Simplicial map
In the mathematical discipline of simplicial homology theory, a simplicial map is a map between simplicial complexes with the property that the images of the vertices of a simplex always span a simplex. Note that this implies that vertices have vertices for images.
Simplicial maps are thus determined by their effects on vertices. In particular, there are a finite number of simplicial maps between two given finite simplicial complexes.
Simplicial maps induce continuous maps between the underlying polyhedra of the simplicial complexes: one simply extends linearly using barycentric coordinates.
Simplicial maps which are bijective are called simplicial isomorphisms.
Simplicial approximation
Let  be a continuous map between the underlying polyhedra of simplicial complexes and let us write
be a continuous map between the underlying polyhedra of simplicial complexes and let us write 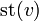 for the star of a vertex. A simplicial map
for the star of a vertex. A simplicial map 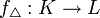 such that
such that 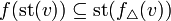 , is called a simplicial approximation to
, is called a simplicial approximation to  .
.
A simplicial approximation is homotopic to the map it approximates.
References
- Munkres, James R.: Elements of Algebraic Topology, Westview Press, 1995. ISBN 978-0-201-62728-2.