Suosan
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Suosan | ||
|---|---|---|
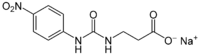 | ||
| IUPAC name Sodium 3-[(4-nitrophenyl)carbamoylamino]propanoate | ||
| Other names N-(((4-Nitrophenyl)amino)carbonyl)-β-alanine monosodium salt | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 140-46-5 | |
| PubChem | 8803 | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C1=CC(=CC=C1NC(=O)NCCC(=O)O)[N+](=O)[O-]|Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C10H10N3NaO5 | |
| Molar mass | 275.19 g mol−1 | |
| Melting point | 240 °C; 464 °F; 513 K | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Suosan is calorie-free artificial sweetener derived from β-alanine.
Suosan is a sodium salt of β-4-nitroanilide aspartic acid and is 700 times sweeter than sucrose (table sugar)[1] with a bitter aftertaste.[2]
References
- ↑ Santhosh, C.; Mishra, P. C. (1994). "Electrostatic potential and electric field mapping of some sweeteners of the suosan series: A search for the structure-activity relationship". International Journal of Quantum Chemistry 51 (5): 335. doi:10.1002/qua.560510510.
- ↑ AD Kinghorn & CM Compadre (2001). "Less common high-potency sweeteners". In Marcel Dekker. Alernative Sweeteners (Third ed.). New York. pp. 208–234. ISBN 0-8247-0437-1.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.