Shoebill
| Shoebill | |
|---|---|
.jpg) | |
| Shoebill (Balaeniceps rex) | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Pelecaniformes |
| Family: | Balaenicipitidae Bonaparte, 1853 |
| Genus: | Balaeniceps Gould, 1850 |
| Species: | B. rex |
| Binomial name | |
| Balaeniceps rex Gould, 1850 | |
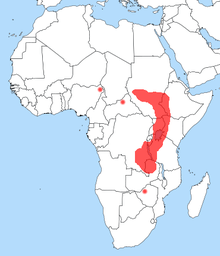 | |
| Shoebill range | |
The Shoebill (Balaeniceps rex) also known as Whalehead or Shoe-billed Stork, is a very large stork-like bird. It derives its name from its massive shoe-shaped bill. Although it has a somewhat stork-like overall form and has previously been classified in the order Ciconiiformes, its true affiliations with other living birds is ambiguous. Some authorities now reclassify it with the Pelecaniformes. The adult is mainly grey while the juveniles are browner. It lives in tropical east Africa in large swamps from Sudan to Zambia.[2]
Taxonomy and systematics

The Shoebill was only classified in the 19th century when some skins were brought to Europe. It was not until years later that live specimens reached the scientific community. However, the bird was known to both ancient Egyptians and Arabs. Traditionally allied with the storks (Ciconiiformes), it was retained there in the Sibley-Ahlquist taxonomy which lumped a massive number of unrelated taxa into their "Ciconiiformes". More recently, the shoebill has been considered to be closer to the pelicans (based on anatomical comparisons)[3] or the herons (based on biochemical evidence; Hagey et al., 2002).[4] A recent DNA study suggests they are part of the Pelecaniformes.[5]
The dispute has turned out to be mainly one of where to draw the boundary between Ciconiiformes and Pelecaniformes, or whether to draw it at all. Since cormorants and relatives are probably not actually Pelecaniformes, a solution adopted by some modern authors is to merge the "core" Pelecaniformes with the Ciconiiformes. The Shoebill and the Hammerkop (Scopus umbretta) are the "missing links" that connect pelicans and storks, and including the pelican lineage in the Ciconiiformes expresses this more adequately than other treatments do.
So far, two fossil relatives of the shoebill have been described: Goliathia from the early Oligocene of Egypt and Paludavis from the Early Miocene of the same country. It has been suggested that the enigmatic African fossil bird Eremopezus was a relative too, but the evidence for that is unconfirmed. All that is known of Eremopezus is that it was a very large, probably flightless bird with a flexible foot, allowing it to handle either vegetation or prey.
Description

The Shoebill is a tall bird, with a typical height range of 110 to 140 cm (43 to 55 in) and some specimens reaching as much as 152 cm (60 in). Length from tail to beak can range from 100 to 140 cm (39 to 55 in) and wingspan is 230 to 260 cm (7 ft 7 in to 8 ft 6 in). Weight has reportedly ranged from 4 to 7 kg (8.8 to 15.4 lb) in the Shoebill.[6][7] A male will weigh on average around 5.6 kg (12 lb) and is larger than a typical female of 4.9 kg (11 lb).[8] The signature feature of the species is its huge, bulbous bill, which is straw-colored with erratic grayish markings. The exposed culmen (or the measurement along the top of the upper mandible) is 18.8 to 24 cm (7.4 to 9.4 in).[8] The sharp edges in the mandibles help the Shoebill to decapitate their prey and also to discard any vegetation after prey has been caught. As in the pelicans, the upper mandible is strongly keeled, ending in a sharp nail. The dark colored legs are fairly long, with a tarsus length of 21.7 to 25.5 cm (8.5 to 10.0 in). The Shoebill's feet are exceptionally large, with the middle toe reaching 16.8 to 18.5 cm (6.6 to 7.3 in) in length, likely assisting the species in its ability to stand on aquatic vegetation while hunting. The neck is relatively shorter and thicker than other long-legged wading birds such as herons and cranes. The wings are broad, with a wing chord length of 58.8 to 78 cm (23.1 to 30.7 in), and well-adapted to soaring.
Flight pattern
Its wings are held flat while soaring and, as in the pelicans and the storks of the genus Leptoptilos, the Shoebill flies with its neck retracted. Its flapping rate, at an estimated 150 flaps per minute, is one the slowest of any bird, with the exception of the larger stork species. The pattern is alternating flapping and gliding cycles of approximately 7 seconds each, putting its gliding distance somewhere between the larger storks and the Andean Condor (Vultur gryphus). When flushed, Shoebills usually try to fly no more than 100 to 500 m (330 to 1,640 ft) from their prior location.[8] Long flights of the Shoebill are rare, and only a few flights beyond its minimum foraging distance of 20 m (66 ft) have been captured.
