Suevite






Suevite is a rock consisting partly of melted material, typically forming a breccia containing glass and crystal or lithic fragments, formed during an impact event. It forms part of a group of rock types and structures that are known as impactites.
Formation
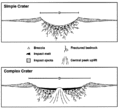
Suevite is thought to form in and around impact craters by the sintering of molten fragments together with unmelted clasts of the country rock. Wholesale melt rocks found in the crater floor are known as tagamites. Suevite is distinct from the pseudotachylite in an impact structure as the latter is thought to have formed by frictional effects within the crater floor and below the crater during the initial compression phase of the impact and the subsequent formation of the central uplift.[1]
Occurrence
Suevite is one of the diagnostic rock-types for large impact structures. It has been described from many of the larger impact structures identified on earth.
- Nördlinger Ries[2][3]
- Sudbury Basin
- Popigai crater[4]
- Chicxulub crater[5]
- Kara crater
- Azuara impact structure[6]
See also
References
- ↑ French, B.M. 1998. Traces of Catastrophe, A handbook of shock-metamorphic effects in terrestrial meteorite impact structures, Lunar and Planetary Institute Chapter 5. (PDF) . Retrieved on 2011-06-22.
- ↑ Baier, J. 2009. Zur Herkunft und Bedeutung der Ries-Auswurfprodukte für den Impakt-Mechanismus. – Jber. Mitt. oberrhein. geol. Ver., N. F. 91, 9–29.
- ↑ Baier, J. 2012. Die Bedeutung von Wasser während der Suevit-Bildung (Ries-Impakt, Deutschland). - Jber. Mitt. oberrhein. geol. Ver., N. F. 94, 55-69.
- ↑ Vishnevsky, S.A. (2003). "Suevite-tagamite megamixtures: an impact formation on the floor of the Popigai suevite strata". Third International Conference on Large Meteorite Impacts, to be held August 5–7, 2003, Nördlingen, Germany, abstract no.4024: 4024. Bibcode:2003lmim.conf.4024V. Retrieved 2011-06-22.
- ↑ Claeys, P.; Heuschkel, S.; Lounejeva-Baturina, E.; Sanchez-Rubio, G.; Stöffler, D. (2003). "The suevite of drill hole Yucatàn 6 in the Chicxulub impact crater". Meteoritics &Planetary Science 38 (9): 1299–1317. Bibcode:2003M&PS...38.1299C. doi:10.1111/j.1945-5100.2003.tb00315.x.
- ↑ Azuara suevites from the Impact Structures website. Impact-structures.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-22.
External links
Page on Suevites from website on Impact Structures by Kord Ernstson & Fernando Claudin
Virtual field-trips to impact structures (N.B. Site still partly under construction)