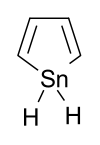
Stannole
| Stannole | ||
|---|---|---|
 |
 | |
| IUPAC name 1H-Stannole | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 288-07-3 | |
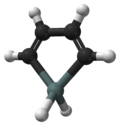
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[SnH2]1C=CC=C1C1=CC=CSn1|Image 1 Image 2 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C4H6Sn | |
| Molar mass | 172.80 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Stannole is an organotin compound with the formula (CH)4SnH2. It is classified as a metallole, i.e. an unsaturated five-membered ring containing a heteroatom. It is a structural analog of pyrrole, with tin replacing the nitrogen. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, are also called stannoles.[1]
Examples
1,1-Dibutylstannole is a pale yellow oil prepared from 1,4-dilithio-1,3-butadiene and dibutyltin dichloride [2]
Reactions
1,1-Dimethyl-2,3,4,5-tetraphenyl-1H-stannole, for example, can be formed by the reaction of 1,4-dilithio-1,2,3,4-tetraphenyl-1,3-butadiene and dimethyltin dichloride.[3] 1,1-Disubstituted stannoles can be formed in the [2+2+1] cycloaddition reaction of two acetylene molecules with an organotin molecule SnR2.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Dubac, Jacques; Laporterie, Andre; Manuel, Georges (1990). "Group 14 metalloles. 1. Synthesis, organic chemistry, and physicochemical data". Chemical Reviews 90: 215. doi:10.1021/cr00099a008.
- ↑ Ashe, Arthur J.; Mahmoud, Samir. (1988). "1,4-Dilithio-1,3-butadienes". Organometallics 7 (8): 1878. doi:10.1021/om00098a034.
- ↑ J.I.G. Cadogan, S.V. Ley, G. Pattenden, R.A. Raphael, C.W. Rees, ed. (1996). Dictionary of Organic Compounds 3 (6 ed.). Chapman & Hall. p. 4219. ISBN 978-0-412-54090-5. Retrieved 2010-03-04.
- ↑ Davies, A.G. (2004). Organotin Chemistry (2 ed.). Wiley-VCH. p. 129. ISBN 978-3-527-31023-4. Retrieved 2010-03-04.
