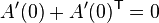Rotation group SO(3)
In mechanics and geometry, the 3D rotation group is the group of all rotations about the origin of three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 under the operation of composition.[1] By definition, a rotation about the origin is a transformation that preserves the origin, Euclidean distance (so it is an isometry), and orientation (i.e. handedness of space). A distance-preserving transformation which reverses orientation is an improper rotation, that is a reflection or, in the general position, a rotoreflection. The origin in Euclidean space establishes a one-to-one correspondence between points and their coordinate vectors. Rotations about the origin can be thought of as magnitude-preserving linear transformations of Euclidean 3-dimensional vectors (whose vector space is also denoted as R3).
Composing two rotations results in another rotation; every rotation has a unique inverse rotation; and the identity map satisfies the definition of a rotation. Owing to the above properties (along with the associative property, which rotations obey), the set of all rotations is a group under composition. Moreover, the rotation group has a natural manifold structure for which the group operations are smooth; so it is in fact a Lie group. The rotation group is often denoted SO(3) (or, less ambiguously, SO(3, R)) for reasons explained below.
Length and angle
Besides just preserving length, rotations also preserve the angles between vectors. This follows from the fact that the standard dot product between two vectors u and v can be written purely in terms of length:
It follows that any length-preserving transformation in R3 preserves the dot product, and thus the angle between vectors. Rotations are often defined as linear transformations that preserve the inner product on R3. This is equivalent to requiring them to preserve length.
Orthogonal and rotation matrices
Every rotation maps an orthonormal basis of R3 to another orthonormal basis. Like any linear transformation of finite-dimensional vector spaces, a rotation can always be represented by a matrix. Let R be a given rotation. With respect to the standard basis e1, e2, e3 of R3 the columns of R are given by (Re1, Re2, Re3). Since the standard basis is orthonormal, the columns of R form another orthonormal basis. This orthonormality condition can be expressed in the form
where RT denotes the transpose of R and I is the 3 × 3 identity matrix. Matrices for which this property holds are called orthogonal matrices. The group of all 3 × 3 orthogonal matrices is denoted O(3), and consists of all proper and improper rotations.
In addition to preserving length, proper rotations must also preserve orientation. A matrix will preserve or reverse orientation according to whether the determinant of the matrix is positive or negative. For an orthogonal matrix R, note that det RT = det R -1 implies (det R)2 = 1 so that det R = ±1. The subgroup of orthogonal matrices with determinant +1 is called the special orthogonal group, denoted SO(3).
Thus every rotation can be represented uniquely by an orthogonal matrix with unit determinant. Moreover, since composition of rotations corresponds to matrix multiplication, the rotation group is isomorphic to the special orthogonal group SO(3).
Improper rotations correspond to orthogonal matrices with determinant −1, and they do not form a group because the product of two improper rotations is a proper rotation.
Group structure
The rotation group is a group under function composition (or equivalently the product of linear transformations). It is a subgroup of the general linear group consisting of all invertible linear transformations of the real 3-space R3.[2]
Furthermore, the rotation group is nonabelian. That is, the order in which rotations are composed makes a difference. For example, a quarter turn around the positive x-axis followed by a quarter turn around the positive y-axis is a different rotation than the one obtained by first rotating around y and then x.
The orthogonal group, consisting of all proper and improper rotations, is generated by reflections. Every proper rotation is the composition of two reflections, a special case of the Cartan–Dieudonné theorem.
Axis of rotation
Every nontrivial proper rotation in 3 dimensions fixes a unique 1-dimensional linear subspace of R3 which is called the axis of rotation (this is Euler's rotation theorem). Each such rotation acts as an ordinary 2-dimensional rotation in the plane orthogonal to this axis. Since every 2-dimensional rotation can be represented by an angle φ, an arbitrary 3-dimensional rotation can be specified by an axis of rotation together with an angle of rotation about this axis. (Technically, one needs to specify an orientation for the axis and whether the rotation is taken to be clockwise or counterclockwise with respect to this orientation).
For example, counterclockwise rotation about the positive z-axis by angle φ is given by
Given a unit vector n in R3 and an angle φ, let R(φ, n) represent a counterclockwise rotation about the axis through n (with orientation determined by n). Then
- R(0, n) is the identity transformation for any n
- R(φ, n) = R(−φ, −n)
- R(π + φ, n) = R(π − φ, −n).
Using these properties one can show that any rotation can be represented by a unique angle φ in the range 0 ≤ φ ≤ π and a unit vector n such that
- n is arbitrary if φ = 0
- n is unique if 0 < φ < π
- n is unique up to a sign if φ = π (that is, the rotations R(π, ±n) are identical).
Topology
The Lie group SO(3) is diffeomorphic to the real projective space RP3.
Consider the solid ball in R3 of radius π (that is, all points of R3 of distance π or less from the origin). Given the above, for every point in this ball there is a rotation, with axis through the point and the origin, and rotation angle equal to the distance of the point from the origin. The identity rotation corresponds to the point at the center of the ball. Rotation through angles between 0 and −π correspond to the point on the same axis and distance from the origin but on the opposite side of the origin. The one remaining issue is that the two rotations through π and through −π are the same. So we identify (or "glue together") antipodal points on the surface of the ball. After this identification, we arrive at a topological space homeomorphic to the rotation group.
