Small cardiac vein
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Vein: Small cardiac vein | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Base and diaphragmatic surface of heart (small cardiac vein labeled at lower righ.) | |
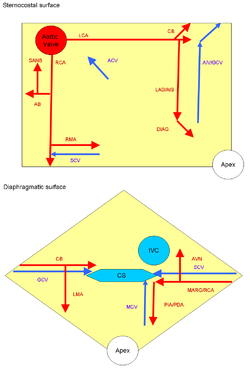 | |
| Arteries: RCA = right coronary AB = atrial branches SANB = sinuatrial nodal RMA = right marginal LCA = left coronary CB = circumflex branch LAD/AIB = anterior interventricular LMA = left marginal PIA/PDA = posterior descending AVN = atrioventricular nodal Veins: SCV = small cardiac ACV = anterior cardiac AIV/GCV = great cardiac MCV = middle cardiac CS = coronary sinus | |
| Latin | Vena cardiaca parva, vena cordis parva |
| Gray's | p.642 |
| Drains to | Coronary sinus |
The small cardiac vein runs in the coronary sulcus between the right atrium and ventricle and opens into the right extremity of the coronary sinus.
It receives blood from the back of the right atrium and ventricle.
It may drain to the coronary sinus, right atrium, middle cardiac vein, or be absent.[1]
References
- ↑ Paul A. Iaizzo (7 July 2009). Handbook of Cardiac Anatomy, Physiology, and Devices. Springer. pp. 83–. ISBN 978-1-60327-371-8. Retrieved 31 October 2010.
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.