Rock hyrax
| Rock hyrax[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Hyracoidea |
| Family: | Procaviidae |
| Genus: | Procavia Storr, 1780 |
| Species: | P. capensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Procavia capensis (Pallas, 1766) | |
 | |
| Rock hyrax range | |
The rock hyrax (Procavia capensis) or Cape hyrax is one of the four living species of the order Hyracoidea, and the only living species in the genus Procavia. Like all hyraxes, it is a medium-sized (~4 kg) terrestrial mammal, superficially resembling a guinea pig with short ears and tail. The closest living relatives to hyraxes are the modern-day elephants and sirenians. The rock hyrax is found across Africa and the Middle East, in habitats with rock crevices in which to escape from predators. Hyraxes typically live in groups of 10–80 animals, and forage as a group. They have been reported to use sentries: one or more animals take up position on a vantage point and issue alarm calls on the approach of predators.
The rock hyrax has incomplete thermoregulation, and is most active in the morning and evening, although their activity pattern varies substantially with season and climate.
Over most of its range, the rock hyrax is not endangered, and in some areas is considered a minor pest. In Ethiopia, Israel and Jordan, they have been shown to be a reservoir of the leishmaniasis parasite.
Characteristics
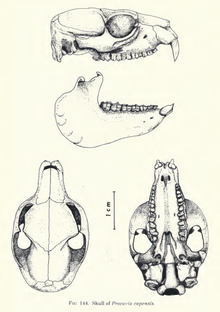




The rock hyrax is squat and heavily built, adults reaching a length of 50 cm (20 in) and weighing around 4 kg (8.8 lb), with a slight sexual dimorphism; males being approximately 10% heavier than females. Their fur is thick and grey-brown color, although this varies strongly between different environments; from dark brown in wetter habitats, to light gray in desert living individuals.[3] Hyrax size (as measured by skull length and humerus diameter) is correlated to precipitation, probably because of the effect on preferred hyrax forage.[4]
Prominent in and apparently unique to hyraxes is the dorsal gland, which excretes an odour used for social communication and territorial marking. The gland is most clearly visible in dominant males.[5]
The head of the rock hyrax is pointed, having a short neck with rounded ears. They have long black whiskers on their muzzles.[6] The rock hyrax has a prominent pair of long, pointed tusk-like upper incisors which are reminiscent of the elephant, to which the hyrax is distantly related (see below). The forefeet are plantigrade, and the hindfeet semi-digitigrade. The soles of the feet have large, soft pads that are kept moist with sweat-like secretions. In males, the testes are permanently abdominal, another anatomical feature that hyraxes share with their relatives elephants and sirenians.[5]
Thermoregulation in the rock hyrax has been subject to much research, as their body temperature varies with a diurnal rhythm. However, animals kept in constant environmental conditions also display such variation[5] and this internal mechanism may be related to water balance regulation.[7]
Distribution
The rock hyrax occurs across sub-Saharan Africa, with the exception of the Congo basin and Madagascar. A larger, longer-haired subspecies is abundant in the glacial moraines in the alpine zone of Mount Kenya[citation needed]. The distribution continues into northern Algeria, Libya and Egypt, and the Middle East, with populations in Israel, Jordan, Syria, the Arabian peninsula and eastern Turkey.[5]
Ecology and behaviour
Hyraxes live in colonies of up to 80 individuals. These colonies are subdivided into smaller groups consisting of a few families. These consist of 3 to 15 related adult females, a dominant male, and several young. The dominant male defends and watches over the group. The male also marks its territory.[8]
In Africa, hyraxes are preyed on by leopards, Egyptian cobras, puff adders, caracals, wild dogs, and eagles.[9] Verreaux's Eagle in particular is a specialist hunter of hyrax.[10][11] In Israel, the rock hyrax is reportedly rarely preyed upon by terrestrial predators, as their system of sentries and their reliable refuges provide considerable protection. Hyrax remains are almost absent from the droppings of wolves in the Judean Desert.[12]
Feeding and foraging

Hyraxes feed on a wide variety of different plants, including both grasses[8] and broad-leafed plants.[13] They also have been reported to eat insects and grubs.[6] The rock hyraxes forage for food up to about 50 metres from their refuge, usually feeding as a group and with one or more acting as sentries from a prominent lookout position. On the approach of danger, the sentries give an alarm call, and the animals quickly retreat to their refuge.[14] They are able to go for many days without water due to the moisture they obtain through their food.[15] Despite their seemingly clumsy build, they are able to climb trees (although not as readily as Heterohyrax), and will readily enter residential gardens to feed on the leaves of citrus and other trees.
