Schinderhannes (genus)
| Schinderhannes Temporal range: Lower Devonian[1] | |
|---|---|
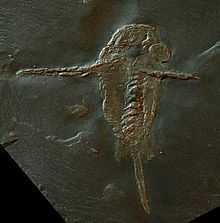 | |
| The one known specimen of Schinderhannes. Credit: Steinmann Institute/University of Bonn | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Stem-group: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | †Dinocaridida |
| Order: | †Radiodonta |
| Family: | †Anomalocarididae |
| Genus: | †Schinderhannes |
| Binomial name | |
| Schinderhannes bartelsi Kühl, Briggs & Rust, 2009 | |
Schinderhannes bartelsi is an anomalocarid known from one specimen from the lower Devonian Hunsrück Slates. Its discovery was astonishing because previously, anomalocaridids were known only from exceptionally well-preserved fossil beds (Lagerstätten) from the Cambrian, 100 million years earlier.[1]
Anomalocaridids, such as Anomalocaris, were organisms thought to be distantly related to the arthropods. These creatures looked quite unlike any organism living today—they had segmented exoskeletons, with lateral lobes used for swimming, typically large compound eyes, often set on stalks, and most strikingly, a pair of large, claw-like great appendages that resembled headless shrimp. These appendages are thought to have passed food to the animal's mouth, which resembled a ring of pineapple.[2]
Discovery
The single specimen was discovered in the Eschenbach-Bocksberg Quarry in Bundenbach, and is named after the outlaw Schinderhannes who frequented the area. Its specific epithet bartelsi honours Christoph Bartels, a Hunsrück Slate expert. The specimen is now housed in the Naturhistorisches Museum, Mainz.[1]
Morphology

Schinderhannes is about 10 centimetres (3.9 in) long; like other anomalocaridids, it bears a pair of great appendages (very similar to those of Hurdia),[3] a radial Peytoia 'pineapple-ring' mouth, and large, stalked, compound eyes. It has 12 body segments; large flap-like structures used for swimming protrude from the 11th segment, and from just behind the head.[1]
Ecology
The preserved contents of its digestive tract are typical of those of other predators',[4] and this lifestyle is supported by the raptor-like nature of the spiny great appendages and the size of the eyes.[1] The organism was clearly a competent swimmer, propelling itself with the 'flippers' attached to its head, and using its wing-like lobes on the 11th segment to steer.[1] These lobes presumably derived from the lateral lobes of Cambrian anomalocaridids, ancestors that used lobes along their sides to swim, and lacked the specializations of Schinderhannes.[1]
Significance
The organism allows the classification of early arthropods to be resolved, to some degree. The organism is classified basally to the true arthropods, but is closer to that group than Anomalocaris. By analogy, Schinderhannes could be thought of as an 'aunt' to the arthropods, and Anomalocaris a 'great-aunt'. This suggests that the anomalocaridid group is in fact paraphyletic—that is, that the arthropods are descended from anomalocaridids.[1] It also seems to suggest that the biramous limb of arthropods arose through fusion of anomalocaridid lateral lobes and gills.[3] The fossil has other implications—it shows that the group of early arthropods with short 'great appendages' are not a natural grouping.
The organism's discovery was most significant because of the huge range extension of the anomalocaridids it caused: the group was only previously known from lagerstatte of the lower-to-middle Cambrian, 100 million years before. This underlined the utility of lagerstatte like the Hunsrück slate: these exceptionally preserved fossil horizons may be the only available opportunity to observe non-mineralised forms.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Gabriele Kühl, Derek E. G. Briggs & Jes Rust (2009). "A great-appendage arthropod with a radial mouth from the Lower Devonian Hunsrück Slate, Germany". Science 323 (5915): 771–773. Bibcode:2009Sci...323..771K. doi:10.1126/science.1166586. PMID 19197061.
- ↑ Stephen Jay Gould (1989). Wonderful Life: The Burgess Shale and the Nature of History. W. W. Norton & Company. ISBN 978-0-393-02705-1.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Allison C. Daley, Graham E. Budd, Jean-Bernard Caron, Gregory D. Edgecombe & Desmond Collins (2009). "The Burgess Shale anomalocaridid Hurdia and its significance for early euarthropod evolution". Science 323 (5921): 1597–1600. Bibcode:2009Sci...323.1597D. doi:10.1126/science.1169514. PMID 19299617.
- ↑ Nicholas J. Butterfield (2002). "Leanchoilia, and the interpretation of three-dimensional structures in Burgess Shale-type fossils". Paleobiology 28 (1): 155–171. doi:10.1666/0094-8373(2002)028<0155:LGATIO>2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 3595514.
- ↑ Nicholas J. Butterfield (1995). "Secular distribution of Burgess-Shale-type preservation". Lethaia 28 (1): 1–13. doi:10.1111/j.1502-3931.1995.tb01587.x.
External links
- Origin of claws seen in 390-million-year-old fossil
- Panda's Thumb: Schinderhannes bartelsi
- ScienceBlogs: Schinderhannes bartelsi, by PZ Myers showing a cladogram as proposed by G. Kühl et al., placing Schinderhannes (but not Anomalocaris) into the group of Euarthropoda.