Slovene language
| Slovene | |
|---|---|
| Slovenian | |
| slovenski jezik, slovenščina | |
| Pronunciation | [sloˈʋenski ˈjɛzik], [sloˈʋenʃtʃina] |
| Native to | Slovenia, Italy (in Friuli Venezia Giulia), Austria (in Carinthia and Styria), Hungary (in Vas); emigrant communities in various countries |
Native speakers | 2.5 million (2010)[1] |
|
Indo-European
| |
| Dialects |
Prekmurje dialect
approx. 32 unstandardised dialects
|
|
Latin (Slovene alphabet) Slovene Braille | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
Regional or local official language in: |
| Regulated by | Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 | sl |
| ISO 639-2 | slv |
| ISO 639-3 | slv |
| Linguasphere | 53-AAA-f (51 varieties) |
 Slovene-speaking areas | |
| South Slavic languages and dialects | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Western South Slavic
|
||||||
|
Eastern South Slavic |
||||||
|
Transitional dialects
|
||||||
|
Alphabets
|
||||||
Slovene or Slovenian (slovenski jezik or slovenščina, not to be confused with slovenčina, the native name of Slovak) belongs to the group of South Slavic languages. It is spoken by approximately 2.5 million speakers worldwide, the majority of whom live in Slovenia. It is the first language of about 1.85 million people and is one of the 24 official and working languages of the European Union.
Standard Slovene
Standard Slovene is the national standard language that was formed in the 18th century, mostly based on Upper and Lower Carniolan dialect groups, the latter being a dialect spoken by Primož Trubar. Since Prekmurje dialect has been omitted from the formation of the standard that was finalized in the 19th and 20th centuries, its speakers still feel disconnected from it and use the dialect more widely than in other regions. In some regions of the Slovene Lands, where the compulsory schooling was in German and Italian, i.e. in the Austrian state of Carinthia and in case of the Slovene minority in Italy, the dialects are more preserved. For example, Resian and Torre (Ter) dialects in the Italian Province of Udine differ most from other Slovene dialects.
The distinctive characteristics of Slovene are dual grammatical number, two accentual norms (one characterized by pitch accent), and abundant inflection (a trait shared with many Slavic languages). Although Slovene is basically an SVO language, word order is very flexible, often adjusted for emphasis or stylistic reasons. Slovene has a T-V distinction: second-person plural forms are used for individuals as a sign of respect. Also, Slovene and Slovak are the two modern Slavic languages whose names for themselves literally mean "Slavic" (slověnьskъ in old Slavonic).
Classification
Slovene is an Indo-European language belonging to the Western subgroup of the South Slavic branch of the Slavic languages, together with Serbo-Croatian. It is close to the Kajkavian and Chakavian dialects of Serbo-Croatian, but further from the Shtokavian dialect, the basis for the Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin, and Serbian standard languages.[2] Furthermore, Slovene shares certain linguistic characteristics with all South Slavic languages, including those of the Eastern subgroup, such as Bulgarian. Although Slovene is almost completely intelligible with the Kajkavian dialects of Serbo-Croatian (especially the variant spoken in Hrvatsko Zagorje on the border with Slovenia), mutual intelligibility with other varieties of Serbo-Croatian is hindered by differences in vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation. The Slovene language also has many commonalities with the West Slavic languages.[3]
History
Early history

Like all Slavic languages, Slovene traces its roots to the same proto-Slavic group of languages that produced Old Church Slavonic. The earliest known examples of a distinct, written Slovene dialect are from the Freising Manuscripts, known in Slovene as Brižinski spomeniki. The consensus estimate of their date of origin is between 972 and 1093 (most likely before 1000). These religious writings are among the oldest surviving manuscripts in any Slavic language.
The Freising Manuscripts are a record of a proto-Slovene language that was spoken in a much larger territory than modern Slovene, which included most of the present-day Austrian states of Carinthia and Styria, as well as East Tyrol, the Val Pusteria in South Tyrol, and some areas of Upper and Lower Austria.[4] By the 15th century, most of the northern areas were gradually Germanized: the northern border of the Slovene-speaking territory stabilized on the line going from north of Klagenfurt to south of Villach and east of Hermagor in Carinthia, while in Styria it was pretty much identical with the current Austrian-Slovenian border. This linguistic border remained almost unchanged until the late 19th century, when a second process of Germanization took place, mostly in Carinthia. Between the 9th and 12th century, proto-Slovene spread into northern Istria and in the areas around Trieste.
