Scalenus posterior
| Scalenus posterior | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Position of scalenus posterior (shown in red). | |
 | |
| The anterior vertebral muscles (scalenus posterior visible at bottom right). | |
| Latin | Musculus scalenus posterior |
| Gray's | p.396 |
| Origin | Transverse processes of C4, C5 and C6 |
| Insertion | Second rib |
| Artery | Ascending cervical artery and superficial cervical artery. |
| Nerve | C6, C7 and C8, |
| Actions | Elevate second rib, tilt the neck to the same side |
The Scalenus posterior (scalenus posticus), the smallest and most deeply seated of the three scalene muscles, arises, by two or three separate tendons, from the posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the lower two or three cervical vertebrae, and is inserted by a thin tendon into the outer surface of the second rib, behind the attachment of the scalenus anterior.
It is occasionally blended with the scalenus medius.
Additional images
-

Position of scalenus posterior (shown in red). Animation.
-

Close up.
-
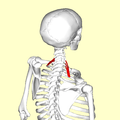
Still image.
-

Second rib.
-
Posterior scalene muscle
-
Scalenus posterior
-
Scalenus posterior
-
Scalenus posterior
-
Brachial plexus.Deep dissection.
-
Brachial plexus.Deep dissection.Anterolateral view
See also
- Scalene muscles
- Accessory muscles of respiration
References
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Scalenus posterior. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.JPG)




