Scalenus anterior
| Anterior scalene | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Psotion of scalenus anterior (shown in red.) | |
 | |
| The anterior vertebral muscles. (Scalenus anterior visible at bottom left in red.) | |
| Latin | Musculus scalenus anterior |
| Gray's | p.396 |
| Origin | Transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebræ (C3, C4, C5 and C6) |
| Insertion | First rib |
| Artery | Ascending cervical artery (branch of Inferior thyroid artery) |
| Nerve | Ventral ramus of C5, C6 |
| Actions | Elevates first rib, rotate the neck to the opposite side |
The Scalenus anterior (scalenus anticus), also known as anterior scalene muscle, lies deeply at the side of the neck, behind the Sternocleidomastoideus.
Anatomy
It arises from the anterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebræ, and descending, almost vertically, is inserted by a narrow, flat tendon into the scalene tubercle on the inner border of the first rib, and into the ridge on the upper surface of the rib in front of the subclavian groove.
Clinical significance
It can be involved in certain forms of Thoracic outlet syndrome.
Additional images
-

Position of scalenus anterior. Animation.
-

Close up.
-

Same as the left without skull.
-

Still image.
-

A cervical vertebra
-
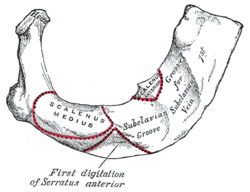
Right first rib.
-

Muscles of the neck. Lateral view. Scalenus anterior shown in red.
-

Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries.
-

Horizontal section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. Showing the arrangement of the fascia coli. (Scalenus anterior visible at center left in green.)
-

The internal mammary artery and its branches.
-

The right brachial plexus with its short branches, viewed from in front.
-
Anterior scalene muscle
-
Anterior scalene muscle
-
Scalenus anterior
-
Scalenus anterior
-
Scalenus anterior
See also
- Scalene muscles
- Accessory muscles of respiration
References
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Scalenus anterior. |
- LUC sa
- 1074135100 at GPnotebook
- scalenus+anterior+muscle at eMedicine Dictionary
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
.JPG)