The plumage of adult birds is blue-grey with darker slaty-grey flight feathers. The breast presents some elongated feathers, which have dark shafts. The juvenile has a similar plumage color, but is a darker grey with a brown tinge.[2] When they are first born, Shoebills have a more modestly-sized bill, which is initially silvery-grey in color. The bill becomes more noticeably large when the chicks are 23 days old and becomes well developed by 43 days.[8]
Identification
At close range, it can be easily identified by its unique features. In flight, if its unique bill cannot be seen, the Shoebill's silhouette resembles that of a stork or condor, but its feathers are a distinctive medium blue-gray. Unusually also, its tail is the same color as its wings. Under poor viewing conditions, its size and wingspan compared to other birds in its habitat can identify it. Its legs, roughly the length of storks, extend straight back far past its tail when in flight. The wing to tail size can't be used for identification; it's similar to several other birds.

Distribution and habitat
The Shoebill is distributed in freshwater swamps of central tropical Africa, from southern Sudan through parts of eastern Congo, Rwanda, Uganda and western Tanzania. The species is most numerous in the West Nile sub-region and adjacent areas of the south Sudan, significant also in wetlands of Uganda and western Tanzania. More isolated records have been reported of Shoebills in Kenya, the Central African Republic, northern Cameroon, southwestern Ethiopia, Malawi. Vagrant strays to the Okavango Basin, Botswana and the upper Congo River have also been sighted. The distribution of this species seem to largely coincide with that of papyrus and lungfish. The Shoebill is non-migratory with limited seasonal movements due to habitat changes, food availability and disturbance by humans.[8]
The Shoebill occurs in extensive, dense freshwater marshes. Almost all wetlands that attract the species have undisturbed Cyperus papyrus and reedbeds of Phragmites and Typha. Although their distribution largely seems to correspond with the distribution of papyrus in central Africa, the species seems to avoid pure papyrus swamps and often attracted to areas with mixed vegetation. More rarely, the species has been seen foraging in rice fields and flooded plantations.[8]
Behaviour and ecology
The Shoebill is noted for its slow movements and tendency to remain still for long periods, resulting in repeated descriptions of the species as "statue-like". They are quite sensitive to human disturbance and may abandon their nests if flushed by humans. However, while foraging, if dense vegetation stands between it and humans, this wader can be fairly tame. The Shoebill is attracted to poorly oxygenated waters where fish frequently surface to breathe. Exceptionally for a bird this large, the Shoebill often stands and perches on floating vegetation, making them appear somewhat like a giant jacana, although the similarly-sized and occasionally sympatric Goliath heron (Ardea goliath) is also known to stand on aquatic vegetation. Shoebills typically feed in muddy waters and, being solitary birds, forage at a minimum distance of 20 m (66 ft) from one another even where relatively densely populated. This species stalks its prey patiently, in a slow and lurking fashion. While hunting, the Shoebill strides very slowly and is frequently motionless. Unlike some other large waders, this species hunts entirely using vision and is not known to engage in tactile hunting. When prey is spotted, it launches a quick, violent strike. However, depending on the size of the prey, handling time after the strike can exceed 10 minutes. Around 60% of strikes are successful in yielding prey. Frequently water and vegetation is snatched up during the strike and is spilled out from the edges of the mandibles. Occasionally, the activity of hippopotamus may inadvertently benefit the Shoebill, as the huge mammals occasionally force fish to the surface of the water while they are submerged.[8]
Shoebills are largely piscivorous but are assured predators of a considerable range of wetland vertebrates. Preferred prey species have reportedly included Marbled lungfish (Protopterus aethiopicus) and Senegal Bichir (Polypterus senegalus) as well as various Tilapia species and catfish, the latter mainly in the genus Clarias. Other prey eaten by this species has included frogs, water snakes, Nile monitors (Varanus niloticus) and baby crocodiles. More rarely, turtles, snails, rodents and small waterfowl have reportedly been predated. There exists a single report of Shoebills feeding on Lechwe (Kobus leche) calves, although this would need confirmation. Given its sharp-edged beak, huge bill and wide gape, the Shoebill can hunt large prey, often targeting prey bigger than other large wading birds. Fish eaten by this species are commonly in the range of 15 to 50 cm (5.9 to 19.7 in) long and weigh around 500 g (1.1 lb), though lungfish of as much as 1 m (3.3 ft) have been attacked. Snakes preyed upon are commonly from 50 to 60 cm (20 to 24 in) long. In the Bangweulu Swamps of Zambia, the main prey items fed to young by the parents consisted of the catfish Clarias gariepinus (syn. C. mossambicus) and water snakes. In Uganda, lungfish and catfish were mainly fed to the young.[8]
