SR9009
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
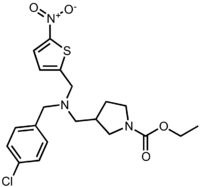 | |
|---|---|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| ethyl-3-(((4-chlorobenzyl)((5-nitrothiophen-2-yl)methyl)amino)methyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxylate | |
| Clinical data | |
| Legal status | ? |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 1379686-30-2 |
| ATC code | ? |
| PubChem | CID 57394020 |
| ChemSpider | 28487410 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1961796 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C20H24ClN3O4S |
| Mol. mass | 437.94026 |
| SMILES
| |
| |
SR9009 is a research drug that was developed by Professor Thomas Burris of the Scripps Research Institute as an agonist of Rev-ErbA (i.e., increases the constitutive repression of genes regulated by Rev-ErbA)[1] with a half-maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) = 670 nM for Rev-ErbAα and IC50 = 800 nM for Rev-ErbAβ.[2]
Activation of Rev-erb-α by in mice SR9009 increases exercise capacity in mice by increasing mitochondria in skeletal muscle.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Dodson B (2013-08-20). "New drug mimics the beneficial effects of exercise". Health and Wellbeing. Gizmag. Retrieved 2013-08-21.
- ↑ Solt LA, Wang Y, Banerjee S, Hughes T, Kojetin DJ, Lundasen T, Shin Y, Liu J, Cameron MD, Noel R, Yoo SH, Takahashi JS, Butler AA, Kamenecka TM, Burris TP (May 2012). "Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic REV-ERB agonists". Nature 485 (7396): 62–8. doi:10.1038/nature11030. PMC 3343186. PMID 22460951. Lay summary – Nature Magazine.
- ↑ Woldt E, Sebti Y, Solt LA, Duhem C, Lancel S, Eeckhoute J, Hesselink MK, Paquet C, Delhaye S, Shin Y, Kamenecka TM, Schaart G, Lefebvre P, Nevière R, Burris TP, Schrauwen P, Staels B, Duez H (August 2013). "Rev-erb-α modulates skeletal muscle oxidative capacity by regulating mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy". Nat. Med. 19 (8): 1039–46. doi:10.1038/nm.3213. PMID 23852339. Lay summary – Voice of America (2013-07-19).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.