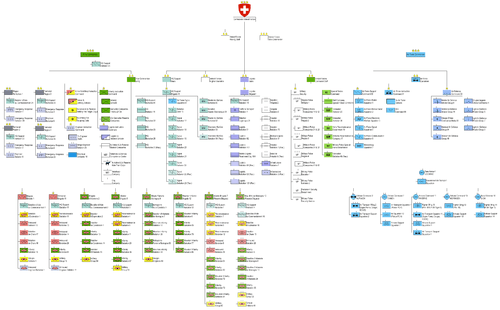
High Command

In peacetime, the armed forces are led by the Chief of the Armed Forces (Chef der Armee), who reports to the head of the Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports and to the Swiss Federal Council as a whole. The current Chief of the Armed Forces is Lieutenant-General (Korpskommandant) André Blattmann. Lt-Gen Blattmann replaced Lieutenant-General (Korpskommandant) Roland Nef who resigned on 25 July 2008 following allegations of sexual harassment.[10]
In times of crisis or war, the Federal Assembly elects a full General (OF-9) as Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces (Oberbefehlshaber der Armee). The rank is distinct and particular, as it is associated exclusively with wartime fighting or a national crisis due to wartime fighting among the neighbours on the border.[ 1] In addition, in Switzerland the word General itself is distinct and particular, as the subordinate appointments of general-officer status omit the word itself.
Throughout Swiss history, there have only been 4 officers formally designated as General:[ 1]
- Henri Dufour (1847–1848) - Sonderbund War; and 1856–57, Neuchâtel Crisis
- Hans Herzog (1871–1872) - Franco-Prussian War
- Ulrich Wille (1914–1918) - World War I
- Henri Guisan (1939–1945) - World War II
In Switzerland, the word General is reserved for the wartime, or emergency, Commander-in-Chief, so the subordinate officers who would have had the title of 'general' in other armies have alternative designations to describe the appointment:
- OF-8: Korpskommandant or Commandant de corps
- OF-7: Divisionär or Divisionnaire
- OF-6; Brigadier[11]
The distinctive feature of their rank insignia are traditionally stylized edelweiss rank-insignia. One exception, however, is that when Swiss officers are involved in peacekeeping missions abroad, they are often given temporary ranks that do not exist in the Swiss Army, to give them rank-styles readily understood by foreign officers. For example, the head of the Swiss delegation at the NNSC in Korea (see below) had a rank of major general.
Land Forces
Under "Armee 61" the land forces were organised into Field Army Corps 1, 2, and 4, and Mountain Army Corps 3. This structure was superseded by the "Armee 95" and thereafter the "Armee XXI" structures.
Since the Army XXI reform in 2004, the basic structure of the Land Forces has been reorganised in the following units: infantry brigades (2 and 5); mountain infantry brigades (9 and 12); armoured brigades (1 and 11).[1] Additionally two large reserve brigades (Infantry Brigade 7 and Mountain Brigade 10) exist. Four territorial regions link the Land Forces with the cantons by coordinating territorial tasks inside of their sector and are immediately responsible for the security of their regions, depending only on the decisions of the Federal Council.[12]
The Territorial Regions have their headquarters located as follows: Territorial Region 1, Morges (Vaud), Territorial Region 2, Kriens, Territorial Region 3 (Altdorf), and Territorial Region 4 (St. Gallen). According to Commons, Territoral Region 3 includes Emergency Aid Battalion 3 ('Bat acc 3'?), and Engineer Battalions 9, 12, and 24.





The Formations of the Land Forces
The Swiss Land Forces are organised into the following all-arms brigades:
- The Armoured Brigades
- Armoured Brigade 1 (see la brigade blindée 1)
- Command Support Battalion 1 (Bataillon d'aide au commandement 1)
- Reconnaissance Battalion 1 (Bataillon d'exploration 1)
- Armoured Battalion 12 (Bataillon de chars 12)
- Armoured Battalion 17 (Bataillon de chars 17)
- Armoured Battalion 18 (Bataillon de chars 18)
- Infantry Battalion 16
- Artillery Battalion 1
- Armoured Engineer Battalion 1
- Armoured Brigade 11 (see de:Panzerbrigade 11)
- Command Support Battalion 11
- Reconnaissance battalion 11
- Armoured Battalion 13
- Armoured Battalion 14
- Mechanized Infantry battalion 29
- Infantry Battalion 61
- Artillery Battalion 16
- Armoured Engineer Battalion 11
During 2010, the armoured and mechanized infantry battalions were restructured as Combined Arms Battalions; as from 1 January 2011, each had a Staff Company, a Logistics Company, two Tank Companies and two Mechanized Infantry Companies equipped with infantry fighting vehicles.
