Sakuranetin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Sakuranetin | ||
|---|---|---|
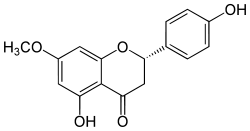 | ||
| IUPAC name (2S)-5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-methoxy-2,3-dihydrochromen-4-one | ||
| Other names 4',5-Dihydroxy-7-methoxyflavanone | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 2957-21-3 | |
| PubChem | 73571 | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28927 | |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL448297 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C16H14O5 | |
| Molar mass | 286.27 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Sakuranetin is a flavanone, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Polymnia fruticosa[1] and rice, where it acts as a phytoalexin against spore germination of Pyricularia oryzae.[2]
Glycosides
Sakuranin is the -O-glucoside of sakuranetin.
Metabolism
- biosynthesis
Naringenin 7-O-methyltransferase uses naringenin to yield sakuranetin, with S-adenosyl-methionine as the methyl donor.[3]
- biodegradation
In compounds like 7-methoxylated flavanones like sakuranetin, demethylation followed by sulfation occur in model organism Cunninghamella elegans.[4]
References
- ↑ Sakuranetin on home.ncifcrf.gov
- ↑ Sakuranetin, a flavonone phytoalexin from ultraviolet-irradiated rice leaves, Kodama O., Miyakawa J., Akatsuka T., Kiyosawa S, 1992
- ↑ A Methyltransferase for Synthesis of the Flavanone Phytoalexin Sakuranetin in Rice Leaves, Randeep Rakwala, Morifumi Hasegawab and Osamu Kodama, 1996
- ↑ Ibrahim, A. R.; Galal, A. M.; Ahmed, M. S.; Mossa, G. S. (2003). "O-demethylation and sulfation of 7-methoxylated flavanones by Cunninghamella elegans". Chemical & pharmaceutical bulletin 51 (2): 203–206. doi:10.1248/cpb.51.203. PMID 12576658. INIST:14569933.
| ||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.