Skew-Hermitian
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
An  by
by  complex or real matrix
complex or real matrix 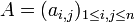 is said to be anti-Hermitian, skew-Hermitian, or said to represent a skew-adjoint operator, or to be a skew-adjoint matrix, on the complex or real
is said to be anti-Hermitian, skew-Hermitian, or said to represent a skew-adjoint operator, or to be a skew-adjoint matrix, on the complex or real  dimensional space
dimensional space  , if its adjoint is the negative of itself: :
, if its adjoint is the negative of itself: : .
.
Note that the adjoint of an operator depends on the scalar product considered on the  dimensional complex or real space
dimensional complex or real space  . If
. If  denotes the scalar product on
denotes the scalar product on  , then saying
, then saying 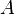 is skew-adjoint means that for all
is skew-adjoint means that for all 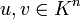 one has
one has

In the particular case of the canonical scalar products on  , the matrix of a skew-adjoint operator satisfies
, the matrix of a skew-adjoint operator satisfies 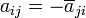 for all
for all  .
.
Imaginary numbers can be thought of as skew-adjoint (since they are like 1-by-1 matrices), whereas real numbers correspond to self-adjoint operators.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.