Breeding
The solitary nature of Shoebills extends to their breeding habits. Nests typically occur at less than 3 nests per square kilometer, unlike herons, cormorants, pelicans and storks which predominantly nest in colonies. The breeding pair of Shoebills vigorously defends a territory of 2 to 4 km2 (0.77 to 1.54 sq mi) from conspecifics. In the extreme north and south of the species' range, nesting starts right after the rains end. In more central regions of the range, it may nest near end of wet season in order to hatch around the beginning of the following wet season. Both parents engage in building the nest on floating platform, after clearing out an area of approximately 3 m (9.8 ft) across. The large, flattish nesting platform is often partially submerged in water and can be as much as 3 m (9.8 ft) deep. The nest itself is about 1 to 1.7 m (3.3 to 5.6 ft) across. Both the nest and platform are made of aquatic vegetation. In Sudan, the nests apparently was able to support the weight of an adult man, although this was not the case in Zambia. From one to three white eggs are laid. These eggs measure 80 to 90 mm (3.1 to 3.5 in) high by 56 to 61 mm (2.2 to 2.4 in) and weigh around 164 g (5.8 oz). Incubation lasts for approximately 30 days. Both parents actively brood, shade, guard and feed the nestling, though the females are perhaps slightly more attentive. Food items are regurgitated whole from the gullet straight into the bill of the young. Shoebills rarely raise more than one chick, but will hatch more. The younger chicks are intended as back-ups in case the eldest dies or is weak. Fledging is reached at around 105 days and the young birds can fly well by 112 days. However, they are still fed for possibly a month or more after this. It will take the young Shoebills 3 years before they become fully sexually mature.[8]
Voice
The Shoebill is normally silent, but they perform bill-clattering displays at the nest.[2] When engaging in these displays, adult birds have also been noted to utter a cow-like moo as well as high-pitched whines. Both nestlings and adults engage in bill-clattering during the nesting season as a means of communication. When young are begging for food, they call out with a sound uncannily like human hiccups. In one case, a flying adult bird was heard uttering hoarse croaks, apparently as a sign of aggression at a nearby Marabou Stork (Leptoptilos crumeniferus).[8]
Status and conservation
The population is estimated at between 5,000 and 8,000 individuals, the majority of which live in swamps in Sudan, Uganda, eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Zambia.[9] BirdLife International have classified it as Vulnerable with the main threats being habitat destruction, disturbance and hunting.
Relationship to humans
This species is considered to be one of the five most desirable birds in Africa by ornithologists.[10] There are Egyptian images depicting the Shoebill, while the Arabs referred to the bird as abu markub, which means one with a shoe, a reference to the bird's distinctive bill.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2012). "Balaeniceps rex". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 del Hoyo, J. Elliott, A. & Sargatal, J. (editors). (1992) Handbook of the Birds of the World. Volume 1: Ostrich to Ducks. Lynx Edicions. ISBN 84-87334-10-5
- ↑ Mayr, Gerald (2003). "The phylogenetic affinities of the Shoebill (Balaeniceps rex)". Journal für Ornithologie. doi:10.1046/j.1439-0361.2003.03002.x.
- ↑ Hagey, J. R.; Schteingart, C. D.; Ton-Nu, H.-T. & Hofmann, A. F. (2002). "A novel primary bile acid in the Shoebill stork and herons and its phylogenetic significance". Journal of lipid research 43 (5): 685–90. PMID 11971938.
- ↑ Hackett, SJ; Kimball, RT; Reddy, S; Bowie, RC; Braun, EL; Braun, MJ; Chojnowski, JL; Cox, WA; Han, KL et al. (2008). "A phylogenomic study of birds reveals their evolutionary history". Science 320 (5884): 1763–8. doi:10.1126/science.1157704. PMID 18583609.
- ↑ Balaeniceps rex. Fsbio-hannover.de. Retrieved on 2012-08-21.
- ↑ Stevenson, Terry and Fanshawe, John (2001). Field Guide to the Birds of East Africa: Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi. Elsevier Science, ISBN 978-0856610790
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 8.6 8.7 8.8 8.9 Hancock & Kushan, Storks, Ibises and Spoonbills of the World. Princeton University Press (1992), ISBN 978-0-12-322730-0.
- ↑ Williams, J.G; Arlott, N. A Gield Guide to the Birds of East Africa. Collins. ISBN 0-00-219179-2.
- ↑ Matthiessen, Peter (1991). African Silences. New York: Random House. p. 56. ISBN 0-679-40021-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Balaeniceps rex. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Balaeniceps rex |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Shoe-bill. |
- Shoebill Fact - Zoo
- ARKive – images and movies of the Shoebill (Balaeniceps rex)
- BirdLife Species Factsheet
- The Internet Bird Collection - Video capture of a Shoebill in flight