During most of the Middle Ages, Slovene was a vernacular language of the peasantry, although it was also spoken in most of the towns on Slovene territory, together with German or Italian. Although during this time, German emerged as the spoken language of the nobility, Slovene had some role in the courtly life of the Carinthian, Carniolan and Styrian nobility, as well. This is proved by the survival of certain ritual formulas in Slovene (such as the ritual installation of the Dukes of Carinthia). The words "Buge waz primi, gralva Venus!" ("God be With You, Queen Venus!"), with which Bernhard von Spanheim greeted the poet Ulrich von Liechtenstein upon his arrival to Carinthia in 1227 (or 1238),[5] is another example of some level of Slovene knowledge among high nobility in the region.[6]
The first printed Slovene words, stara pravda (meaning 'old justice'), appeared in 1515 in Vienna in a poem of the German mercenaries who suppressed the Slovene peasant revolt.[7] Standard Slovene emerged in the second half of the 16th century, thanks to the works of Slovene Lutheran authors, who were active during the Protestant Reformation. The most prominent authors from this period are Primož Trubar, who wrote the first books in Slovene; Adam Bohorič, the author of the first Slovene grammar; and Jurij Dalmatin, who translated the entire Bible into Slovene.
From the high Middle Ages up to the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1918, in the territory of present-day Slovenia, German was the language of the elite, and Slovene was the language of the common people. During this period, German had a strong influence on Slovene, and many Germanisms are preserved in contemporary colloquial Slovene. Many Slovene scientists before the 1920s also wrote in foreign languages, mostly German, which was the lingua franca of science throughout Central Europe at the time.
Recent history
During the rise of Romantic Nationalism in the 19th century, the cultural movements of Illyrism and Pan-Slavism brought words from Serbo-Croatian and Czech into standard Slovene, mostly to replace words previously borrowed from German. Most of these innovations have remained, although some were dropped in later development. In the second half of the 19th century, many nationalist authors made an abundant use of Serbo-Croatian words: among them were Fran Levstik and Josip Jurčič, who wrote the first novel in Slovene in 1866. This tendency was reversed in the Fin de siècle period by the first generation of modernist Slovene authors (most notably the writer Ivan Cankar), who resorted to a more "pure" and simple language without excessive Serbo-Croatian borrowings.
During the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in the 1920s and 1930s, the influence of Serbo-Croatian increased again. This was opposed by the younger generations of Slovene authors and intellectuals; among the most fierce opponents of an excessive Serbo-Croatian influence on Slovene were the intellectuals associated with the leftist journal Sodobnost, as well as some younger Catholic activists and authors. After 1945, numerous Serbo-Croatian words that had been used in the previous decades were dropped. The result was that a Slovene text from the 1910s is frequently closer to modern Slovene than a text from the 1920s and 1930s.
Between 1920 and 1941, the official language of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was defined as "Serbian-Croatian-Slovene". In practice, Slovene was used in Slovenia, both in education and administration. Many state institutions used only Serbo-Croatian, and a Slovene–Serbo-Croatian bilingualism was applied in many spheres of public life in Slovenia. For examples, at the post offices, railways and in administrative offices, Serbo-Croatian was used together with Slovene. However, state employees were expected to be able to speak Slovene in Slovenia.
During the same time, western Slovenia (the Slovenian Littoral and the western districts of Inner Carniola) was under Italian administration and submitted to a violent policy of Fascist Italianization; the same policy was applied to Slovene speakers in Venetian Slovenia, Gorizia and Trieste. Between 1923 and 1943, all public use of Slovene language in these territories was strictly prohibited, and Slovene language activists were persecuted by the state.
After the Carinthian Plebiscite of 1920, a less severe policy of Germanization took place in the Slovene-speaking areas of southern Carinthia which remained under Austrian administration. After the Anschluss of 1938, the use of Slovene was strictly forbidden in Carinthia, as well. This accelerated a process of language shift in Carinthia, which continued throughout the second half of the 20th century: according to the Austro-Hungarian census of 1910, around 17% of inhabitants of Carinthia spoke Slovene in their daily communication; in 1951, this figure dropped under 10%, and by 2001 to a mere 2.8%.
During World War II, Slovenia was divided among the Axis Powers of Fascist Italy, Nazi Germany, and Hungary. Each of the occupying powers tried to either discourage or entirely suppress the Slovene language.
Following World War II, Slovenia became part of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Slovene was one of the official languages of the federation. In the territory of Slovenia, it was commonly used in almost all areas of public life. One important exception was the Yugoslav army, where Serbo-Croatian was used exclusively, even in Slovenia.
