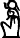The Ancient Egyptian Sun hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. N5 for the sun-disc;[1] it is also one of the hieroglyphs that refers to the god Ra.
The sun hieroglyph is used in the
Ancient Egyptian language hieroglyphs as a
determinative to refer to events of time, for example when referring to
'"day xx" (of month yy') . Even the "snap-of-the-finger", a 'moment', or 'instant' of time is represented using a Hippopotamus head (hieroglyph), Gardiner no. F3:
, with the sun-disc:
, as the time determinative in a hieroglyphic
composition block.
Other sun-based hieroglyphs
Some other common hieroglyphs based on the
sun hieroglyph, are the Sun-with-rays (hieroglyph), Gardiner no. N8:
, and
Sun-rising (hieroglyph)-(
Coronations), no. N28.
Sun-god Ra
Ra, the Sun-god is Gardiner listed no. C1, of the listed:
Anthropomorphic Deities–(more than 20 listed, and other Gardiner unlisted forms used in Ancient Egypt). The God Ra is shown with a
sun-disc upon his head
– or another common form with the
Sun disc, encircled with Uraeus, (the cobra):
Luwian hieroglyhs, Sa-sub4
The Luwian language hieroglyphs, Luwian hieroglyphs has 7 varieties for the syllable of 's' and 'a'. For 'sa' number 4 the same hieroglyph in both Eyptian and Luwian languages exist; it is Sa-sub4 (Luwian hieroglyph).
See also
- Gardiner's Sign List#N. Sky, Earth, Water
- Sun rising-Coronation (hieroglyph)
References
- ↑ Collier and Manley, 1998, How to Read Egyptian Hieroglyphs, C1, sun-disc, p. 136.
- Collier, Mark, and Manley, Bill, How to Read Egyptian Hieroglyphs, c 1998, University of California Press, 179 pp, (with a word Glossary, p 151-61: Title Egyptian-English vocabulary; also an "Answer Key", 'Key to the exercises', p 162-73) (hardcover, ISBN 0-520-21597-4)