- The Infantry Brigades
- Infantry Brigade 2 (Brigade d'infanterie 2)[13] (HQ Saint-Maurice, Switzerland)
- Command Support Battalion 2 (Bataillon d'aide au commandement 2)
- Reconnaissance Battalion 2 (Bataillon d'exploration 2)
- Rifle battalion 1 (Bataillon de Carabiniers 1)
- Infantry Battalion 13 (Infanteriebataillon 13)
- Rifle battalion 14 (Bataillon de Carabiniers 14)
- Infantry Battalion 19 (Bataillon d'infanterie 19)
- Artillery Battalion 54 (Artillerie Abteilung 54)
- Infantry Brigade 5[14]
- Command Support Battalion 5
- Reconnaissance Battalion 5
- Infantry battalion 11
- Infantry Battalion 20
- Infantry Battalion 56
- Infantry Battalion 97
- Artillery Battalion 10
- The Mountain Infantry Brigades
- Mountain Infantry Brigade 9 (Brigata fanteria montagna 9)[15]
- Command Support Battalion 9 (Battaglione aiuto condotta 9)
- Mountain Infantry battalion 7 (Bataillon d'infanterie de montagne 7)
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 17 (Gebirgsinfanteriebataillon 17)
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 29 (Gebirgsinfanteriebataillon 29)
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 30 (Battaglione fanteria montagna 30)
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 48 (Gebirgsinfanteriebataillon 48)
- Artillery Battalion 49 (Gruppo artiglieria 49)
- Mountain Infantry Brigade 12[16]
- Command Support Battalion 12
- Mountain Rifle battalion 6 (Gebirgsschützenbataillon 6)
- Infantry Battalion 65
- Infantry Battalion 70
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 77
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 85
- Fortress Artillery Battalion 13
- The Reserve Brigades
- Infantry Brigade 7[17]
- Command Support Battalion 7
- ISTAR Reconnaissance Battalion 7
- Reconnaissance Battalion 9
- Reconnaissance Battalion 12
- Mechanized Infantry Battalion 8
- Mechanized Infantry Battalion 28
- Infantry Battalion 54
- Infantry Battalion 60
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 72
- Infantry Battalion 73
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 91
- Artillery Battalion 47
- Mountain Brigade 10[18] (HQ Saint-Maurice, Switzerland)
- Command Support Battalion 10 (Bataillon d'aide au commandement 10)
- Reconnaissance battalion 4
- Reconnaissance Battalion 10 (Bataillon d'exploration 10)
- Armoured Battalion 15 (Bataillon de chars 15)
- Mechanized Infantry battalion 20
- Rifle Battalion 5 (Schützenbataillon 5)
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 8 (Bataillon d'infanterie de montagne 8)
- Mountain Infantry Battalion 10 (Bataillon d'infanterie de montagne 10)
- Infantry Battalion 24 (Bataillon d'infanterie 24)
- Infantry Battalion 36
- Artillery Battalion 32
- Artillery Battalion 41
Air Force


The Swiss Air Force has been traditionally a militia-based service, including its pilots, with an inventory of approximately 456 aircraft whose lengthy service lives (many for more than 30 years) overlapped several eras. However, beginning with its separation from the Army in 1996, the Air Force has been downsizing; it now has a strength of approximately 270 fixed- and rotary-wing aircraft, and is moving towards a smaller, more professional force.
