Sinus Meridiani

Sinus Meridiani is a feature name for an albedo feature on Mars stretching east-west just south of that planet's equator. It was named by the French astronomer Camille Flammarion in the late 1870s. It has a diameter of 1622 km, and its center is located at 7.12 S and 4 E.[1]
Observational History
The name Sinus Meridiani was given to the a classic albedo feature on Mars by the French astronomer Camille Flammarion in the late 1870s. Prior astronomers, notably the German team of Wilhelm Beer and Johann Heinrich Mädler and then the Italian Giovanni Schiaparelli, had chosen a particular point on Mars as being the location of its prime meridian when they charted their observations. Accepting suggestions that dark areas on the surface of Mars were seas or oceans, Flammarion named a dark area at that point "Sinus Meridiani", literally "Meridian Bay", when he worked on his compilation and analysis of all prior observations of Mars.
Since flyby and orbital spacecraft imagery of Mars began to become available in the 1960s, dark-light albedo features on the planet have seen shifting of names to reflect the true nature of the topography, and Sinus Meridiani consequently was given a new designation, Terra Meridiani ("Meridian Land"). . However, the older and the newer designations are both in current use. The U.S. Geological Survey considers the "Sinus Meridiani" nomenclature canonical [2]
Meridiani Planum
The name Meridiani Planum ("Meridian Plain") is used to refer specifically to the landing site of Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity, in the western portion of Sinus Meridiani. This site was chosen by the Mars Exploration Rover team both for its characteristic as a flat and mostly rock-free plain (and hence a safe landing site), and also as a site which showed the spectral signature of the mineral hematite, which is often a sign of deposition in an aqueous environment.
What Opportunity Rover Discovered about Rocks and Minerals at Meridiani Planum


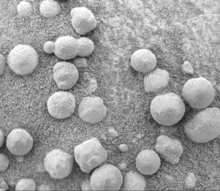
Opportunity Rover found that the soil at Meridiani Planum was very similar to the soil at Gusev crater and Ares Vallis; however in many places at Meridiani the soil was covered with round, hard, gray spherules that were named “blueberries.”[3] These blueberries were found to be composed almost entirely of the mineral hematite. It was decided that the spectra signal spotted from orbit by Mars Odyssey was produced by these spherules. After further study it was decided that the blueberries were concretions formed in the ground by water.[4] Over time, these concretions weathered from what was overlying rock, and then became concentrated on the surface as a lag deposit. The concentration of spherules in bedrock could have produced the observed blueberry covering from the weathering of as little as one meter of rock.[5][6] Most of the soil consisted of olivine basalt sands that did not come from the local rocks. The sand may have been transported from somewhere else.[7]
-

Drawing showing how "blueberries" came to cover much of surface in Meridiani Planum.
Minerals in Dust
A Mössbauer spectrum was made of the dust that gathered on Opportunity’s capture magnet. The results suggested that the magnetic component of the dust was titanomagnetite, rather than just plain magnetite, as was once thought. A small amount of olivine was also detected which was interpreted as indicating a long arid period on the planet. On the other hand, a small amount of hematite that was present meant that there may have been liquid water for a short time in the early history of the planet.[8] Because the Rock Abrasion Tool (RAT) found it easy to grind into the bedrocks, it is thought that the rocks are much softer than the rocks at Gusev crater.
Bedrock Minerals