National independence has revitalized the language: since 1991, when Slovenia gained independence, Slovene has been used as an official language in all areas of public life. In 2004 it became one of the official languages of the European Union upon Slovenia's admission.
Joža Mahnič, a literary historian and the then president of Slovenska matica, a prestigious publishing house, said in February 2008 that Slovene is a language rich enough to express everything, including the most sophisticated and specialised texts.[8] In February 2010, Janez Dular, a prominent Slovenian linguist, commented that, although Slovene is not an endangered language, its scope has been shrinking, especially in science and higher education.[9][10]
Geographic distribution
The language is spoken by about 2.5 million people, mainly in Slovenia, but also by Slovene national minorities in Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Italy (around 90,000 in Venetian Slovenia, Resia Valley, Canale Valley, Province of Trieste and in those municipalities of the Province of Gorizia bordering with Slovenia), in southern Carinthia and some parts of Styria in Austria (25,000). It is also spoken in Croatia, especially in Istria, Rijeka and Zagreb (11,800-13,100), in southwestern Hungary (3-5,000), in Serbia (5,000), and by the Slovene diaspora throughout Europe and the rest of the world (around 300,000), particularly in the United States (most notably Ohio home to estimated 3,400 speakers),[11] Canada, Argentina, Australia and South Africa.[2]
Dialects
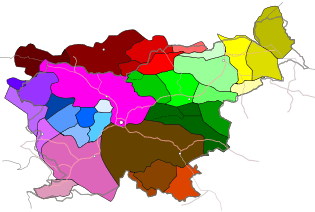
Slovene is sometimes characterized as the most diverse Slavic language in terms of dialects,[12] with different degrees of mutual intelligibility.[citation needed] Accounts of the number of dialects range from as few as seven[13][14][15] dialects, often considered dialect groups or dialect bases that are further subdivided into as many as 50 dialects.[16] Other sources characterize the number of dialects as nine[17] or eight.[18] Although pronunciation differs greatly from area to area, those differences do not pose major obstacles to understanding. The standard language is mainly used in public presentations or on formal occasions.
The Prekmurje and Resian dialects, being the furthest from the standard language, have been standardized. Speakers of those two dialects have considerable difficulties with being understood by speakers of other varieties of Slovene, needing code-switching to the Standard Slovene. Other dialects are mutually intelligible when speakers avoid the excessive usage of regionalisms.
Regionalisms are mostly limited to culinary and agricultural expressions, although there are many exceptions. Some loanwords have become so deeply rooted into the local language, that people have considerable difficulties in finding a standard expression for the dialectical term (for instance, kovter meaning blanket is prešita odeja in Standard Slovene, but the latter term is never used in speech). Western dialects incorporate a great deal of calques and loanwords from Italian, whereas eastern dialects remain replete with remnants of the German reign. Usage of those words is considered bad style even in colloquial language and is discouraged because it hinders intelligibility between dialects.
Phonology
Slovene has a phoneme set consisting of 21 consonants and 8 vowels.
Consonants
Slovene has 21 distinctive consonant phonemes. Conditional allophones are shown in parentheses.
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Dental | Palato- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | (ŋ) | |||||||||
| Plosive | p | b | t | d | k | ɡ | ||||||
| Affricate | t͡s | (d͡z) | t͡ʃ | d͡ʒ | ||||||||
| Fricative | f | (v) | s | z | ʃ | ʒ | x | (ɣ) | ||||
| Approximant | (w) | ʋ | l | j | ||||||||
| Trill | r | |||||||||||
All voiced obstruents are devoiced at the end of words unless immediately followed by a word beginning with a vowel or a voiced consonant. In consonant clusters, voicing distinction is neutralized and all consonants assimilate the voicing of the rightmost segment. In this context, [v], [ɣ] and [d͡z] may occur as voiced allophones of /f/, /x/ and /t͡s/, respectively (e.g. vŕh drevésa [ʋrɣ dreˈʋesa]).[20]
/ʋ/ has several allophones depending on context.
- Before a vowel, pronunciation is labiodental, [ʋ] or [v].
- After a vowel, pronunciation is bilabial [w] and forms a diphthong.
- At the beginning of a syllable, before a consonant (for example in vsi "all"), the pronunciation varies more widely by speaker and area. Many speakers convert /ʋ/ into a full vowel [u] in this position. For those speakers that retain a consonantal pronunciation, it may be pronounced [w] or [v], while before a voiceless consonant it devoices to [ʍ] or [f] respectively. Thus, vsi may be pronounced as disyllabic [uˈsi] or monosyllabic [ʍsi] or [fsi].