The primary front-line air-defence fleet consists of 33 F-18 Hornets (34 aircraft were originally purchased, with one aircraft lost in a crash) organized into three squadrons (11, 17 and 18) along with 54 F-5 Tiger IIs (110 originally purchased). In October 2008, the Swiss Hornet fleet reached the 50,000 flight hour milestone.[19]
A report in the Swiss news magazine FACTS reveals that the Swiss Air Force provides ready-to-takeoff aircraft only during office hours on working days. The air force staff declared that, due to financial limits, they are not operational all the time.[20] The difficulty of defending Swiss airspace is illustrated by the mountainous character and the small size of the country; the maximum extension of Switzerland is 348 km, a distance that can be flown in a little over 20 minutes by commercial aircraft. Furthermore, Switzerland's policy of neutrality means that they are unlikely to be deployed elsewhere.
Intelligence gathering
The Swiss military department maintains the Onyx intelligence gathering system, similar to but much smaller than the international Echelon system.
The Onyx system was launched in 2000 in order to monitor both civil and military communications, such as telephone, fax or Internet traffic carried by satellite. It was completed in late 2005 and currently consists in three interception sites, all based in Switzerland. In a way similar to Echelon, Onyx uses lists of keywords to filter the intercepted content for information of interest.
On 8 January 2006, the Swiss newspaper Sonntagsblick (Sunday edition of the Blick newspaper) published a secret report produced by the Swiss government using data intercepted by Onyx.[citation needed] The report described a fax sent by the Egyptian department of Foreign Affairs to the Egyptian Embassy in London, and described the existence of secret detention facilities (black sites) run by the CIA in Central and Eastern Europe. The Swiss government did not officially confirm the existence of the report, but started a judiciary procedure for leakage of secret documents against the newspaper on 9 January 2006.[citation needed]
Lakes flotilla
Contrary to popular belief, there is actually a naval element in Switzerland. The landlocked state obviously does not require a high-seas navy, but there are several sizeable lakes in Switzerland, and most lie along the international borders. The country therefore operates a flotilla of military patrol boats. The maritime branch is subordinate to the Army and as well as security patrols, the flotilla-divisions serve in the Search and Rescue (SAR) role. This force includes the Aquarius-class Patrouillenboot 80 PBRs, which are operated by Motorboat Company 10 of the Corps of Engineers and which patrol:
Conscription
Switzerland has mandatory military service for all able-bodied male citizens, who are conscripted when they reach the age of majority,[22] though women may volunteer for any position.[23] People determined unfit for service, where fitness is defined as "satisfying physically, intellectually and psychically requirements for military service or civil protection service and being capable of accomplishing these services without harming oneself or others",[24] are exempted from service but pay a 3% additional annual income tax until the age of 30, unless they are affected by a disability.[25] Almost 20% of all conscripts were found unfit for military or civilian service in 2008; the rate is generally higher in urban cantons such as Zurich and Geneva than in the rural ones.[26] Swiss citizens living abroad are generally exempted from conscription in time of peace[27] while dual citizenship by itself does not grant such exemption.[28]
Roles
The prime role of the Swiss Armed Forces is Home Defence. Switzerland is not part of any multinational war-fighting structure, but individual Armed Forces members do take part in international missions.
Peacekeeping Overseas

Operating from a neutral country, Switzerland's army does not take part in armed conflicts in other countries. However, over the years, the Swiss army has been part of several peacekeeping missions around the world.
From 1996 to 2001, the Swiss Army was present in Bosnia and Herzegovina with headquarters in Sarajevo. Its mission, part of the Swiss Peacekeeping Missions, was to provide logistic and medical support to the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), protection duties and humanitarian demining. The mission was named SHQSU, standing for Swiss Headquarters Support Unit to BiH. It was composed of 50 to 55 elite Swiss soldiers under contract for six to 12 months. None of the active soldiers were armed during the duration of the mission. The Swiss soldiers were recognized among the other armies present on the field by their distinctive yellow beret. The SHQSU is not the same as the more publicized Swisscoy, which is the Swiss Army Mission to Kosovo.