Reproduction
Rock hyraxes give birth to two or three young after a gestation period of 6–7 months (long, for their size). The young are well developed at birth with fully opened eyes and complete pelage. Young can ingest solid food after two weeks and are weaned at ten weeks. After 16 months, the rock hyraxes become sexually mature, they reach adult size at three years, and they typically live about ten years.[5] During seasonal changes, the weight of the male reproductive organs (testis, seminal vesicles) changes due to sexual activity. A study showed that between May and January, the males were inactive sexually. From February onward, there was a dramatic increase to the weight of these organs, and the males are able to copulate.[16]
Social behaviour
Rock hyraxes are very noisy and sociable.[8] In a study of their social networks, it was found that hyraxes that live in more "egalitarian" groups, in which social associations are spread more evenly among group members, survive longer.[17] In addition, hyraxes are the first non-human species in which structural balance was described, i.e. they follow the "the friend of my friend is my friend" rule, and avoid unbalanced social configurations.[18]
Adults make use of at least 21 different vocal signals. The most familiar signal is a high trill, given in response to perceived danger.[6] Rock hyrax calls can provide important biological information such as size, age, social status, body weight, condition, and hormonal state of the caller, as determined by measuring their call length, patterns, complexity, and frequency.[19] More recently, researchers have found rich syntactic structure and geographical variations in the calls of rock hyraxes, a first in the vocalization of mammalian taxa other than primates, cetaceans, and bats.[20]
The rock hyrax also makes a loud grunting sound while moving its jaws as if chewing, and this behaviour may be a sign of aggression. Some authors[21] have proposed that observation of this behavior by ancient Israelites gave rise to the misconception given in Leviticus 11:4-8 that the hyrax chews the cud; in fact, hyraxes are not ruminants.[5]
The rock hyrax spends approximately 95% of its time resting.[5] During this time, they can often be seen basking in the sun, which is thought to be an element of their complex thermoregulation.
Dispersal
Male hyraxes have been categorised into four classes: territorial, peripheral, early dispersers, and late dispersers. The territorial males are dominant. Peripheral males are more solitary and sometimes take over a group when the dominant male is missing. Early-dispersing males are juveniles that leave the birth site around 16 to 24 months of age. Late dispersers are also juvenile males, but they leave the birth site much later; around 30 or more months of age.[22]
Names
They are known as dassies in South Africa, and sometimes rock rabbits. The Swahili names for them are pimbi, pelele and wibari, though the latter two names are nowadays reserved for the tree hyraxes. The Dutch name is klipdas.[23] This species has many subspecies, many of which are also known as rock or Cape hyrax, although the former usually refers to African varieties. In Arabic, the rock hyrax is called الوبر ("wabr") or طبسون ("tabsoun"). In Hebrew, the rock hyrax is called שפן סלע (shafan sela), meaning rock "shafan", where the meaning of shafan is obscure, but is colloquially used as a synonym for rabbit in modern Hebrew.[21] Gerald Durrell wrote that in Bafut, in Cameroon, the locals call the rock hyrax the n'eer.[24]
Pharmaceutical use
Rock hyraxes produce large quantities of hyraceum—a sticky mass of dung and urine that has been employed as a South African folk remedy in the treatment of several medical disorders, including epilepsy and convulsions.[25] Hyraceum is now being used by perfumers who tincture it in alcohol to yield a natural animal musk.[26]
Culture
Rock hyraxes are classified as non-kosher in the Old Testament/Jewish Torah.[27] Nonetheless, they are also included in Proverbs 30:26 as one of a number of remarkable animals for being small but exceedingly wise, in this case because "the rock badgers are a people not mighty, yet they make their homes in the cliffs".[28]
In Joy Adamson's books and the associated movie Born Free, a rock hyrax that she called Pati-Pati was her companion for six years before Elsa and her siblings came along and took the role of nanny and watched over them with great care.[29]
Gallery
-

Basking on Table Mountain
-

A colony of hyrax in northern Israel
-
Dassie in the botanical garden of Pretoria (South Africa)
-
Collar tagged rock hyrax, Ein Gedi
References
- ↑ http://www.bucknell.edu/msw3/browse.asp?s=y&id=11400040
- ↑ Barry, R., Bloomer, P., Hoeck, H. & Shoshani, H. (2008). Procavia capensis. In: IUCN 2008. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 29 December 2008.
- ↑ Bothma J.d.P. (1966) Color Variation in Hyracoidea from Southern Africa. Journal of Mammalogy 47: 687–693.
