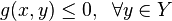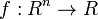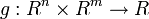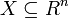Semi-infinite programming
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In optimization theory, semi-infinite programming (SIP) is an optimization problem with a finite number of variables and an infinite number of constraints, or an infinite number of variables and a finite number of constraints. In the former case the constraints are typically parameterized.[1]
Mathematical formulation of the problem
The problem can be stated simply as:
where
SIP can be seen as a special case of bilevel programs (multilevel programming) in which the lower-level variables do not participate in the objective function.
Methods for solving the problem
In the meantime, see external links below for a complete tutorial.
Examples
In the meantime, see external links below for a complete tutorial.
See also
- Optimization
- Generalized semi-infinite programming (GSIP)
References
- ↑
- Bonnans, J. Frédéric; Shapiro, Alexander (2000). "5.4 and 7.4.4 Semi-infinite programming". Perturbation analysis of optimization problems. Springer Series in Operations Research. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 496–526 and 581. ISBN 0-387-98705-3. MR 1756264.
- M. A. Goberna and M. A. López, Linear Semi-Infinite Optimization, Wiley, 1998.
- Hettich, R.; Kortanek, K. O. (1993). "Semi-infinite programming: Theory, methods, and applications". SIAM Review 35 (3). pp. 380–429. doi:10.1137/1035089. JSTOR 2132425. MR 1234637.
- Edward J. Anderson and Peter Nash, Linear Programming in Infinite-Dimensional Spaces, Wiley, 1987.
- Bonnans, J. Frédéric; Shapiro, Alexander (2000). "5.4 and 7.4.4 Semi-infinite programming". Perturbation analysis of optimization problems. Springer Series in Operations Research. New York: Springer-Verlag. pp. 496–526 and 581. ISBN 0-387-98705-3. MR 1756264.
- M. A. Goberna and M. A. López, Linear Semi-Infinite Optimization, Wiley, 1998.
- Hettich, R.; Kortanek, K. O. (1993). "Semi-infinite programming: Theory, methods, and applications". SIAM Review 35 (3). pp. 380–429. doi:10.1137/1035089. JSTOR 2132425. MR 1234637.
- David Luenberger (1997). Optimization by Vector Space Methods. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-18117-X.
- Rembert Reemtsen and Jan-J. Rückmann (Editors), Semi-Infinite Programming (Nonconvex Optimization and Its Applications). Springer, 1998, ISBN 0-7923-5054-5, 1998
External links
- Description of semi-infinite programming from INFORMS (Institute for Operations Research and Management Science).
- A complete, free, open source Semi Infinite Programming Tutorial is available here from Elsevier as a pdf download from their Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, Volume 217, Issue 2, 1 August 2008, Pages 394–419
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.