Septum pellucidum
| Brain: Septum pellucidum | |
|---|---|
 Scheme of rhinencephalon (septum pellucidum visible at top center) | |
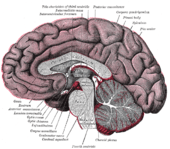 Median sagittal section of brain (septum pellucidum visible at center) | |
| Latin | Septum pellucidum |
| Gray's | p.840 |
| NeuroNames | hier-238 |
| MeSH | Septum+Pellucidum |
| Dorlands/Elsevier | Septum pellucidum |
The septum pellucidum (also called the septum Pellucidum), and not to be confused with the medial septum, is a thin, triangular, vertical membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right lateral ventricles of the brain. It runs as a sheet from the corpus callosum down to the fornix.
Structure
The septum pellucidum is located in the midline of the brain, between the two cerebral hemispheres. It is attached superiorly to the corpus callosum, the large collection of nerve fibers that connect the two cerebral hemispheres. It is attached to the anterior part of the fornix, and on either side of the structure are the two lateral ventricles.
The septum pellucidum actually consists of two layers or laminae of both white and gray matter,[1] called the laminae septi pellucidi. During fetal development there is a space between the two laminae called the cavum septi pellucidi which, in ninety per cent of cases, disappears during infancy.[2][3] The cavum is occasionally referred to as the fifth ventricle but the term has lost favor in recent years, as the space is usually not continuous with the ventricular system.[4] Indeed fifth ventricle has been used for other purposes in recent years.[5]
Confusion over the term
The septum pellucidum is often confused with the septal nuclei. Logically, the septum pellucidum is a septum in the medial plane and could therefore be termed 'medial septum', but this is incorrect. The term medial septum is reserved for a small group of nuclei which are closely associated with the septum pellucidum.
Clinical significance
Absence of the septum pellucidum occurs in septo-optic dysplasia, a rare developmental disorder also characterized by abnormal development of the optic disk and pituitary deficiencies. Symptoms of septo-optic dysplasia are highly variable and may include vision difficulties, low muscle tone, hormonal problems, seizures, intellectual problems, and jaundice at birth.[6]
Additional images
-

Mesal aspect of a brain sectioned in the median sagittal plane.
-

Horizontal section of right cerebral hemisphere.
-

Coronal section through anterior cornua of lateral ventricles.
-

Coronal section of brain through anterior commissure.
-
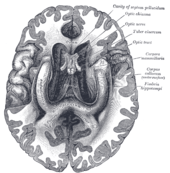
The fornix and corpus callosum from below.
-

Diagram showing the positions of the three principal subarachnoid cisternæ.
-
Septum pellucidum
-
Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere.Medial view.Deep dissection.
-
Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere.Medial view.Deep dissection.
-
Medial surface of cerebral hemisphere.Medial view.Deep dissection.
References
- ↑ Lennart Heimer; Gary W. Van Hoesen (16 November 2007). Anatomy of neuropsychiatry: the new anatomy of the basal forebrain and its implications for neuropsychiatric illness. Academic Press. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-12-374239-1. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- ↑ David L. Clark; Nash N. Boutros; Mario F. Mendez (2010). The Brain and Behavior: An Introduction to Behavioral Neuroanatomy. Cambridge University Press. pp. 217–8. ISBN 978-0-521-14229-8. Retrieved 24 December 2010.
- ↑ Love J, Hollenhorst R (1956). "Bilateral palsy of the sixth cranial nerve caused by a cyst of the septum pellucidum (fifth ventricle) and cured by pneumoencephalography". Mayo Clin Proc 31 (2): 43–6. PMID 13289891.
- ↑ Alonso J, Coveñas R, Lara J, Piñuela C, Aijón J (1989). "The cavum septi pellucidi: a fifth ventricle?". Acta Anat (Basel) 134 (4): 286–90. doi:10.1159/000146704. PMID 2741657.
- ↑ Liccardo G, Ruggeri F, De Cerchio L, Floris R, Lunardi P (2005). "Fifth ventricle: an unusual cystic lesion of the conus medullaris". Spinal Cord 43 (6): 381–4. doi:10.1038/sj.sc.3101712. PMID 15655569.
- ↑ "NINDS Septo-Optic Dysplasia Information Page". National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. 1 August 2008. Retrieved 18 October 2013.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Septum pellucidum. |
This article uses anatomical terminology; for an overview, see anatomical terminology.
External links
| |||||||||||||||||||