The preposition v is always bound to the following word; however its phonetic realization follows the normal phonological rules for /ʋ/.
The sequences /lj/, /nj/ and /rj/ occur only before a vowel. Before a consonant or word-finally, they are reduced to /l/, /n/ and /r/ respectively. This is reflected in the spelling in the case of /rj/, but not for /lj/ and /nj/.
Under certain (somewhat unpredictable) circumstances, /l/ at the end of a syllable may become [w], merging with the allophone of /ʋ/ in that position.
Vowels
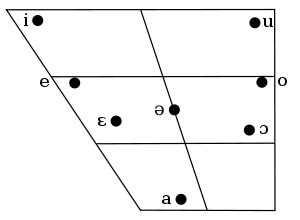
Slovene has an eight-vowel system, in comparison to the five-vowel system of Serbo-Croatian.
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Close-mid | e | ə | o |
| Open-mid | ɛ | ɔ | |
| Open | a | ||
Slovene also distinguishes vowel length, but vowel length and stress are closely intertwined. This is therefore discussed in the prosody section, below.
In the colloquial spoken language, unstressed and most short stressed vowels tend to be reduced or elided. For example kȕp "heap" > [kǝ̏p], právimo "we say" > [prâwmo].[21]
Prosody
All dialects of Slovene have phonemic stress, but the same word can be accented quite differently in different dialects. Most words have a single syllable that carries stress. Some compounds, but not all, have multiple stresses, inherited from the parts that make up the compound. There are also a few small words and clitics, including prepositions, that have no inherent stress at all and attach prosodically to another word.
Stressed syllables are generally characterized by dynamic accent (increased loudness). In non-final syllables, quantitative accent (increased syllable length) is also present in almost all words. In tonemic varieties, stressed syllables also have a distinction of phonemic tone (high or low). Stress and vowel length are closely intertwined:[22]
- A non-final syllable that bears stress will automatically have a long vowel. Conversely, at most one vowel in a Slovene word is long, and it automatically bears the stress.
- If a word has no long vowels, the stress usually falls on the final syllable. However, a limited number of words have non-final stress on short syllables.
- The combination /ǝr/, although phonetically short, may be stressed and behaves as a long vowel in that case. In particular, it may carry tonal distinctions.
- Schwa /ǝ/ in other positions can also carry the stress, but does not have tonal distinctions and thus behaves as a short vowel.
Note that vowel length is clearly phonemic in stressed final syllables, which can be either long or short. In other syllables, however, whether vowel length or stress, or both, are phonemic depends on the underlying phonological analysis. Generally speaking, stress and length co-occur in all but the final syllable, so one feature or the other is phonetically redundant in those words.
Tone
The standard language has two varieties, tonemic and non-tonemic. These differ only in the presence of phonemic tonal distinctions on stressed syllables (i.e. pitch accent) in the former. Phonemic tone exists only in a north-south band of dialects in the center of the country (the Upper and Lower Carniolan dialect groups and part of the Carinthian dialect group).[23] However, because the Slovenian capital city Ljubljana is located within the central tonemic dialect area, phonemic tone was included in the standard language, and in fact the tonemic variety is more prestigious and is universally used in formal TV and radio broadcasts.
In the tonemic variety, the following additional rules apply to stressed vowels (unstressed vowels never carry tonal distinction):
- Long vowels as well as tautosyllabic stressed /ǝr/ (i.e. stressed /ǝr/ not directly followed by a vowel in the same word) can bear either a high or low tone. (The terms falling or circumflex are sometimes used in place of high; likewise, rising or acute may be used in place of low.)
- High-tone low-mid /ɛ́ː/ /ɔ́ː/ are uncommon.
- Short vowels other than /ǝ/ are always high-tone.
- /ǝ/ (when not part of a stressed /ǝr/ combination) is normally tonemically high in final syllables and low elsewhere.
This leads to the following possible combinations of tone/length and vowel quality:
|
|
Note that tautosyllabic stressed /ǝr/ behaves like a long vowel in terms of the tones it can bear, and in fact it is notated as such in the tonemic writing system (see below). Examples: pr̂stnica "phalange" (high tone) vs. pŕstanǝc "finger" (low tone). However, since it does not have any length distinction, it is equally valid to class it as a short vowel.
The non-tonemic system is identical to the tonemic system above in terms of vowel length and stress, but lacks any phonemic tone. This means that, for those dialects, the first and second rows merge, as do the third and fourth.
Grammar
Nouns
Slovene nouns retain six of the seven Slavic noun cases: nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, locative and instrumental. There is no distinct vocative; the nominative is used in that role. Nouns, adjectives and pronouns have three numbers: singular, plural and a special dual form that indicates exactly two objects.
