Robert Bosch GmbH
 Logo since 2002 | |
| Type | GmbH (Private company) |
|---|---|
| Industry |
Engineering Electronics |
| Founded | 15 November 1886 (adopted current name in 1937) |
| Founder(s) | Robert Bosch |
| Headquarters | Stuttgart, Germany |
| Area served | Worldwide |
| Key people | Volkmar Denner (CEO) |
| Products | Automotive parts, Power tools, Security systems, Home appliance |
| Revenue |
|
| Employees | 306,000 (2012) |
| Website | www.bosch.com |
Robert Bosch GmbH (![]() pronunciation (help·info)), or Bosch, is a German multinational engineering and electronics company headquartered in Gerlingen, near Stuttgart, Germany. It is the world's largest supplier of automotive components measured by 2011 revenues.[1] The company was founded by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 1886.[2]
pronunciation (help·info)), or Bosch, is a German multinational engineering and electronics company headquartered in Gerlingen, near Stuttgart, Germany. It is the world's largest supplier of automotive components measured by 2011 revenues.[1] The company was founded by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 1886.[2]
Bosch's core products are automotive components (including brakes, controls, electrical drives, electronics, fuel systems, generators, starter motors and steering systems), industrial products (including drives and controls, packaging technology and consumer goods) and building products (including household appliances, power tools, security systems and thermotechnology).[3] Bosch is also one of the first companies to implement the use of soft robots in its factories.
Bosch has more than 350 subsidiaries across over 60 countries and its products are sold in around 150 countries.[3] Bosch employs around 306,000 people and had revenues of approximately €52.5 billion in 2012. In 2012 it invested around €4.8 billion in research and development and applied for around 4,800 patents worldwide.[3] In 2009 Bosch was the leader in terms of numbers of patents at the German Patent and Trade Mark Office (GPTO) with 3,213 patents.
However, Bosch continued to extend its international footprint through company acquisitions and investments in new plants, and will continue along with this path in 2013. For example, the Bosch Group is planning to set up a manufacturing site for automotive windshield-wiper systems near Belgrade, Serbia. By 2019 some 70 million euros will be invested. Construction work was set to begin in early 2012, with production due to commence at the start of 2013. Initially, some 60 associates will work in manufacturing operations with a floor area of around 22,000 square meters. By 2019 the number of associates is set to rise to some 620. Its objectives are to achieve a better increase in sales than in 2012 and to improve result significantly.[4]
Robert Bosch GmbH is privately owned, and 92% of its share capital is held by Robert Bosch Stiftung GmbH, a charitable foundation.[3] The majority of voting rights are held by Robert Bosch Industrietreuhand KG, an industrial trust.[3] The remaining shares are held by the Bosch family and by Robert Bosch GmbH.[3] The Bosch logo represents a simple magneto armature and casing, one of the company's first products.
History
19th century

- 1886 - Opening of Workshop for Precision Mechanics and Electrical Engineering in Stuttgart on 15 November
- 1887 - First low-voltage magneto from Bosch for stationary petrol engines
- 1897 - First low-voltage magneto ignition for motor vehicle internal combustion engines
20th century

- 1901 - First plant in Stuttgart
- 1902 - First commercially viable high-voltage spark plug
- 1906 - Production of 100,000th magneto ignition
- 1906 - Introduction of eight-hour working day
- 1910 - Opening of plant in Stuttgart-Feuerbach
- 1913 - Start of production of headlights
- 1918 - American assets seized; later become American Bosch Magneto
- 1926 - Start of production of windscreen wipers
- 1927 - First diesel fuel injection pump
- 1929 - First TV Set from Fernseh AG division
- 1932 - Formation of Junkers & Co.
