Suboesophageal ganglion
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The suboesophageal ganglion (acronym: SOG; synonym: subesophageal ganglion) of insects is part of the central nervous system (CNS). As indicated by its name, it is located below the oesophagus, inside the head. As part of the ventral nerve cord, it is connected (via pairs of connectives) to the brain (or supraoesophageal ganglion) and to the first thoracic ganglion (or protothoracic ganglion). Its nerves innervate the sensory organs and muscles of the mouthparts and the salivary glands.
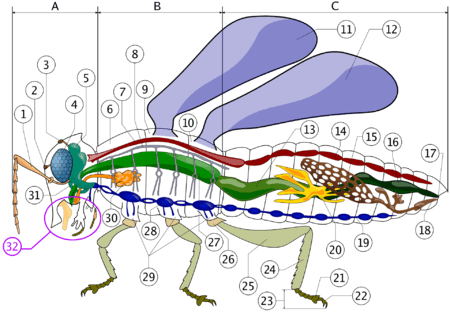
Supraesophageal ganglion(5), Subesophageal ganglion(31)
It is composed of three pairs of fused ganglia, each of which is associated with a pair of mouthparts. Therefore the fused parts are called the mandibular, maxillary and labial ganglia.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.