Nouns in Slovene are either masculine, feminine or neuter gender. In addition, there is a distinction between animate and inanimate nouns, although this is only relevant for masculine nouns and only in the singular. Animate nouns have an accusative singular form that is identical to the genitive, while for inanimate nouns the accusative singular is the same as the nominative. Animacy is based mostly on semantics and is less rigid than gender. Generally speaking a noun is animate if it refers to something that is generally thought to have free will and/or the ability to move of its own accord. This includes all nouns for people and animals. All other nouns are inanimate, including plants and other non-moving life forms, and also groups of people or animals. However, there are some nouns for inanimate objects that are generally animate, which mostly include inanimate objects that are named after people or animals. This includes:[24]
- Dead people or animals
- Brands of cars
- Certain diseases (named after animals)
- Certain devices (named after animals or people)
- Works of art (named after their creator)
- Chess pieces and playing cards (named for the people they represent)
- Wines and mushrooms (named as demonyms)
Vocabulary
T–V distinction

An additional nonstandard but widespread use of a singular participle combined with a plural auxiliary verb (known as polvikanje) signals a somewhat more friendly and less formal attitude while maintaining politeness:
- Vi ga niste videli. ('You did not see him': both the auxiliary verb niste and the participle videli are plural masculine. Standard usage.)
- Vi ga niste videl/videla. ('You did not see him': the auxiliary verb niste is plural but the participle videl/videla is singular masculine/feminine. Nonstandard usage.)
The use of nonstandard forms (polvikanje) might be frowned upon by many people and would not likely be used in a formal setting.
The use of the 3rd person plural oni ('they') form (known as onikanje in both direct address and indirect reference) as an ultra-polite form is now archaic or dialectal; it is associated with servant-master relationships in older literature, the child-parent relationship in certain conservative rural communities, and parishioner-priest relationships.
Foreign words
Foreign words used in Slovene are of various types depending on the assimilation they have undergone. The types are:
- sposojenka (loan word) – fully assimilated; e.g. pica ('pizza').
- tujka (foreign word) – partly assimilated, either in writing and syntax and/or in pronunciation; e.g. jazz, wiki.
- polcitatna beseda ali besedna zveza (half-quoted word or phrase) – partly assimilated, either in writing and syntax and/or in pronunciation; e.g. Shakespeare, but Shakespearja in genitive case.
- citatna beseda ali besedna zveza (quoted word or phrase) – kept as in original, although pronunciation may be altered to fit into speech flow; e.g. first lady in all cases.
Articles
There are no definite or indefinite articles as in English (a, an, the) or German (der, die, das, ein, eine). A whole verb or a noun is described without articles and the grammatical gender is found from the word's termination. It is enough to say barka (a or the barge), Noetova barka ('Noah's ark'). The gender is known in this case to be feminine. In declensions, endings are normally changed; see below. If one should like to somehow distinguish between definiteness or indefiniteness of a noun, one would say (prav/natanko/ravno) tista barka ('that (exact) barge') for "the barge" and neka/ena barka ('one barge') for "a barge".
Definiteness of a noun phrase can also be discernible through the ending of the accompanying adjective. One should say rdeči šotor ([exactly that] red tent) or rdeč šotor ([a] red tent). This difference is observable only for masculine nouns in nominative or accusative case. Because of the lack of article in Slovene and audibly insignificant difference between the masculine adjective forms, most dialects do not distinguish between definite and indefinite variants of the adjective, leading to hypercorrection when speakers try to use Standard Slovenian.[25]
Numbers
Writing system
This alphabet (Slovene: abeceda) was derived in the mid-1840s from the system created by Croatianist Ljudevit Gaj. Intended for the Serbo-Croatian language (in all its varieties), it was patterned on the Czech alphabet of the 1830s. Before that /s/ was, for example, written as ⟨ʃ⟩, ⟨ʃʃ⟩ or ⟨ſ⟩; /tʃ/ as ⟨tʃch⟩, ⟨cz⟩, ⟨tʃcz⟩ or ⟨tcz⟩; /i/ sometimes as ⟨y⟩ as a relic from the now modern Russian yery character ⟨ы⟩, usually transliterated as "y"; /j/ as ⟨y⟩; /l/ as ⟨ll⟩; /ʋ/ as ⟨w⟩; /ʒ/ as ⟨ʃ⟩, ⟨ʃʃ⟩ or ⟨ʃz⟩.
