Sorbitan
| Sorbitan | ||
|---|---|---|
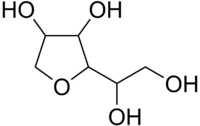 | ||
| IUPAC name (3S)-2-(1,2-Dihydroxyethyl)tetrahydrofuran-3,4-diol | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 12441-09-7 | |
| PubChem | 103023 | |
| UNII | 6O92ICV9RU | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C1C([C@@H](C(O1)C(CO)O)O)O|Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C6H12O5 | |
| Molar mass | 164.16 g/mol | |
| Appearance | colourless solid | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Sorbitan is a mixture of isomeric organic compounds derived from the dehydration of sorbitol. The mixture can vary, but usually consists of 1,4-anhydrosorbitol, 1,5-anhydrosorbitol and 1,4,3,6-dianhydrosorbitol.[1] Sorbitan is primarily used in the production of surfactants such as polysorbates. Sorbitan is an intermediate in the conversion of sorbitol to isosorbide.[2]
Sorbitan esters ( also known as Spans ) are lipophilic nonionic surfactants that are used as emulsifying agents in the preparation of emulsions, creams, and ointments for pharmaceutical and cosmetic use. When used alone they produce stable water-in-oil emulsions but they are frequently used with a polysorbate in varying proportions to produce water-in-oil or oil-in-water emulsions or creams with a variety of different textures and consistencies. Sorbitan esters are also used as emulsifiers and stabilisers in food. [3]
References
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition, 8872
- ↑ Rose, Marcus; Palkovits, Regina (2012). "Isosorbide as a Renewable Platform chemical for Versatile Applications-Quo Vadis?". ChemSusChem 5 (1): 167–76. doi:10.1002/cssc.201100580. PMID 22213713.
- ↑ Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. The Pharmaceutical Press. 2005.