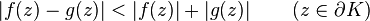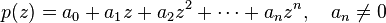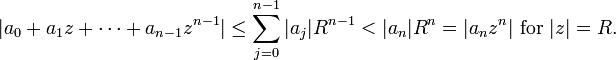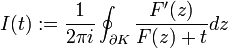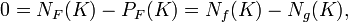Rouché's theorem
Rouché's theorem, named after Eugène Rouché, states that if the complex-valued functions f and g are holomorphic inside and on some closed contour K, with |g(z)| < |f(z)| on K, then f and f + g have the same number of zeros inside K, where each zero is counted as many times as its multiplicity. This theorem assumes that the contour K is simple, that is, without self-intersections. Rouché's theorem is an easy consequence of a stronger Symmetric Rouché's theorem described below.
Symmetric version
Theodor Estermann (1902–1991) proved in his book Complex Numbers and Functions the following relation: Let 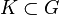 be a bounded region with continuous boundary
be a bounded region with continuous boundary 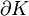 . Two holomorphic functions
. Two holomorphic functions 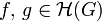 have the same number of roots in
have the same number of roots in  , if the strict inequality
, if the strict inequality
holds on the boundary 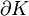 .
.
The original Rouché's theorem then follows by setting 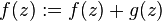 and
and 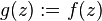 .
.
Usage
The theorem is usually used to simplify the problem of locating zeros, as follows. Given an analytic function, we write it as the sum of two parts, one of which is simpler and grows faster than (thus dominates) the other part. We can then locate the zeros by looking at only the dominating part. For example, the polynomial 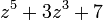 has exactly 5 zeros in the disk
has exactly 5 zeros in the disk 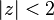 since
since 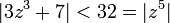 for every
for every 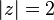 , and
, and 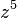 , the dominating part, has five zeros in the disk.
, the dominating part, has five zeros in the disk.
Geometric explanation
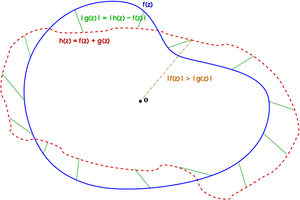
It is possible to provide an informal explanation of Rouche's theorem.
Let C be a closed, simple curve (i.e., not self-intersecting). Let h(z) = f(z) + g(z). If f and g are both holomorphic on the interior of C, then h must also be holomorphic on the interior of C. Then, with the conditions imposed above, the Rouche's theorem in its original (and not symmetric) form says that
- If |f(z)| > |h(z) − f(z)|, for every z in C, then f(z) and h(z) have the same number of zeros in the interior of C.
Notice that the condition |f(z)| > |h(z) − f(z)| means that for any z, the distance from f(z) to the origin is larger than the length of h(z) − f(z), which in the following picture means that for each point on the blue curve, the segment joining it to the origin is larger than the green segment associated with it. Informally we can say that the blue curve f(z) is always closer to the red curve h(z) than it is to the origin.
The previous paragraph shows that h(z) must wind around the origin exactly as many times as f(z). The index of both curves around zero is therefore the same, so by the argument principle, f(z) and h(z) must have the same number of zeros inside C.
One popular, informal way to summarize this argument is as follows: If a person were to walk a dog on a leash around and around a tree, and if the length of the leash is less than the minimum radius of the walk, then the person and the dog go around the tree an equal number of times.
Applications
Consider the polynomial  (where
(where 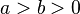 ). By the quadratic formula it has two zeros at
). By the quadratic formula it has two zeros at 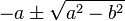 . Rouché's theorem can be used to obtain more precise positions of them. Since
. Rouché's theorem can be used to obtain more precise positions of them. Since
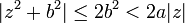 for every
for every 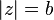 ,
,
Rouché's theorem says that the polynomial has exactly one zero inside the disk  . Since
. Since 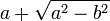 is clearly outside the disk, we conclude that the zero is
is clearly outside the disk, we conclude that the zero is 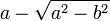 . This sort of arguments can be useful in locating residues when one applies Cauchy's Residue theorem.
. This sort of arguments can be useful in locating residues when one applies Cauchy's Residue theorem.
Rouché's theorem can also be used to give a short proof of the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra. Let
and choose 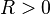 so large that:
so large that:
Since 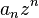 has
has  zeros inside the disk
zeros inside the disk 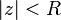 (because
(because 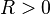 ), it follows from Rouché's theorem that
), it follows from Rouché's theorem that  also has the same number of zeros inside the disk.
also has the same number of zeros inside the disk.
One advantage of this proof over the others is that it shows not only that a polynomial must have a zero but the number of its zeros is equal to its degree (counting, as usual, multiplicity).
Another use of Rouché's theorem is to prove the open mapping theorem for analytic functions. We refer to the article for the proof.
Proof of symmetric form of Rouché's theorem
The hypothesis ensures both that  and
and 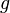 do not have any roots on the boundary
do not have any roots on the boundary 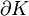 and that
and that  is not a negative real number for
is not a negative real number for 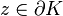 . Thus the homotopy
. Thus the homotopy
is well defined for  , where
, where 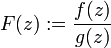 .
.
Clearly, 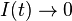 as
as  . As
. As  is continuous and integer valued, it follows that
is continuous and integer valued, it follows that 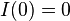 .
By the argument principle, this winding number is given by
.
By the argument principle, this winding number is given by
where NF(K) is the number of zeros of F inside K, PF(K) is the number of poles inside K. Hence NF = PF. But F is the ratio of two holomorphic functions f and g inside K, and so the zeros are those of f and the poles are the zeros of g (after canceling out the common zeros of f and g). That is,
as required.
See also
- Hurwitz's theorem (complex analysis)
- Sturm's theorem
- Rational root theorem
- Properties of polynomial roots
- Riemann mapping theorem
References
- Beardon, Alan (1979). Complex Analysis: the Winding Number principle in analysis and topology. John Wiley and Sons. p. 131. ISBN 0-471-99672-6.
- Titchmarsh, E. C. (1939). The Theory of Functions (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 117–119,198–203. ISBN 0-19-853349-7.
External links
Module for Rouche’s Theorem by John H. Mathews