- ↑ Klein R.G., CruzUribe, K . (1996) "Size variation in the rock hyrax (Procavia capensis) and late Quaternary climatic change in South Africa." Quaternary Research 46 (2): 193–207.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 Olds, N., Shoshani, J. (1982). "Procavia capensis". Mammalian Species 171: 1–7.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 http://www.livingdesert.org/animals/rock_hyrax.asp
- ↑ Meltzer, A. (1973) Heat balance and water economy of the rock hyrax (Procavia capensis syriaca Schreber 1784). Unpubl. Ph.D. dissert., Tel-Aviv Univ., Israel, 135 pp.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Rock hyrax. (n.d.). Retrieved April 17, 2009, from EBSCO Animals database. MAIN <http://0-search.ebscohost.com.patris.apu.edu/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ani&AN=9500100073&site=ehost-live>
- ↑ Turner, M. I. M., and R. M. Watson. 1965. An introductory study on the ecology of hyrax (Dendrohyrax brucei and Procavia johnstoni) in the Serengeti National Park. E. African Wildl. J., 3:49-60.
- ↑ Estes, Richard D. (1999). The Safari Companion. Chelsea Green Publishing Company. ISBN 1-890132-44-6.
- ↑ Mike, Unwin (2003). Southern African Wildlife. Bradt Travel Guides. ISBN 1-84162-060-2.
- ↑ Margolis, E. (2008). "Dietary composition of the wolf Canis lupus in the Ein Gedi area according to analysis of their droppings (in Hebrew)". Proceedings of the 45th Meeting of the Israel Zoological Society.
- ↑ http://natureniche.tripod.com/hyrax.html
- ↑ Kotler B.P., Brown J.S. & Knight M.H. (1999) Habitat and patch use by hyraxes: there's no place like home? In, pp. 82–88
- ↑ African Wildlife Foundation: Hyrax
- ↑ Glover, T.D. & Millar, R.P. (1970) Seasonal Changes in the Reproductive Tract of the Male Rock Hyrax. J. Reprod. Fert. 23, 497-499
- ↑ Barocas A, Ilany A, Koren L, Kam M, Geffen E (2011) Variance in Centrality within Rock Hyrax Social Networks Predicts Adult Longevity. PLoS ONE 6(7): e22375. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022375
- ↑ Amiyaal Ilany, Adi Barocas, Lee Koren, Michael Kam, Eli Geffen. Structural balance in the social networks of a wild mammal. Animal Behaviour, Volume 85, Issue 6, June 2013, Pages 1397–1405 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2013.03.032
- ↑ Koren, Lee, and Eli Geffen. "Complex call in male rock hyrax (Procavia capensis): a multi-information distributing channel." Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology. 63.4 (2009 Feb): p. 581–590.
- ↑ Arik Kershenbaum, Amiyaal Ilany, Leon Blaustein, Eli Geffen (2012). "Syntactic structure and geographical dialects in the songs of male rock hyraxes". Proc. R. Soc. B (Royal Society). doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.0322. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Slifkin, Nosson (March 1, 2004). 6 (PDF). "Shafan– The Hyrax". The camel, the hare & the hyrax: a study of the laws of animals with one kosher sign in light of modern zoology. Southfield, MI; Nanuet, NY: Zoo Torah in association with Targum/Feldheim Distributed by Feldheim. pp. 99–135. ISBN 1-56871-312-6. Retrieved April 25, 2012. ISBN 978-1-56871-312-0.
- ↑ http://www.jaxzoo.org/things/biofacts/RockHyrax.asp
- ↑
 Rines, George Edwin, ed. (1920). "Dassy". Encyclopedia Americana.
Rines, George Edwin, ed. (1920). "Dassy". Encyclopedia Americana.
- ↑ Durrell, Gerald (1954). The Bafut Beagles. Rupert Hart-Davies.
- ↑ Olsen, A., Prinsloo, L. C., Scott, L., Jägera, A, K. (2008) "Hyraceum, the fossilized metabolic product of rock hyraxes (Procavia capensis), shows GABA-benzodiazepine receptor affinity". South African Journal of Science 103.
- ↑ http://www.profumo.it/title/Hyraceum/pid/5076
- ↑ Leviticus 11:4-5; Deuteronomy 14:7
- ↑ Prov 30:26, ESV
- ↑ Joy Adamson, Elsa - The Story Of A Lioness, London: Collins & Harvill Press, 1961, p.3
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Procavia capensis. |
| Wikispecies has information related to: Procavia capensis |
- Animal Diversity : Procavia capensis
- View the hyrax genome on Ensembl
| |||||||||||||||||||


