Sinapine
| Sinapine | ||
|---|---|---|
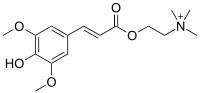 | ||
| IUPAC name 2-{[3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acryloyl]oxy}-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium | ||
| Other names Sinapoylcholine; Sinapic acid choline ester | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| PubChem | 5280385 | |
| ChemSpider | 80576 | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O=C(OCC[N+](C)(C)C)C=Cc1cc(OC)c(O)c(OC)c1|Image 1 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C16H24NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 310.37 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Sinapine is an alkaloidal amine found in black mustard seeds. It is the choline ester of sinapic acid.
Sinapine was discovered by Etienne Ossian Henry in 1825.[1]
Metabolism
Sinapine esterase is an enzyme whose two substrates are sinapine and H2O and whose two products are sinapic acid and choline.
Sinapoylglucose—choline O-sinapoyltransferase is an enzyme whose two substrates are 1-O-sinapoyl-β-D-glucose and choline, whereas its two products are D-glucose and sinapine.
References
- ↑ Tzagoloff, A. (1963). "Metabolism of Sinapine in Mustard Plants. I. Degradation of Sinapine into Sinapic Acid & Choline". Plant physiology 38 (2): 202–206. PMC 549906. PMID 16655775.