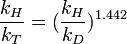Swain equation
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Swain equation relates the kinetic isotope effect for the protium/tritium combination with that of the protium/deuterium combination according to:
where kH,D,T are the reaction rate constants for the protonated, deuterated and tritiated reactants respectively.
External links
References
- Use of Hydrogen Isotope Effects to Identify the Attacking Nucleophile in the Enolization of Ketones Catalyzed by Acetic Acid C. Gardner Swain, Edward C. Stivers, Joseph F. Reuwer, Jr. Lawrence J. Schaad; J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1958; 80(21); 5885-5893. First Page
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.