The standard Slovene orthography, used in almost all situations, uses only the letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet plus ⟨č⟩, ⟨š⟩, and ⟨ž⟩:
| letter | phoneme | example word | word pronunciation |
|---|---|---|---|
| A a | /aː/ /a/ | dan "day" abeceda "alphabet" | /ˈdáːn/, dȃn /abɛˈtséːda/, abecẹ̑da |
| B b | /b/ | beseda "word" | /bɛˈséːda/, besẹ̑da |
| C c | /t͡s/ | cvet "bloom" | /ˈtsʋéːt/, cvẹ̑t |
| Č č | /t͡ʃ/ | časopis "newspaper" | /tʃasɔˈpíːs/, časopı̑s |
| D d | /d/ | danes "today" | /ˈdàːnəs/, dánəs |
| E e | /eː/ /ɛː/ /ɛ/ /ə/ | sedem "seven" reči "to say" medved "bear" sem "I am" | /ˈséːdəm/, sẹ́dəm /ˈrɛ̀ːtʃi/, réči /ˈmɛ̀ːdʋɛt/, médved /ˈsə́m/, sə̏m |
| F f | /f/ | fant "boy" | /ˈfánt/, fȁnt |
| G g | /ɡ/ | grad "castle" | /ˈɡráːt/, grȃd |
| H h | /x/ | hiša "house" | /ˈxìːʃa/, híša |
| I i | /iː/ /i/ | biti "to be" imeti "to have" | /ˈbìːti/, bíti /iˈmèːti/, imẹ́ti |
| J j | /j/ | jabolko "apple" | /ˈjàːbɔwkɔ/, jábołko |
| K k | /k/ | kmèt "peasant" | /ˈkmɛ́t/, kmȅt |
| L l | /l/ /w/ | letalo "airplane" zrel "mature" | /lɛˈtàːlɔ/, letálo /ˈzrɛ́w/, zrȅł |
| M m | /m/ | misliti "to think" | /ˈmìːsliti/, mísliti |
| N n | /n/ | novice "news" | /nɔˈʋìːtsɛ/, novíce |
| O o | /oː/ /ɔː/ /ɔ/ | opica "monkey" okno "window" gospa "lady" | /ˈóːpitsa/, ọ̑pica /ˈɔ̀ːknɔ/, ókno /ɡɔˈspàː/, gospá |
| P p | /p/ | pomoč "help" | /pɔˈmóːtʃ/, pomọ̑č |
| R r | /r/ /ər/ | riž "rice" trg "square" | /ˈríːʃ/, rȋž /ˈtə́rk/, tȓg |
| S s | /s/ | svet "world" | /ˈsʋéːt/, svẹ̑t |
| Š š | /ʃ/ | šola "school" | /ˈʃóːla/, šọ̑la |
| T t | /t/ | tip "type" | /ˈtíːp/, tȋp |
| U u | /uː/ /u/ | ulica "street" mamut "mammoth" | /ˈùːlitsa/, úlica /ˈmáːmut/, mȃmut |
| V v | /ʋ/ /w/ | voda "water" lev "lion" | /ˈʋɔ̀ːda/, vóda /ˈlɛ́w/, lȅv |
| Z z | /z/ | zima "winter" | /ˈzìːma/, zíma |
| Ž ž | /ʒ/ | življenje "life" | /ʒiwˈljɛ̀ːnjɛ/, življénje |
The orthography thus underdifferentiates several phonemic distinctions:
- Stress, vowel length and tone are not distinguished, except with optional diacritics when it is necessary to distinguish between similar words with a different meaning.
- The two distinct mid-vowels are also not distinguished, both written as simply ⟨e⟩ and ⟨o⟩.
- The schwa /ǝ/ is also written as ⟨e⟩. However, the combination /ǝr/ is written as simply ⟨r⟩ between consonants and is thus distinguishable.
- Vocalised el /w/ is written as ⟨l⟩, but cannot be predictably distinguished from /l/ in that position.
In the tonemic varieties of Slovene, the ambiguity is even worse: e in a final syllable can stand for any of /éː/ /èː/ /ɛ́ː/ /ɛ̀ː/ /ɛ/ /ǝ/ (although /ɛ̀ː/ is rare).
