Stibole
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Stibole | ||
|---|---|---|
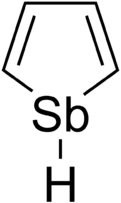 | ||
| IUPAC name 1H-Stibole | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 288-04-0 | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[SbH]1C=CC=C1C1=CC=CSb1|Image 1 Image 2 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C4H5Sb | |
| Molar mass | 174.84 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Stibole is a theoretical heterocyclic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4H4SbH. It is classified as a metallole. It can be viewed as an structural analog of pyrrole, with antimony replacing the nitrogen atom of pyrrole. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, are called stiboles.
Reactions
2,5-Dimethyl-1-phenyl-1H-stibole, for example, can be formed by the reaction of 1,1-dibutyl-2,5-dimethylstannole and dichlorophenylstibine.[1] Stiboles can be used to form ferrocene-like sandwich compounds.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ J.I.G. Cadogan, S.V. Ley, G. Pattenden, R.A. Raphael, C.W. Rees, ed. (1996), Dictionary of Organic Compounds 3 (6 ed.), Chapman & Hall, p. 2710, ISBN 978-0-412-54090-5, retrieved 2010-03-04
- ↑ A.R. Katritzky, Otto Meth-Cohn, C.W. Rees, ed. (1995), Comprehensive Organic Functional Group Transformations 4, Elsevier, pp. 1038–1040, ISBN 978-0-08-042325-8, retrieved 2010-03-04
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.