Samoan crisis
| Samoan Crisis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the First Samoan Civil War | |||||||
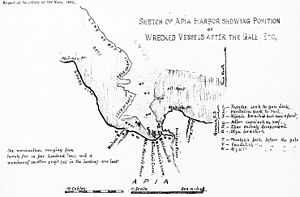 A sketch featuring the locations of the wrecked German and American ships. |
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 1 sloop-of-war 1 steamer 1 gunboat | 3 gunboats | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 62 killed 1 sloop-of-war sunk 1 steamer sunk 1 gunboat grounded | ~73 killed 1 gunboat sunk 2 gunboats grounded |
||||||
|
|||||||
The Samoan Crisis was a confrontation standoff between the United States, Imperial Germany and Great Britain from 1887–1889 over control of the Samoan Islands during the Samoan Civil War. The incident involved three American warships, USS Vandalia, USS Trenton and USS Nipsic and three German warships, SMS Adler, SMS Olga, and SMS Eber, keeping each other at bay over several months in Apia harbour, which was monitored by the British warship HMS Calliope.
The standoff ended on 15 and 16 March when a cyclone wrecked all six warships in the harbour. Calliope was able to escape the harbour and survived the storm. Robert Louis Stevenson witnessed the storm and its aftermath at Apia and later wrote about what he saw.[1] The Samoan Civil War continued, involving Germany, United States and Britain, eventually resulting, via the Tripartite Convention of 1899, in the partition of the Samoan Islands into American Samoa and German Samoa.[2]
Gallery
-

Salvaged guns from the wrecked American ships at Apia.
-

A view of the sunken USS Vandalia from the deck of USS Trenton.
-

Apia and the beach covered in driftwood and debris from the wrecked warships.
-

Wrecked vessels at Apia.
-

USS Nipsic's wreck
-

SMS Adler, knocked over on the beach, 1889.
-

SMS Adler, view of her deck, 1889.
-

SMS Adler´s wreck, circa 1938
-

Illustrated London News for 27 April 1889; artist’s conception of HMS Calliope being cheered on by the crew of USS Trenton as Calliope escapes from Apia Harbour. Calliope actually passed to Trenton´s port.
-

A memorial at Mare Island Naval Yard for the Americans killed in the cyclone.
-

Wrecked ships in Apia Harbour. German gunboat SMS Eber is on the beach, the stern of USS Trenton is at right, with the sunken USS Vandalia alongside. SMS 'Adler is on her side in the center distance.
-

Another angle of the wrecked warships.
-

Wrecked warships off Apia
Sources
- Conroy, Robert (2002). "Only luck kept the United States from being occupied by Kaiser Wilhelm II's army between 1899 and 1904". Military History 18 (August).
- Gray, J.A.C. (1960). Amerika Samoa: A History of American Samoa and Its United States Naval Administration. Annapolis: U. S. Naval Institute. ISBN 0-405-13038-4.
- "Hurricane at Apia, Samoa, 15–16 March 1889". Events of the 1880s. Naval Historical Center. 2002. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- Kimberly, L.A.. "Samoan Hurricane". Events of the 1880s. Naval Historical Center. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- LaFeber, Walter (1963). The New Empire: An Interpretation of American Expansion, 1860–1898. Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press.
- Lind, L.J. "The Epic of HMS Calliope". Naval Historical Society of Australia. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- Rousmaniere, John (2002). After the Storm: True Stories of Disaster and Recovery at Sea. Camden, MN: International Marine/McGraw-Hill. pp. 87–106. ISBN 0-07-137795-6.
- Sisung, Kelle S. (2002). "The Benjamin Harrison Administration". Presidential Administration Profiles for Students (Detroit: Gale Group).
- Stevenson, Robert Louis (1892). A Footnote to History, Eight Years of Trouble in Samoa. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- Wilson, Graham (May/July 1996). "Glory for the Squadron: HMS Calliope in the Great Hurricane at Samoa 1889". Journal of the Australian Naval Institute 22 (2): 51–54.
Notes
- ↑ Stevenson, Robert Louis (1892). A Footnote to History: Eight Years of Trouble in Samoa. BiblioBazaar. ISBN 1-4264-0754-8.
- ↑ Ryden, George Herbert. The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa. New York: Octagon Books, 1975. (Reprint by special arrangement with Yale University Press. Originally published at New Haven: Yale University Press, 1928), p. 574; the Tripartite Convention (United States, Germany, Great Britain) was signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