Few rocks were visible on the surface where Opportunity landed, but bedrock that was exposed in craters was examined by the suit of instruments on the Rover.[9] Bedrock rocks were found to be sedimentary rocks with a high concentration of sulfur in the form of calcium and magnesium sulfates. Some of the sulfates that may be present in bedrocks are kieserite, sulfate anhydrate, bassanite, hexahydrite, epsomite, and gypsum. Salts, such as halite, bischofite, antarcticite, bloedite, vanthoffite, or gluberite may also be present.[10][11]
The rocks contained the sulfates had a light tone compared to isolated rocks and rocks examined by landers/rovers at other locations on Mars. The spectra of these light toned rocks, containing hydrated sulfates, were similar to spectra taken by the Thermal Emission Spectrometer on board the Mars Global Surveyor. The same spectrum is found over a large area, so it is believed that water once appeared over a wide region, not just in the area explored by Opportunity Rover.[12]
The Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) found rather high levels of phosphorus in the rocks. Similar high levels were found by other rovers at Ares Vallis and Gusev Crater, so it has been hypothesized that the mantle of Mars may be phosphorus-rich.[13] The minerals in the rocks could have originated by acid weathering of basalt. Because the solubility of phosphorus is related to the solubility of uranium, thorium, and rare earth elements, they are all also expected to be enriched in rocks.[14]
When Opportunity Rover traveled to the rim of Endeavour crater, it soon found a white vein that was later identified as being pure gypsum.[15][16] It was formed when water carrying gypsum in solution deposited the mineral in a crack in the rock. A picture of this vein, called "Homestake" formation, is shown below.
Evidence for Water

Examination of Meridiani rocks found strong evidence for past water. The mineral called jarosite which only forms in water was found in all bedrocks. This discovery proved that water once existed in Meridiani Planum[17] In addition, some rocks showed small laminations (layers) with shapes that are only made by gently flowing water.[18] The first such laminations were found in a rock called “The Dells.” Geologists would say that the cross-stratification showed festoon geometry from transport in subaqueous ripples.[19] A picture of cross-stratification, also called cross-bedding, is shown on the left.
Box-shaped holes in some rocks were caused by sulfates forming large crystals, and then when the crystals later dissolved, holes, called vugs, were left behind.[20] The concentration of the element bromine in rocks was highly variable probably because it is very soluble. Water may have concentrated it in places before it evaporated. Another mechanism for concentrating highly-soluble bromine compounds is frost deposition at night that would form very thin films of water that would concentrate bromine in certain spots.[21]
-

Voids or "vugs" inside the rock
Rock from Impact
One rock, “Bounce Rock,” found sitting on the sandy plains was found to be ejecta from an impact crater. Its chemistry was different than the bedrocks. Containing mostly pyroxene and plagioclase and no olivine, it closely resembled a part, Lithology B, of the shergottite meteorite EETA 79001, a meteorite known to have come from Mars. Bounce rock received its name by being near an airbag bounce mark.[22]
Meteorites
Opportunity Rover found meteorites just sitting on the plains. The first one analyzed with Opportunity’s instruments was called “Heatshield Rock,” as it was found near where Opportunity’s headshield landed. Examination with the Miniature Thermal Emission Spectrometer (Mini-TES), Mossbauer spectrometer, and APXS lead researchers to, classify it as an IAB meteorite. The APXS determined it was composed of 93% iron and 7% nickel. The cobble named “Fig Tree Barberton” is thought to be a stony or stony-iron meteorite (mesosiderite silicate),[23][24] while “Allan Hills,” and “Zhong Shan” may be iron meteorites.
-

Heat Shield Rock was the first meteorite ever identified on another planet.
-

Heat shield, with Heat Shield Rock just above and to the left in the background.
Geological History
Observations at the site have led scientists to believe that the area was flooded with water a number of times and was subjected to evaporation and desiccation.[25] In the process sulfates were deposited. After sulfates cemented the sediments, hematite concretions grew by precipitation from groundwater. Some sulfates formed into large crystals which later dissolved to leave vugs. Several lines of evidence point toward an arid climate in the past billion years or so, but a climate supporting water, at least for a time, in the distant past.[26]
More images from Sinus Meridiani
-

Layered mesas, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program. Location in Terra Meridiani.
-