- 1932 - First power drill from Bosch
- 1932 - First Blaupunkt car audio
- 1936 - First diesel fuel injection pump for passenger cars, such as the Mercedes-Benz 260D
- 1942 - Death of the company founder Robert Bosch on 12 March
- 1962 - Worcester Bosch Group opens in England
- 1964 - Robert Bosch Foundation
- 1970 - Company headquarter moves to Gerlingen
- 1976 - First oxygen sensors
- 1982 - Company acquires photographic equipment division from Braun AG
- 1986 - Traction control system (TCS) on the market
- 1995 - Acquisition of Atco-Qualcast Ltd[5]
- 1995 - First Electronic Stability Control - Electronic Stability Program (ESP)
- 1997 - Common rail diesel fuel injection
21st century
- 2000 - DI-Motronic gasoline direct injection system
- 2000 - Acquisition of Rexroth*2002 - Brand Relaunched with new logo
- 2003 - Acquisition of Buderus AG
- 2003 - Digital car radio with MP3 drive and digital recorder (Blaupunkt)
- 2003 - The formation of the Robert Bosch Tool Corporation and acquisition of S-B Power Tool Corporation and Vermont American Corporation including the brand names for Bosch Power Tools, Skil Power Tools, Dremel, Vermont-American, Primark brands, and Gilmours[6]
- 2004 - Third-generation common rail diesel injection for cars, with piezo injectors
- 2004 - Bosch opens new Technology Center in Abstatt
- 2006 - Bosch acquires Telex Communications, a maker of hearing aids, headsets and audio equipment, and partners with Daewoo to build Bosch refrigerators in Mexico
- 2007 - The Bosch Communications Systems business unit is created to manage the brands and products of former Telex Communications
- 2007 - Bosch acquires Health Hero Network
- 2008 - Tata Nano, the $2,500 People's Car powered by Bosch-designed engine is unveiled at Auto Expo in New Delhi. Bosch plans to acquire majority stake in Ersol photovoltaics. Bosch acquires CST/berger, maker of professional measuring equipment.
- 2009 - Bosch acquires LR Nelson, a maker of lawn and garden products, including ponds, and merges the Gilmour and Nelson brands into Bosch - Garden and Watering.[7]
- 2009 - Robert Bosch acquires Akustica
- 2012 - Purchased SPX Service Solutions
- 2012 - Shanti Auto Electricals, Budaun
- 2013 - Bosch announced, it will exit its solar business
Operations
Bosch comprises more than 350 subsidiary companies. In addition to automotive components, which generate around 60% of its revenues, Bosch produces industrial machinery and hand tools.[8]
Locations
Although most of the company's plants and employees are located in Germany (112,300 employees), Bosch is a worldwide company.[2]
In North America, Robert Bosch LLC (a wholly owned Bosch subsidiary) has corporate headquarters in Farmington Hills, MI; with factories and distribution facilities in Mt. Prospect, Illinois; Hoffman Estates, Illinois; Broadview, Illinois; Kentwood, Michigan; Waltham, Massachusetts; Clarksville, Tennessee; Anderson, South Carolina; Charleston, South Carolina; South Bend, Indiana (to close 2011[9]); and 11 other cities. The Research Technology Center is located in Palo Alto, California near Stanford University. There are also two corporate sites in Brazil and ten in Mexico where a central purchasing office for all divisions of Bosch Group is located in Broadview, Illinois. In North America, Bosch employs about 24,750 people in 80 locations, generating $8.8 billion in sales in 2006.[10]
There are other wholly owned Bosch subsidiaries in:
- India (18,450)
- Brazil (14,190)
- China (12,370)
- France (9,720 including 70 long term/ short term assignees[11] )
- Czech Republic (8,690)
- Japan (8,130)
- Spain (7,950)
- Turkey (7,000 employees in Bursa and Istanbul, 500 in Manisa)
- Hungary (6,280)
- Italy (5,160)
- United Kingdom (4,920)
- Portugal (3,940)
- Romania
- Netherlands (3,320)
- Switzerland (2,780)
- Australia (2,300)
- Malaysia (2,220)
- Austria (2,140)
- Belgium (2,040)
- South Korea (2,000)
- Russia (1,730)
- Poland (1,640)
- Sweden (1,230)
- South Africa (1,010)
- Viet Nam (1,000)
- Tunisia (770)
and other countries. Bosch employs over 281,717 people in more than 50 countries, supplying a complex distribution network of new products and parts.[12]
Activities
Automotive components
About 60% of Bosch's worldwide annual sales are produced in automotive technology. Bosch invented the first practical magneto, an early ignition electrical source, which provided the spark to ignite the fuel in most of the earliest internal combustion engines. Bosch's corporate logo to this date depicts the armature from a magneto. Bosch was an early manufacturer of Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), and as time passed, Bosch became a leader in such specialized fields as traction control systems (TCS), the Electronic Stability Program (ESP), body electronics (such as central locking, doors, windows and seats), and oxygen sensors, injectors and fuel pumps. Even in such humble technological areas as spark plugs, wiper blades, engine cooling fans and other aftermarket parts, Bosch has over $1 billion in annual sales.