Switzerland is part of the Neutral Nations Supervisory Commission (NNSC), which was created to monitor the armistice between North and South Korea. Since the responsibilities of the NNSC have been much reduced over the past few years, only five people are still part of the Swiss delegation, which is located near the Korean DMZ.[29][30][31]
Military and civil defence
After World War II, Swiss began building homes with 40cm-thick concrete ceilings that might survive firebombing of the type that destroyed Hamburg and Dresden. In the 1960s they began constructing radiation and blast shelters that could survive one to three bars of pressure from a nuclear explosion.[32] Building codes require blast shelters, which are said to be able to accommodate 114% of the Swiss population.[33] Small towns have large underground parking garages that can serve as sealed community shelters.[ 1] There are also hospitals and command centres in such shelters, aimed at keeping the country running in case of emergencies. Every family or rental agency has to pay a replacement tax to support these shelters, or alternatively own a personal shelter in their place of residence;[34] many private shelters serve as wine cellars and closets.[ 1]

Thousands of tunnels, highways, railroads, and bridges are built with tank traps and primed with demolition charges to be used against invading forces; often, the civilian engineer who designed the bridge plans the demolition as a military officer. Hidden guns are aimed to prevent enemy forces from attempting to rebuild.[ 1] Permanent fortifications were established in the Alps, as bases from which to retake the fertile valleys after a potential invasion. They include underground air bases that are adjacent to normal runways; the aircraft, crew and supporting material are housed in the caverns.
However, a significant part of these fortifications was dismantled between the 1980s and during the "Army 95" reformation. The most important fortifications are located at Saint-Maurice, Gotthard Pass area and Sargans. The fortification on the left side of the Rhône at Saint-Maurice is no longer used by the army since the beginning of the 1990s. The right side (Savatan) is still in use.
During the Cold War the military expected that any invasion would likely come from the northeast, as the Soviet Union associated the country with NATO despite its stated neutrality.[ 1] The Swiss government thought that the aim of an invasion would be to control the economically important transport routes through the Swiss Alps, namely the Gotthard, the Simplon and Great St. Bernard passes, because Switzerland does not possess any significant natural resources.
Equipment
Weapons marked in bold are considered personal equipment of the soldier, who is responsible for their well-functioning and must keep them at home until the end of the military service (unless living near an external border of Switzerland).[35] Between brackets is the number of such weapons in personal equipment as of 31 January 2009.[36] Swiss Army knives are also issued, but are not considered weapons.
Small arms




Individual weapons
- Sturmgewehr 90 assault rifle (200,000)
- Sturmgewehr 57 battle rifle (2,000)
- Pistole 75 semi-automatic pistol (30,000)
- Pistole 49 semi-automatic pistol (1,000)
- FN Minimi
- Heckler & Koch MP5 submachinegun
- Brügger & Thomet MP9 machine pistol
- Tuma MTE 224 VA machine pistol
- Remington 870 multipurpose shotgun (known as Mehrzweckgewehr 91)
- Sako TRG-42 8.6 mm anti-personnel sniper rifle (Scharfschützengewehr 04)
- PGM Hecate II 12.7 mm anti-materiel heavy sniper rifle (Präzisionsgewehr 04)
Crew served weapons
- MG51 machine gun
- MG 710 machine gun / MG55 (still stocked, but neither trained on nor used in rep courses; same as MG3)
Other weapons
- Gewehraufsatz 97 40mm grenade launcher (mounted under "Sturmgewehr 90" assault rifle for grenadiers and fusiliers)
- HG 85 hand grenade
- Panzerfaust 3 shoulder-launched recoilless anti-tank weapon
- M47 Dragon anti-tank guided rocket (being phased out without replacement due to cost-intensive maintenance)
Armoured Fighting Vehicles (AFV)
- Leopard 87 - Leopard 2A4 main battle tank (200 in service)
- M113 armored personnel carrier (600 in service)
- APC 2000 – variant of CV9030 infantry fighting vehicle (200 in service)
- APC 93 – variant of Piranha II 8×8 wheeled APC (500 in service)
- Reconnaissance vehicles 93, 93/97 – variants of Eagle I-II armoured patrol vehicle (300 in service)
- M109 – self-propelled howitzer (200 in service)
- Piranha TOW – anti-tank variant of the Piranha I 6×6 (100 in service)
- DURO GMTF – APC (130 on order)[37]
Source: Swiss Armed Forces: Land forces weapon systems (p. 12)[1]
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "The basic organisation of the Swiss Armed Forces". Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ "Ausgaben der Landesverteidigung". Statistik Schweiz (in german). 2006. Retrieved 20 May 2009.