Indeed, the ball with antipodal surface points identified is a smooth manifold, and this manifold is diffeomorphic to the rotation group. It is also diffeomorphic to the real 3-dimensional projective space RP3, so the latter can also serve as a topological model for the rotation group.
These identifications illustrate that SO(3) is connected but not simply connected. As to the latter, in the ball with antipodal surface points identified, consider the path running from the "north pole" straight through the interior down to the south pole. This is a closed loop, since the north pole and the south pole are identified. This loop cannot be shrunk to a point, since no matter how you deform the loop, the start and end point have to remain antipodal, or else the loop will "break open". In terms of rotations, this loop represents a continuous sequence of rotations about the z-axis starting and ending at the identity rotation (i.e. a series of rotation through an angle φ where φ runs from 0 to 2π).
Surprisingly, if you run through the path twice, i.e., run from north pole down to south pole, jump back to the north pole (using the fact that north and south poles are identified), and then again run from north pole down to south pole, so that φ runs from 0 to 4π, you get a closed loop which can be shrunk to a single point: first move the paths continuously to the ball's surface, still connecting north pole to south pole twice. The second half of the path can then be mirrored over to the antipodal side without changing the path at all. Now we have an ordinary closed loop on the surface of the ball, connecting the north pole to itself along a great circle. This circle can be shrunk to the north pole without problems. The Balinese plate trick and similar tricks demonstrate this practically.
The same argument can be performed in general, and it shows that the fundamental group of SO(3) is cyclic group of order 2. In physics applications, the non-triviality of the fundamental group allows for the existence of objects known as spinors, and is an important tool in the development of the spin-statistics theorem.
The universal cover of SO(3) is a Lie group called Spin(3). The group Spin(3) is isomorphic to the special unitary group SU(2); it is also diffeomorphic to the unit 3-sphere S3 and can be understood as the group of versors (quaternions with absolute value 1). The connection between quaternions and rotations, commonly exploited in computer graphics, is explained in quaternions and spatial rotations. The map from S3 onto SO(3) that identifies antipodal points of S3 is a surjective homomorphism of Lie groups, with kernel {±1}. Topologically, this map is a two-to-one covering map.
Lie algebra
Since SO(3) is a Lie subgroup of the general linear group GL(3), its Lie algebra can be identified with a Lie subalgebra of gl(3), the algebra of 3 × 3 matrices with the commutator given by
The condition that a matrix A belong to SO(3) is that
- (*)
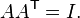
If A(t) is a one-parameter subgroup of SO(3) parametrised by t, then differentiating (*) with respect to t gives
and so the Lie algebra SO(3) consists of all skew-symmetric 3 × 3 matrices.
Representations of rotations
We have seen that there are a variety of ways to represent rotations:
- as orthogonal matrices with determinant 1,
- by axis and rotation angle
- in quaternion algebra with versors and the map 3-sphere S3 → SO(3) (see quaternions and spatial rotations).
Another method is to specify an arbitrary rotation by a sequence of rotations about some fixed axes. See:
- Euler angles
See charts on SO(3) for further discussion.
Generalizations
The rotation group generalizes quite naturally to n-dimensional Euclidean space, Rn with its standard Euclidean structure. The group of all proper and improper rotations in n dimensions is called the orthogonal group O(n), and the subgroup of proper rotations is called the special orthogonal group SO(n), which is a Lie group of dimension n(n-1)/2.
In special relativity, one works in a 4-dimensional vector space, known as Minkowski space rather than 3-dimensional Euclidean space. Unlike Euclidean space, Minkowski space has an inner product with an indefinite signature. However, one can still define generalized rotations which preserve this inner product. Such generalized rotations are known as Lorentz transformations and the group of all such transformations is called the Lorentz group.
The rotation group SO(3) can be described as a subgroup of E+(3), the Euclidean group of direct isometries of Euclidean R3. This larger group is the group of all motions of a rigid body: each of these is a combination of a rotation about an arbitrary axis and a translation along the axis, or put differently, a combination of an element of SO(3) and an arbitrary translation.
In general, the rotation group of an object is the symmetry group within the group of direct isometries; in other words, the intersection of the full symmetry group and the group of direct isometries. For chiral objects it is the same as the full symmetry group.
See also
- Orthogonal group
- Angular momentum
- Coordinate rotations
- Charts on SO(3)
- Euler angles
- Rodrigues' rotation formula
- Infinitesimal rotation
- Pin group
- Quaternions and spatial rotations
- Rigid body
- Spherical harmonics
- Plane of rotation
- Lie group
Notes
- ↑ Jacobson (2009), p. 34, Ex. 14.
- ↑ n × n real matrices are identical to linear transformations of Rn expressed in its standard basis.
References
- A. W. Joshi Elements of Group Theory for Physicists (2007 New Age International) pp. 111ff.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Rotation Group", MathWorld.
- Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences by Mary L Boas pp. 120,127,129,155ff and 535
- Jacobson, Nathan (2009), Basic algebra 1 (2nd ed.), Dover, ISBN 978-0-486-47189-1

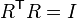
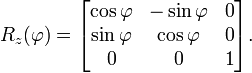
![[A,B]=AB-BA.\,](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/d/b/2/f/db2fa4dd66a807154591f9e8a44e3899.png)