Bosch is a leading player in car stereo systems and in-car navigation systems.
Bosch is supplying hybrid diesel-electric technology to automakers, including PSA Peugeot 3008.[13]
Industrial technology
Bosch's subsidiary Bosch Rexroth is a supplier of industrial technology, producing hydraulic, electric, and pneumatic machinery for driving, controlling, and moving machines in applications ranging from automotive to mining.[2]
Bosch's packaging technology division plans, designs, manufactures and installs packaging lines for manufacturers of pharmaceutical, confectionery, food, and similar products. Bosch is one of the largest supplier of packaging technology.
Consumer goods and power tools

Bosch caters to the areas of consumer goods and building technology with its power tool, thermotechnology, and security systems, as well as with its household appliances business within the BSH Bosch and Siemens Hausgeräte GmbH joint venture. In the US, power tools are provided by the Robert Bosch Tool Corporation based in Mt. Prospect, Illinois.[14][15]
With its brands Bosch, Hawera, Skil, Dremel, RotoZip, Freud, Vermont American, and many more, Bosch is one of the largest manufacturer of portable power tools worldwide. Bosch manufactures power tools for the building trade, industry, and do-it-yourselfers (DIY-ers). In or around 1956, Dr. Hans Erich Slany worked with Bosch to design one of the first plastic power tools. Prior to this time, power tools were metal castings that often conducted electrical sparks or current into the user as well as being very heavy. Today the power tools designed by TEAMS Design have been winning awards worldwide for many years.[16] In 2011, the 12" Dual-Bevel Glide Miter Saw won an EID Silver Award.[17] In 2012, the Dremel Saw Max was awarded a Good Design Award[18] and was chosen as an IDEA Award finalist.[19] The product range also includes accessories such as drill bits and saw blades, under its Vermont American brand, as well as gardening and water gardening products under its Gilmour, LR Nelson, and Sunterra brands.[20]
Bosch is the largest European manufacturer of thermotechnology (heating units, etc.) with its subsidiary BBT Thermotechnik GmbH. It had revenues of €2.8 billion in 2006. Its brands include Bosch, Buderus, Junkers, Dakon, e.l.m leblanc S.A., Florida Heat Pump (FHP), Geminox, IVT, Nefit, Sieger, Vulcano and Worcester.
Security systems
In 2001, Bosch bought Detection Systems and Radionics, Inc., to build their business in the North American security and life safety products manufacturing/supply business. Through the Detection Systems acquisition, Bosch also obtained additional sales channels in Latin America, Asia-Pacific (including Australia), and Europe.[21][22]
In 2002, Bosch acquired Philips Communications and Security, Inc., adding a video surveillance portfolio, as well as sales channels, to its business.[23]
In 2008, Bosch acquired Extreme CCTV, a rugged camera and IP camera manufacturer, to further expand their video surveillance portfolio.[24][25]
Mobile phones
Bosch also used to create mobile phones for a short time. Their first three mobile phones were the Com 906, Com 738 and World 718, all from 1996. In 1997, they released two other phones: Com 207 and Com 607. The Com 908 came out in 1998, and in 1999 they released their final phones: the Com 509, the 909 Dual and the 909 Dual S.
Joint ventures
BSH Bosch und Siemens Hausgeräte
BSH Bosch und Siemens Hausgeräte GmbH, in which Bosch and Siemens AG each hold a 50% share, is one of the world's top three companies in the household appliances industry. In Germany and Western Europe, BSH is the market leader. Its portfolio includes the principal brand names Bosch and Siemens, Gaggenau, Neff, Thermador, Constructa, Viva, and ufesa brands, and further six regional brands. Bosch household appliances for the North American market are mainly manufactured at its factory near New Bern, North Carolina. Its competitors include Viking Range, Fulgor, Sub-Zero Refrigerator, Wolf Appliance (a division of Sub-Zero Refrigerator), Fagor, Dacor, and Miele. The distribution of manufacturing workforce in household appliances is:
- 36% in Germany
- 30% in Western Europe (excluding Germany, but including Turkey)
- 15% in Asia
- 10% in Eastern Europe
- 5% in North America
- 4% in Latin America
with 39,000 employees overall.