- ↑ http://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/Specials/Gun_debate/Background/Archives/Soldiers_can_keep_guns_at_home_but_not_ammo.html?cid=970614
- ↑ "Zwei Drittel der Rekruten diensttauglich (Schweiz, NZZ Online)". Retrieved 23 February 2009.
- ↑ "L'évolution de la politique de sécurité de la Suisse" (in French). NATO. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Volksabstimmung vom 2. Dezember 2001" (in German). Federal Chancellery. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ Armeezahlen www.vbs.admin.ch (German)
- ↑ World War I–Preparation in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- ↑ "L'instruction des cadres" (in French). # Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ "Army chief falls but defence minister to stay". swissinfo. 25 July 2008. Retrieved 15 September 2008.
- ↑ McPhee, John (1983-10-31). "La Place de la Concorde Suisse-I". The New Yorker. p. 50. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- ↑ "Grandes unités" (in French). Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ http://www.he.admin.ch/internet/heer/de/home/verbaende/infbr2/articulation.html
- ↑ http://www.he.admin.ch/internet/heer/de/home/verbaende/infbr5/verbaende.html
- ↑ http://www.he.admin.ch/internet/heer/de/home/verbaende/gebinfbr9/struttura.html
- ↑ http://www.he.admin.ch/internet/heer/de/home/verbaende/gebinfbr12/organisation.html
- ↑ http://www.he.admin.ch/internet/heer/de/home/verbaende/infbr7/truppenkoerper.html
- ↑ http://www.he.admin.ch/internet/heer/de/home/verbaende/gebinfbr10/unterstellte.html
- ↑ "Swiss Hornets reach 50,000 flight hours milestone". Military Aviation Publications. 24 October 2008. Retrieved 14 July 2009.
- ↑ FACTS No. 06/30 - Page 20
- ↑ "Lehrverband Genie/Rettung - Truppen". Swiss Land Forces. Retrieved 19 July 2009.
- ↑ "Conscrits et recrues" (in French). Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ "Femmes dans l'armée" (in French). Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ "Définition de l'aptitude au service" (in French). Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ "Ordonnance sur la taxe d'exemption de l'obligation de servir" (in French). Federal Authorities of the Swiss Confederation. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ "Les chiffres du recrutement en 2008" (in French). Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ "Les Suisses de l'étranger" (in French). Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ "Doubles-nationaux" (in French). Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sports. Retrieved 10 July 2009.
- ↑ "Swiss participation to the mission NNSC in Korea". Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sport. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ "Swiss keep watch over fragile peace". swissinfo. 19 May 2003. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ "Photogallery: NNSC Korea". Photogallery Thomas Mäder. Retrieved 12 July 2009.
- ↑ McPhee, John (1983-11-07). "La Place de la Concorde Suisse-II". The New Yorker. p. 55. Retrieved 22 July 2013.
- ↑ "Bunkers for all". swissinfo. 3 July 2009. Retrieved 13 July 2009.
- ↑ Imogen Foulkes. Swiss still braced for nuclear war. BBC News, 10 February 2007.
- ↑ "Ordonnance concernant l'équipement personnel des militaires" (in French). Federal Authorities of the Swiss Confederation. Retrieved 13 July 2009.
- ↑ "Persönliche Ausrüstung - Waffen" (in German). Logistic Base of the Army. Retrieved 13 July 2009.
- ↑ Army of Switzerland orders 130 Duro GMTF armoured personnel carrier to General Dynamics - Armyrecognition.com, 2 February 2014
Bibliography
- John McPheen, La Place del la Concorde Suisse, New York: Noonday Press (Farrar, Straus & Giroux), 1984.
- Field Army Corps 1, Sécurité au seuil du XXIe siècle: Histoire et vie du Corps d'Armee de Campagne 1, c.2000. ISBN 2-9700264-0-6.
External links
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Switzerland/Army. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Military of Switzerland. |
- Swiss Armed Forces — Official website
- Swiss camouflage patterns
- Articles, books and media by Stephen P. Halbrook
- Clip 15 Minutes with the Swiss Armed Forces
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

