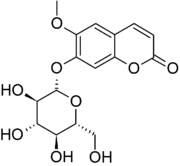
Scopolin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Scopolin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 531-44-2 |
| PubChem | 439514 |
| ChemSpider | 388609 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C=CC(=O)O2)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O)O)O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C16H18O9 |
| Molar mass | 354.31 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Scopolin is a glucoside of scopoletin formed by the action of the enzyme scopoletin glucosyltransferase.[1]
References
- ↑ Hino F, Okazaki M and Miura Y (1982). "Effect of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on glucosylation of scopoletin to scopolin in tobacco tissue-culture". Plant Physiol. 69 (4): 810–813. doi:10.1104/pp.69.4.810. PMC 426310. PMID 16662301.
Bibliography
- Steck, Warren (1967). "Biosynthesis of Scopolin in Tobacco". Canadian Journal of Biochemistry 45 (6): 889–896. doi:10.1139/o67-099. ISSN 1208-6002.
- Steck, Warren (1967). "The Biosynthetic Pathway from Caffeic Acid to Scopolin in Tobacco Leaves". Canadian Journal of Biochemistry 45 (12): 1995–2003. doi:10.1139/o67-233. ISSN 1208-6002.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.