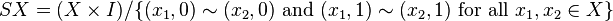Suspension (topology)
In topology, the suspension SX of a topological space X is the quotient space:
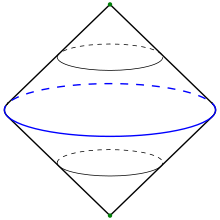
of the product of X with the unit interval I = [0, 1]. Intuitively, we make X into a cylinder and collapse both ends to two points. One views X as "suspended" between the end points. One can also view the suspension as two cones on X glued together at their base (or as a quotient of a single cone).
Given a continuous map 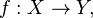 there is a map
there is a map 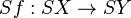 defined by
defined by ![Sf([x,t]):=[f(x),t].](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/e/c/6/b/ec6b81686b942804f1613c6cc06c6547.png) This makes
This makes 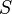 into a functor from the category of topological spaces into itself. In rough terms S increases the dimension of a space by one: it takes an n-sphere to an (n + 1)-sphere for n ≥ 0.
into a functor from the category of topological spaces into itself. In rough terms S increases the dimension of a space by one: it takes an n-sphere to an (n + 1)-sphere for n ≥ 0.
Note that  is homeomorphic to the join
is homeomorphic to the join  where
where  is a discrete space with two points.
is a discrete space with two points.
The space  is sometimes called the unreduced, unbased, or free suspension of
is sometimes called the unreduced, unbased, or free suspension of  , to distinguish it from the reduced suspension described below.
, to distinguish it from the reduced suspension described below.
The suspension can be used to construct a homomorphism of homotopy groups, to which the Freudenthal suspension theorem applies. In homotopy theory, the phenomena which are preserved under suspension, in a suitable sense, make up stable homotopy theory.
Reduced suspension
If X is a pointed space (with basepoint x0), there is a variation of the suspension which is sometimes more useful. The reduced suspension or based suspension ΣX of X is the quotient space:
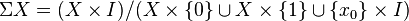 .
.
This is the equivalent to taking SX and collapsing the line (x0 × I) joining the two ends to a single point. The basepoint of ΣX is the equivalence class of (x0, 0).
One can show that the reduced suspension of X is homeomorphic to the smash product of X with the unit circle S1.
For well-behaved spaces, such as CW complexes, the reduced suspension of X is homotopy equivalent to the ordinary suspension.
Σ gives rise to a functor from the category of pointed spaces to itself. An important property of this functor is that it is a left adjoint to the functor  taking a (based) space
taking a (based) space  to its loop space
to its loop space  . In other words,
. In other words,
naturally, where 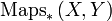 stands for continuous maps which preserve basepoints. This is not the case for unreduced suspension and free loop space.
stands for continuous maps which preserve basepoints. This is not the case for unreduced suspension and free loop space.
See also
References
- Allen Hatcher, Algebraic topology. Cambridge University Presses, Cambridge, 2002. xii+544 pp. ISBN 0-521-79160-X and ISBN 0-521-79540-0
- This article incorporates material from Suspension on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.