The reader is expected to gather the interpretation of the word from the context, as in these examples:
- gol:
- /ˈɡɔ́w/ gȍł "naked"
- /ˈɡóːl/ gọ̑l "goal"
- jesen:
- /ˈjɛ̀ːsɛn/ jésen "ash tree"
- /jɛˈséːn/ jesẹ̑n "autumn"
- kot
- /ˈkòːt/ kọ́t "angle"
- /kɔt/ kot "as"
- med
- /mɛt/ med "between"
- /ˈméːt/ mẹ̑d "honey"
- pol
- /ˈpóːl/ pọ̑l "pole"
- /ˈpóːw/ pọ̑ł "half"
- /ˈpɔ̀ːl/ pól "half an hour before (the hour)"
- precej
- /ˈprɛ́tsɛj/ prȅcej "at once" (archaic)
- /prɛˈtséːj/ precẹ̑j or /prɛˈtsɛ́j/ precȅj "a great deal (of)"
Diacritics
To compensate for the shortcomings of the standard orthography, Slovene also uses standardized diacritics or accent marks to denote stress, vowel length and pitch accent, much like the closely related Serbo-Croatian. However, as in Serbo-Croatian, use of such accent marks is restricted to dictionaries, language textbooks and linguistic publications. In normal writing, the diacritics are almost never used, except in a few minimal pairs where real ambiguity could arise.
Two different and mutually incompatible systems of diacritics are used. The first is the simpler non-tonemic system, which can be applied to all Slovene dialects. It is more widely used and is the standard representation in dictionaries such as SSKJ. The tonemic system also includes tone as part of the representation. However, neither system reliably distinguishes schwa /ǝ/ from the front mid-vowels, nor vocalised l /w/ from regular l /l/. Some sources write these as ǝ and ł respectively, but this is not as common.
Non-tonemic diacritics
In the non-tonemic system, the distinction between the two mid-vowels is indicated, as well as the placement of stress and length of vowels:
- Long stressed vowels are notated with an acute diacritic: á é í ó ú ŕ (IPA: /aː eː iː oː uː ǝr/).
- However, the rarer long stressed low-mid vowels /ɛː/ and /ɔː/ are notated with a circumflex: ê ô.
- Short stressed vowels are notated with a grave: à è ì ò ù (IPA: /a ɛ i ɔ u/). Some systems may also include ǝ̀ for /ǝ/.
Tonemic diacritics
The tonemic system uses the diacritics somewhat differently from the non-tonemic system. The high-mid vowels /eː/ and /oː/ are written ẹ ọ with a subscript dot, while the low-mid vowels /ɛː/ and /ɔː/ are written as plain e o.
Pitch accent and length is indicated by four diacritical marks:
- The acute ( ´ ) indicates long and low pitch: á é ẹ́ í ó ọ́ ú ŕ (IPA: /àː ɛ̀ː èː ìː ɔ̀ː òː ùː ǝ̀r/).
- The inverted breve ( ̑ ) or the circumflex ( ^ ) indicates long and high pitch: ȃ ȇ ẹ̑ ȋ ȏ ọ̑ ȗ ȓ (IPA: /éː ɛ́ː éː íː ɔ́ː óː úː ǝ́r/).
- The grave ( ` ) indicates short and low pitch. This occurs only on è (IPA: /ǝ̀/), optionally written as ǝ̀.
- The double grave ( ̏ ) indicates short and high pitch: ȁ ȅ ȉ ȍ ȕ (IPA: á ɛ́ í ɔ́ ú). ȅ is also used for /ǝ́/, optionally written as ǝ̏.
The schwa vowel /ǝ/ is written ambiguously as e, but its accentuation will sometimes distinguish it: a long vowel mark can never appear on a schwa, while a grave accent can appear only on a schwa. Thus, only ȅ is truly ambiguous.
Regulation
Standard Slovene spelling and grammar are defined by the Orthographic Committee and the Fran Ramovš Institute of the Slovenian Language, which are both part of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts (Slovenska akademija znanosti in umetnosti, SAZU). The newest reference book of standard Slovene spelling (and to some extent also grammar) is the Slovenski pravopis (SP2001; Slovene Normative Guide). The latest printed edition was published in 2001 (reprinted in 2003 with some corrections) and contains more than 130,000 dictionary entries. In 2003, an electronic version was published.
The official dictionary of modern Slovene, which was also prepared by SAZU, is Slovar slovenskega knjižnega jezika (SSKJ; Standard Slovene Dictionary). It was published in five volumes by Državna Založba Slovenije between 1970 in 1991 and contains more than 100,000 entries and subentries with accentuation, part-of-speech labels, common collocations, and various qualifiers. In the 1990s, an electronic version of the dictionary was published and it is available online.
