Roquefortine C
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Roquefortine C | ||
|---|---|---|
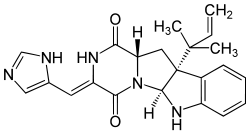 | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 58735-64-1 | |
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C22H23N5O2 | |
| Molar mass | 389.5 g/mol | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid | |
| Solubility in water | Soluble in ethanol, methanol, DMF or DMSO | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Roquefortin C is a mycotoxin produced by various fungi, particularly species from the Penicillium genus.[1] It was first isolated from a strain of Penicillium roqueforti, a species commercially used to make Roquefort, Danish Blue, Stilton and Gorgonzola cheeses.
Roquefortine C is a potent neurotoxin.[2][3]
Related compounds
References
- ↑ Kokkonen M, Jestoi M, Rizzo A (2005). "The effect of substrate on mycotoxin production of selected Penicillium strains". International Journal of Food Microbiology 99 (2): 207–14. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.08.014. PMID 15734568.
- ↑ SCBT. Roquefortine - A potent neurotoxin produced most notably by Penicillium species.
- ↑ EPA. Penicillium roqueforti Final Risk Assessment.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.