Simplicity theory
Simplicity theory is a cognitive theory that seeks to explain the attractiveness of situations or events to human minds. It is based on work done by scientists like Nick Chater, Paul Vitanyi, Jean-Louis Dessalles, and Jürgen Schmidhuber. It claims that interesting situations appear simpler than expected to the observer.
Overview
Technically, simplicity corresponds in a drop in Kolmogorov complexity, which means that, for an observer, the shortest description of the situation is shorter than anticipated. For instance, the description of a consecutive lottery draw, such as 22-23-24-25-26-27, is significantly shorter than a typical one, such as 12-22-27-37-38-42. The former requires only one instantiation (choice of a number among all possible numbers in the lottery), whereas the latter requires six instantiations.
Simplicity theory makes several quantitative predictions concerning the way distance, recency, prominence (places, individuals), or atypicality influence interestingness.
Formalization
The basic concept of simplicity theory is unexpectedness, defined as the difference between expected complexity and observed complexity.
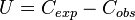
In most contexts,  corresponds to generation complexity, which is the smallest description of all parameters
that must be set in the 'world' for the situation to exist. In the lottery example, generation complexity is identical for a consecutive draw
and a typical draw (as long as no cheating is imagined) and amounts to six instantiations.
corresponds to generation complexity, which is the smallest description of all parameters
that must be set in the 'world' for the situation to exist. In the lottery example, generation complexity is identical for a consecutive draw
and a typical draw (as long as no cheating is imagined) and amounts to six instantiations.
Simplicity theory avoids most criticisms addressed at Kolmogorov complexity by considering only descriptions that are available to a given observer (instead of any imaginable description). This amounts to saying that complexity, and thus unexpectedness, are observer-dependent. For instance, the typical draw 12-22-27-37-38-42 will appear very simple, even simpler than the consecutive one, to the person who played that combination.
Connection with probability
Unexpectedness  is linked to subjective probability
is linked to subjective probability  through formula:
through formula:
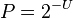
The advantage of this formula is that subjective probability can be assessed without necessarily knowing the alternatives. Classical approaches to probability would consider all situations in the world as having virtually zero probability to have occurred, as each situation is complex and unique. Simplicity theory avoids this trap by considering that subjective improbability is only due to complexity drop.
References
- Chater, N. (1999). The search for simplicity: A fundamental cognitive principle? The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 52 (A), 273-302.
- Chater, N. & Vitányi, P. (2003). Simplicity: a unifying principle in cognitive science?. Trends in cognitive sciences, 7 (1), 19-22.
- Dessalles, Jean-Louis (2008). La pertinence et ses origines cognitives. Paris: Hermes-Science Publications. ISBN 978-2-7462-2087-4.
- Dessalles, Jean-Louis (2010). Have you something unexpected to say? (PDF). The evolution of language - Proceedings of the 8th International Conference (Evolang8 - Utrecht), 99-106. Singapore: World Scientific.
- Feldman, J. (2004). How surprising is a simple pattern? Quantifying ’Eureka!’. Cognition, 93, 199-224.
- Schmidhuber, J. (1997). What’s interesting? Lugano, CH: Technical Report IDSIA-35-97.
External links
- Jean-Louis Dessalles: A tutorial on Simplicity Theory
- Juergen Schmidhuber's page on interest and low complexity