Spectral resolution
The spectral resolution of a spectrograph, or, more generally, of a frequency spectrum, is a measure of its ability to resolve features in the electromagnetic spectrum. It is usually denoted by  , and is closely related to the resolving power of the spectrograph, defined as
, and is closely related to the resolving power of the spectrograph, defined as
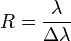 ,
,
where  is the smallest difference in wavelengths that can be distinguished at a wavelength of
is the smallest difference in wavelengths that can be distinguished at a wavelength of 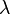 . For example, the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) can distinguish features 0.17 nm apart at a wavelength of 1000 nm, giving it a resolution of 0.17 nm and a resolving power of about 5,900. An example of a high resolution spectrograph is the Cryogenic High-Resolution IR Echelle Spectrograph (CRIRES) installed at ESO's Very Large Telescope, which has a spectral resolving power of up to 100,000.[1]
. For example, the Space Telescope Imaging Spectrograph (STIS) can distinguish features 0.17 nm apart at a wavelength of 1000 nm, giving it a resolution of 0.17 nm and a resolving power of about 5,900. An example of a high resolution spectrograph is the Cryogenic High-Resolution IR Echelle Spectrograph (CRIRES) installed at ESO's Very Large Telescope, which has a spectral resolving power of up to 100,000.[1]
Doppler effect
The spectral resolution can also be expressed in terms of physical quantities, such as velocity; then it describes the difference between velocities 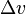 that can be distinguished through the Doppler effect. Then, the resolution is
that can be distinguished through the Doppler effect. Then, the resolution is 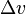 and the resolving power is
and the resolving power is
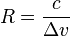
where  is the speed of light. The STIS example above then has a spectral resolution of 51 km/s.
is the speed of light. The STIS example above then has a spectral resolution of 51 km/s.
IUPAC definition
IUPAC defines resolution in optical spectroscopy as the minimum wavenumber, wavelength or frequency difference between two lines in a spectrum that can be distinguished.[2] Resolving power, R, is given by the transition wavenumber, wavelength or frequency, divided by the resolution.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ - CRIRES Instrument page at ESO
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "resolution in optical spectroscopy".
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "resolving power, R, in optical spectroscopy".
Further reading
- Kim Quijano, J., et al. (2003), STIS Instrument Handbook, Version 7.0, (Baltimore: STScI)
- Frank L. Pedrotti, S.J. (2007), Introduction to optics, 3rd version, (San Francisco)