The SAZU considers SP2001 to be the normative source on Slovenian language. When dictionary entries in SP2001 and SSKJ differ, the SP2001 entry takes precedence.[citation needed]
Notes
- ↑ "International Mother Language Day 2010". Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia. 19 February 2010. Retrieved 29 January 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Greenberg, Marc L., A Short Reference Grammar of Slovene, (LINCOM Studies in Slavic Linguistics 30). Munich: LINCOM, 2008. ISBN 3-89586-965-1
- ↑ Dular, Janez (2001). "Jezikovni položaj" [Language Situation] (in Slovene). Government of the Republic of Slovenia. Retrieved 11 May 2012.
- ↑ Bogo Grafenauer, Karantanija: izbrane razprave in članki (Ljubljana: Slovenska matica, 2000)
- ↑ Matičetov, Milko (1993). "Od koroskega gralva 1238 do rezijanskega krajaua 1986". Jezik in slovstvo [Language and Literature] (in Slovene) (Faculty of Arts, University of Ljubljana) (5).
- ↑ Kalin Golob, Monika. Komac, Nataša. Logar, Nataša (2007). "Sounds and letters". In Žnidarko, Mito. On Slovene Language. European Parliament Information Office for Slovenia, Ministry of Culture of the Republic of Slovenia, Government Office for European Affairs of the Republic of Slovenia. p. 33. ISBN 978-92-823-2350-2.
- ↑ Štih, Peter (2000). "Slovenski kmečki upor" [The Slovene Peasant Revolt]. In Vidic, Marko. Ilustrirana zgodovina Slovencev [The Illustrated History of the Slovenes] (in Slovene). Mladinska knjiga. p. 142. ISBN 86-11-15664-1.
- ↑ "Družina: Slovenščina se siromaši "v ustih domišljavih bedakov"" [Slovene Is Impoverished "In the Mouths of Conceited Fools"] (in Slovene). Družina. 24 August 2008.
- ↑ "Linguist Says Slovenian Language Not Endangered". Slovenian Press Agency. 21 February 2010.
- ↑ "Bo slovenščina nekoč le orodje preprostega sporazumevanja?" [Will Slovene Some Day Be Only The Language of Simple Communication] (in Slovene). MMC RTV Slovenia. 21 February 2010.
- ↑ http://www.usefoundation.org/view/29
- ↑ "International Mother Language Day". Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia. 19 February 2009. Retrieved 3 February 2011.
- ↑ McDonald, Gordon C. 1979. Yugoslavia: A Country Study. Washington, DC: American University, p. 93
- ↑ Greenberg, Marc L. 2009. "Slovene." In Keith Brown & Sarah Ogilvie (eds.), Concise Encyclopedia of Languages of the World, pp. 981–984. Oxford: Elsevier, p. 981.
- ↑ Brown, E. K. & Anne Anderson. 2006. Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics: Sca-Spe. Oxford: Elsevier, p. 424
- ↑ Sussex, Roland, & Paul V. Cubberley. 2006. The Slavic languages. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 502.
- ↑ Sławski, Franciszek. 1962. Zarys dialektologii południowosłowiańskiej. Warsaw: PAN.
- ↑ Priestly, Tom M. S. 1993. "On 'Drift' in Indo-European Gender Systems.' Journal of Indo-European Studies 11: 339–363.
- ↑ Herrity (2000:15–16)
- ↑ Herrity (2000:16)
- ↑ Priestley (2002:394)
- ↑ Priestley (2002:390)
- ↑ Priestley (2002:449)
- ↑ Herrity, Peter (2000). Slovene: A Comprehensive Grammar. Routledge. pp. 34–35. ISBN 0415231485.
- ↑ "Kako uporabljati določne pridevnike". ŠUSS. 2 June 2005. Retrieved 30 January 2011.
References
- Herrity, Peter (2000), Slovene: A Comprehensive Grammar, London: Routledge, ISBN 0415231485
- Priestley, T.M.S. (2002), "Slovene", in Comrie, Bernard; Corbett, Greville. G., The Slavonic Languages, London: Routledge, pp. 388–451, ISBN 0-415-28078-8
External links
| Slovenian edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| Slovenian edition of Wikisource, the free library |
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of: Slovene |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Slovene language. |
- Centre for Slovene as a Second/Foreign Language
- Slovenian Phonology
- Reference Grammar for Slovene [PDF] by Mark L. Greenberg
Grammars
Corpora
- Slovenian National Corpus 600 M words corpus of Slovenian FidaPLUS
- 200 M words corpus of Slovenian Nova beseda
Dictionaries
- (Slovene) Standard Slovene Dictionary (SSKJ)
- (Slovene) Comprehensive list of the Slovene dictionaries
- (Slovene) Spletni Slovar (Multilingual Dictionary)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||