Shikimic acid pathway
The shikimic acid pathway is a seven step metabolic route used by bacteria, fungi, algae, parasites and plants for the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids (phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan). This pathway is not found in animals, hence the products of this pathway represent essential amino acids that must be obtained from the animal's diet.
The first enzyme involved is the shikimate kinase, an enzyme that catalyzes the ATP-dependent phosphorylation of shikimate to form shikimate 3-phosphate.[1] Shikimate 3-phosphate is then coupled with phosphoenol pyruvate to give 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate via the enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate (EPSP) synthase.
Then 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate is transformed into chorismate by a chorismate synthase.
Prephenic acid is then synthesized by a Claisen rearrangement of chorismate by Chorismate mutase.[2][3]

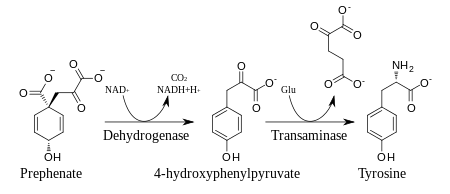
Prephenate is oxidatively decarboxylated with retention of the hydroxyl group to give p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate, which is transaminated using glutamate as the nitrogen source to give tyrosine and α-ketoglutarate.
References
- ↑ Herrmann, K. M.; Weaver, L. M. (1999). "The Shikimate Pathway". Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology 50: 473–503. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.50.1.473. PMID 15012217.
- ↑ Helmut Goerisch (1978). "On the mechanism of the chorismate mutase reaction". Biochemistry 17 (18): 3700. doi:10.1021/bi00611a004.
- ↑ Peter Kast, Yadu B. Tewari, Olaf Wiest, Donald Hilvert, Kendall N. Houk, and Robert N. Goldberg (1997). "Thermodynamics of the Conversion of Chorismate to Prephenate: Experimental Results and Theoretical Predictions". J. Phys. Chem. B 101 (50): 10976–10982. doi:10.1021/jp972501l.
Bibliography
- Brown, Stewart A.; Neish, A. C. (1955). "Shikimic Acid as a Precursor in Lignin Biosynthesis". Nature 175 (4459): 688–689. doi:10.1038/175688a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
- Weinstein, L. H.; Porter, C. A.; Laurencot, H. J. (1962). "Role of the Shikimic Acid Pathway in the Formation of Tryptophan in Higher Plants : Evidence for an Alternative Pathway in the Bean". Nature 194 (4824): 205–206. doi:10.1038/194205a0. ISSN 0028-0836.
- Wilson, D J; Patton, S; Florova, G; Hale, V; Reynolds, K A (1998). "The shikimic acid pathway and polyketide biosynthesis". Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 20 (5): 299–303. doi:10.1038/sj.jim.2900527. ISSN 1367-5435.

