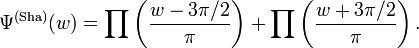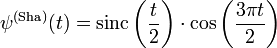Shannon wavelet
In functional analysis, a Shannon wavelet may be either of real or complex type. Signal analysis by ideal bandpass filters defines a decomposition known as Shannon wavelets (or sinc wavelets). The Haar and sinc systems are Fourier duals of each other.
Real Shannon wavelet
The Fourier transform of the Shannon mother wavelet is given by:
where the (normalised) gate function is defined by
The analytical expression of the real Shannon wavelet can be found by taking the inverse Fourier transform:
or alternatively as
where
is the usual sinc function that appears in Shannon sampling theorem.
This wavelet belongs to the  -class of differentiability, but it decreases slowly at infinity and has no bounded support, since band-limited signals cannot be time-limited.
-class of differentiability, but it decreases slowly at infinity and has no bounded support, since band-limited signals cannot be time-limited.
The scaling function for the Shannon MRA (or Sinc-MRA) is given by the sample function:
Complex Shannon wavelet
In the case of complex continuous wavelet, the Shannon wavelet is defined by
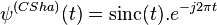 ,
,
References
- S.G. Mallat, A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing, Academic Press, 1999, ISBN 0-12-466606-X
- C.S. Burrus, R.A. Gopinath, H. Guo, Introduction to Wavelets and Wavelet Transforms: A Primer, Prentice-Hall, 1988, ISBN 0-13-489600-9.