Ruda Śląska
| Ruda Śląska | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
| |||
 Ruda Śląska | |||
| Coordinates: 50°16′N 18°42′E / 50.267°N 18.700°E | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Voivodeship |
| ||
| County | city county | ||
| Established | 13th century | ||
| Town rights | 1959 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Grażyna Dziedzic | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 77.73 km2 (30.01 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2013) | |||
| • City | 142,510 | ||
| • Density | 1,800/km2 (4,700/sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 2,746,000 | ||
| • Metro | 4,620,624 | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postal code | 41-700 to 41-718 | ||
| Area code(s) | +48 32 | ||
| Car plates | SRS, SL | ||
| Website | http://www.rudaslaska.pl/ | ||
Ruda Śląska [ˈruda ˈɕlɔ̃ska] (![]() ) (German Ruda in Oberschlesien) is a city in Silesia in southern Poland, near Katowice. It is a district in the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union, a metropolis with a population of 2 million. It is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (tributary of the Oder).
) (German Ruda in Oberschlesien) is a city in Silesia in southern Poland, near Katowice. It is a district in the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union, a metropolis with a population of 2 million. It is located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Kłodnica river (tributary of the Oder).
It has been part of the Silesian Voivodeship since its formation in 1999. Previously, it was in Katowice Voivodeship, and before then, part of the Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship. Ruda Śląska is one of the cities in the Katowice urban area (population 2.7 million) and within the greater Silesian metropolitan area (population 5,294,000).[1] The population of the city is 143,583 (June 2009).[2]
Subdivisions
The city of Ruda Śląska is divided into the following subdivisions:
|
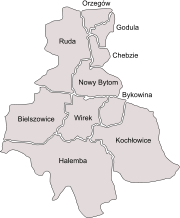 |
History

A large village is known to have existed at the location of the present day city center in 1243. The city name appears to indicate the awareness and perhaps exploitation of ores from early times.
The area underwent rapid industrialization (coal, steel, zinc) in the 19th and the beginning of 20th century. However, it remained a cluster of industrial settlements and villages until the 1950s, when it was administratively united. However, it never developed into a truly unified city.
After the fall of communism in 1989, the significant heavy industry was largely scaled down or restructured. The area has been transforming to a service-based economy. The well-known still operating coal mine is "Halemba".
Since 2007, Ruda Śląska has been a member of the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union, the largest legally recognized urban area in Poland.
Transport and infrastructure
Significant roadways are Highway A4 and the Drogowa Trasa Średnicowa. There are several small railway stations, mainly on the line Katowice-Gliwice.
Since 1950, Ruda Śląska is the site of a transmission facility, which was used from 1950 to 1988 for medium-wave radio broadcasting.
Higher education
The neighboring cities of Katowice and Gliwice are large academic centers. Ruda Śląska is a seat of the Higher Academy of Commerce (Wyższa Szkoła Handlowa).
Sports
- Zgoda Ruda Śląska - women's handball team playing in Polish Ekstraklasa Women's Handball League: Polish Cup winner 2004; 6th place in 2003/2004 season.
Rugby Club IGLOO Ruda Śląska – men's rugby team playing in Polish Ekstraliga Rugby Seven's
Famous people
- Günter Bialas, composer
- Otylia Jędrzejczak (born December 13, 1983) - Olympic gold medalist and world record-holder in swimming
- Karl Godulla
- Ernest Pohl
- Erwin Wilczek
- Marcin Baszczynski
- Paweł Cyganek
- Franciszek Bukal
- Wenanty Fuhl
- Artur Sobiech
Ruda Śląska is the largest population center in Poland never to have been visited by Lech Wałęsa. This is shown on a brass plaque on the side of the ratusz (town hall).
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Ruda Śląska is twinned with:
 Carrickfergus, Northern Ireland
Carrickfergus, Northern Ireland
References
- ↑ European Spatial Planning Observation Network (ESPON)
- ↑ Central Statistical Office, Warsaw 2009, "Population. Size and Structure by Territorial Division, as of June 30, 2009" (PDF). Retrieved 2009-12-31.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ruda Śląska. |
| ||||||||||
Coordinates: 50°18′N 18°53′E / 50.300°N 18.883°E