Close-up of one of mesas in previous photo showing layers. Mesa may be the remains of a lake in which sediments were deposited. Picture obtained with HiRISE, under HiWish program.
See also
- Geography of Mars
- Mars Exploration Rovers
References
- ↑ http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/SearchResults?target=MARS&featureType=Terra%2C%20terrae
- ↑ United States Geological Survey, Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature; accessed MY 21, 2007
- ↑ Yen, A., et al. 2005. An integrated view of the chemistry and mineralogy of martian soils. Nature. 435.: 49-54.
- ↑ Bell, J (ed.) The Martian Surface. 2008. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-86698-9
- ↑ Squyres, S. et al. 2004. The Opportunity Rover’s Athena Science Investigation at Meridiani Planum, Mars. Science: 1698-1703.
- ↑ Soderblom, L., et al. 2004. Soils of Eagle Crater and Meridiani Planum at the Opportunity Rover Landing Site. Science: 306. 1723-1726.
- ↑ Christensen, P., et al. Mineralogy at Meridiani Planum from the Mini-TES Experiment on the Opportunity Rover. Science: 306. 1733-1739.
- ↑ Goetz, W., et al. 2005. Indication of drier periods on Mars from the chemistry and mineralogy of atmospheric dust. Nature: 436.62-65.
- ↑ Bell, J., et al. 2004. Pancam Multispectral Imaging Results from the Opportunity Rover at Meridiani Planum. Science: 306.1703-1708.
- ↑ Christensen, P., et al. 2004 Mineralogy at Meridiani Planum from the Mini-TES Experiment on the Opportunity Rover. Science: 306. 1733-1739.
- ↑ Squyres, S. et al. 2004. In Situ Evidence for an Ancient Aqueous Environment at Meridian Planum, Mars. Science: 306. 1709-1714.
- ↑ Hynek, B. 2004. Implications for hydrologic processes on Mars from extensive bedrock outcrops throughout Terra Meridiani. Nature: 431. 156-159.
- ↑ Dreibus,G. and H. Wanke. 1987. Volatiles on Earth and Marsw: a comparison. Icarus. 71:225-240
- ↑ Rieder, R., et al. 2004. Chemistry of Rocks and Soils at Meridiani Planum from the Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer. Science. 306. 1746-1749
- ↑ http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/mer/news/mer20111207.html
- ↑ http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2012/01/120125093619.htm
- ↑ Klingelhofer, G. et al. 2004. Jarosite and Hematite at Meridiani Planum from Opportunity’s Mossbauer Spectrometer. Science: 306. 1740-1745.
- ↑ Herkenhoff, K., et al. 2004. Evidence from Opportunity’s Microscopic Imager for Water on Meridian Planum. Science: 306. 1727-1730
- ↑ Squyres, S. et al. 2004. In Situ Evidence for an Ancient Aqueous Environment at Meridian Planum, Mars. Science: 306. 1709-1714.
- ↑ Herkenhoff, K., et al. 2004. Evidence from Opportunity’s Microscopic Imager for Water on Meridian Planum. Science: 306. 1727-1730
- ↑ Yen, A., et al. 2005. An integrated view of the chemistry and mineralogy of martian soils. Nature. 435.: 49-54.
- ↑ Squyres, S. et al. 2004. The Opportunity Rover’s Athena Science Investigation at Meridiani Planum, Mars. Science: 1698-1703.
- ↑ Squyres, S., et al. 2009. Exploration of Victoria Crater by the Mars Rover Opportunity. Science: 1058-1061.
- ↑ Schroder,C., et al. 2008. J. Geophys. Res: 113.
- ↑ Squyres, S. et al. 2004. The Opportunity Rover’s Athena Science Investigation at Meridiani Planum, Mars. Science: 1698-1703.
- ↑ Clark, B. et al. Chemistry and mineralogy of outcrops at Meridiani Planum. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 240: 73-94.
External links
- Google Mars scrollable map - centered on Terra meridiani
- Planetary Science Research Discoveries: Gray Iron Oxide in Meridiani, Mars