Solvmanifold
In mathematics, a solvmanifold is a homogeneous space of a connected solvable Lie group. It may also be characterized as a quotient of a connected solvable Lie group by a closed subgroup. (Some authors also require that the Lie group be simply-connected, or that the quotient be compact.) A special class of solvmanifolds, nilmanifolds, was introduced by Malcev, who proved first structural theorems. Properties of general solvmanifolds are similar, but somewhat more complicated.
Examples
- A solvable Lie group is trivially a solvmanifold.
- Every nilpotent group is solvable, therefore, every nilmanifold is a solvmanifold. This class of examples includes n-dimensional tori and the quotient of the 3-dimensional real Heisenberg group by its integral Heisenberg subgroup.
- The Möbius band and the Klein bottle are solvmanifolds that are not nilmanifolds.
- The mapping torus of an Anosov diffeomorphism of the n-torus is a solvmanifold. For n=2, these manifolds belong to Sol, one of the eight Thurston geometries.
Properties
- A solvmanifold is diffeomorphic to the total space of a vector bundle over some compact solvmanifold. This statement was conjectured by G. Mostow and proved by L. Auslander and R. Tolimieri.
- The fundamental group of an arbitrary solvmanifold is polycyclic.
- A compact solvmanifold is determined up to diffeomorphism by its fundamental group.
- Fundamental groups of compact solvmanifolds may be characterized as group extensions of free abelian groups of finite rank by finitely generated torsion-free nilpotent groups.
- Every solvmanifold is aspherical. Among all compact homogeneous spaces, solvmanifolds may be characterized by the properties of being aspherical and having a solvable fundamental group.
Odd section
Let  be a real Lie algebra. It is called a complete Lie algebra if each map
be a real Lie algebra. It is called a complete Lie algebra if each map
- ad
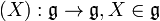
in its adjoint representation is hyperbolic, i.e. has real eigenvalues. Let G be a solvable Lie group whose Lie algebra  is complete. Then for any closed subgroup Γ of G, the solvmanifold G/Γ is a complete solvmanifold.
is complete. Then for any closed subgroup Γ of G, the solvmanifold G/Γ is a complete solvmanifold.
References
- L. Auslander, An exposition of the structure of solvmanifolds I, II, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc., 79:2 (1973), pp. 227–261, 262–285
- Cooper, Daryl; Scharlemann, Martin (1999), The structure of a solvmanifold's Heegaard splittings, "Proceedings of 6th Gökova Geometry-Topology Conference", Turkish Journal of Mathematics 23 (1): 1–18, ISSN 1300-0098, MR 1701636
- V.V. Gorbatsevich (2001), "S/s086100", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4