Sphincter of ampulla
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| sphincter of ampulla | |
|---|---|
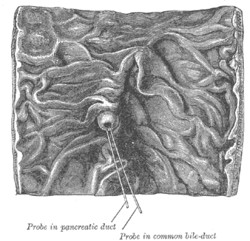 | |
| Interior of the descending portion of the duodenum, showing bile papilla. | |
| Latin | m. sphincter ampullae |
| MeSH | 's+Sphincter Oddi's+Sphincter |
| Code | TA A05.8.02.018 |
The sphincter of ampulla or sphincter of Oddi is a muscular valve that controls the flow of digestive juices (bile and pancreatic juice) through the ampulla of Vater into the second part of the duodenum. It is named after Ruggero Oddi.[1] The sphincter of Oddi is relaxed by the hormone cholecystokinin (CCK) via vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP).[2]
Clinical significance
Main article: sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
Opiates can cause spasms of the sphincter of Oddi, leading to increased serum amylase levels.
References
- Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed. p. 1228.
Further reading
- Ballal, Mansour A.; Sanford, Paul A. (2000). "Physiology of the Sphincter of Oddi - the present and the future? - part 1". The Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology 6 (3): 129–146. PMID 19864708. Retrieved 26 September 2012.
- Ballal, Mansour A.; Sanford, Paul A. (2000). "Physiology of the Sphincter of Oddi - the present and the future? - part 2". The Saudi Journal of Gastroenterology 7 (1): 16–21. PMID 19861760. Retrieved 26 September 2012.
| |||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.