Studium generale
Studium generale is the old customary name for a Medieval university.
Definition
There is no clear official definition of what constituted a Studium generale. The term Studium generale first appeared at the beginning of the 13th century, out of customary usage, and simply meant a place where students from everywhere were welcome (not merely those of the local district or region).[1]
In the course of the 13th century, the term gradually acquired a more precise (but still unofficial) meaning as a place that (1) received students from all places, (2) that it taught not only the Arts, but had at least one of the higher faculties (that is, Theology, Law or Medicine) and (3) that a significant part of the teaching was done by Masters.[2]
A fourth criterion slowly appeared, namely that a Master who had taught and was registered in the Guild of Masters of a Studium Generale was entitled to teach in any other Studium without further examination. This privilege, known as jus ubique docendi, was, by custom, reserved only to the Masters of the three oldest universities—Salerno, Bologna and Paris. Their reputation was so great that its graduates and teachers were welcome to teach in all other Studia, but themselves accepted no outside teachers without an examination.
This lock by was picked by Pope Gregory IX, who seeking to elevate the prestige of the papal-sponsored University of Toulouse which he had founded in 1229, issued a bull in 1233 automatically authorizing Masters of Toulouse to teach in any Studium without an examination. It consequently became customary for Studia generalia, eager to elevate themselves, to apply for similar bulls. The older universities at first disdained requesting such privileges themselves, feeling their reputation was sufficient. But Bologna and Paris eventually stooped down to apply for them too, receiving their papal bulls in 1292.[3]
Arguably the most coveted feature of the papal bulls was the special exemption (instituted by Pope Honorius III in 1219) that allowed teachers and students to continue reaping the fruits of any clerical benefices they might have elsewhere. This dispensed them from the residency requirements set out in Canon Law.[4] As this privilege was granted only to those in Studia generalia, certainly routinely by the 14th century, it began to be considered by many to be not only another (fifth) criterion, but the single semi-official definition of a "Studium generale" - that is, that a school which did not have that privilege, would not be considered "generale". (although the old universities of Oxford and Padua, who resisted asking for a papal bull, had sufficient reputation to be referred to as Studium generale title without it; nonetheless, Oxford masters were not allowed to teach in Paris without examination; Oxford reciprocated by demanding examinations from Paris masters, ignoring the papal privileges Paris enjoyed.)
Finally, the pope could issue bulls guaranteeing the autonomy of the university from the interference of local civil or diocesal authorities (a process begun with the issuing of the 1231 bull for the University of Paris). Although not a necessary criteria, it became customary to bestow the "privileges of Paris" to other Studia generalia.
The Pope was not the only supplier of these privileges. The Holy Roman Emperor also issued imperial charters granting much the same privileges - starting with the University of Naples in 1224.
These criteria - universal student body, one or more higher faculties, teaching by masters, the right to teach in other Studia, retention of benefices, autonomy - are common features found in most Medieval Studia generale (with some notable exceptions). In other respects, e.g. structure, administration, curriculum, etc., Studia generale varied. Generally speaking, most Studia generalia tended to copy one of two old models: the student-centered system of Bologna or the master-centered structure of Paris.
History
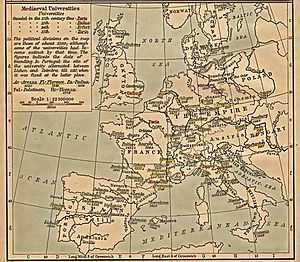
Most of the early studia generalia were found in Italy, France, England, Spain and Portugal, and these were considered the most prestigious places of learning in Europe. The Vatican continues to designate many new universities as studia generalia, although the popular significance of this honour has declined over the centuries.
As early as the 13th century, scholars from a studium generale were encouraged to give lecture courses at other institutes across Europe and to share documents, and this led to the current academic culture seen in modern European universities.
The universities generally considered as studia generalia in the 13th century were:
- University of Bologna
- University of Paris
- University of Oxford
- University of Cambridge
- University of Montpellier
- University of Salamanca
- University of Arezzo
- Complutense University (founded in Alcalá de Henares on May 20, 1293)
- University of Modena
- University of Siena
- University of Vicenza
- University of Salerno (uncertain)
- University of Coimbra (founded in Lisbon in 1290)
Both theological and secular universities were registered. This list quickly grew as new universities were founded throughout Europe. Many of these universities received formal confirmation of their status as studia generalia towards the end of the 13th century by way of papal bull, along with a host of newer universities. While these papal bulls initially did little more than confer the privileges of a specified university such as Bologna or Paris, by the end of the 13th century universities sought a papal bull conferring on them ius ubique docendi, the privilege of granting to masters licences to teach in all universities without further examination (Haskins, 1941:282).
Universities officially recognized as studia generalia in the first part of the 14th century were several, among these:
- University of Lleida (founded on 1301)
- Sapienza University of Rome (founded on 1303)
- University of Perugia (founded on 1308)
- University of Florence (founded on 1321)
- Charles University in Prague (founded on 1348)
Today studium generale is primarily used within a European university context as a description for lectures, seminars and other activities which aim at providing academic foundations for students and the general public. They are in line with the humanistic roots of the traditional universities to reach outside of their boundaries and provide a general education.
Studium particulare
A studium particulare was a version of the Studium that tended to take local students. The studium generale, by contrast, would take students from all regions and all countries.[5]
See also
Notes
References
- Haskins, George L (1941) 'The University of Oxford and the Ius ubique docendi,' The English Historical Review, pp. 281-292.
- Rashdall, H. (1895) The Universities of Europe in the Middle Ages, Vol. 1.