Purolator Filters
Bosch owned 50% of Purolator Filters in a joint venture with Mann+Hummel until 2013. In 2013 the Mann+Hummel Group has takenover the remaining 50% stakes from Bosch.
Bosch owns 50% of the home appliance manufacturer Bosch-Siemens Hausgeräte.[2] The vehicle audio equipment company Blaupunkt was a subsidiary of Bosch until March 2009.[2]
SB LiMotive
In June 2008 Bosch formed SB LiMotive, a 50:50 joint company with Samsung SDI. The company held ground breaking ceremony for a 28.000 m2 lithium-ion battery cell manufacturing plant in September 2009 and it is scheduled to start production for hybrid vehicles in 2011 and for electric vehicles in 2012 The plant will generate a 1.000 jobs in Ulsan, Korea in addition to the 500 employees in Korea, Germany and the USA. SB LiMotive was officially ended in September 2012 with both companies focusing on automotive batteries alone.
Corporate affairs
Robert Bosch GmbH, including its wholly owned subsidiaries such as Robert Bosch LLC in North America, is unusual in that it is an extremely large, privately owned corporation that is almost entirely (92%) owned by a charitable foundation. Thus, while most of the profits are invested back into the corporation to build for the future and sustain growth, nearly all of the profits distributed to shareholders are devoted to humanitarian causes.
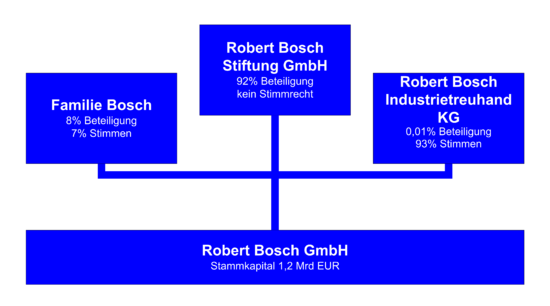
As shown in the diagram (above), the Robert Bosch Stiftung (Robert Bosch Foundation) holds 92% of the shares (Beteiligung) of Robert Bosch GmbH, but no voting rights (Stimmrecht). The Robert Bosch Industrietreuhand KG (Robert Bosch Industrial Trust KG), with old members of the company management, agents of the Bosch family, and other eminent people from the industry (such as Jürgen Hambrecht, CEO of BASF), have 93% of the votes (Stimmen), but no shares (0.01%). The remaining 8% of shares and 7%[2] of voting-rights are held by the descendants of the company founder Robert Bosch (Familie Bosch).[26]
For example, in 2004, the net profit was US$2.1 billion, but only US$78 million was distributed as dividends to shareholders. Of that figure, US$72 million was distributed to the charitable foundation, and the other US$6 million to Bosch family stockholders. The remaining 96% of the profits were invested back into the company. In its core automotive technology business, Bosch invests 9% of its revenue on research and development, nearly double the industry average of 4.7%.[27]
Accreditations
Almost all Bosch locations are both ISO 9001 certified (quality) and ISO 14001 certified (environmental protection).[28] In addition to that, their management is compliant with OHSAS 18001.
See also
References
- ↑ "German Business Confidence Fell for a Second Month in April". Bloomberg Businessweek. 21 April 2011. Retrieved 23 September 2011.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "Robert Bosch GmbH Company Profile". Yahoo! Finance. Yahoo!.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 "Annual Report 2010". Robert Bosch GmbH. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
- ↑ About Bosch in 2012
- ↑ "Atco History Page". Atco.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-06-19.
- ↑ Robert Bosch LLC. "Robert Bosch LLC. - Media Center" (in (German)). Bosch-press.com. Retrieved 2011-06-19.
- ↑ "Robert Bosch GmbH - Business/Economy". Bosch-presse.de. Retrieved 2011-06-19.
- ↑ "Bosch 2010 Annual Report" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-06-01.
- ↑ Ferreira, Colleen (2010-11-16). "Bosch plant to close in South Bend". WSBT-TV. Retrieved 2010-11-17.
- ↑ "About Bosch in the USA". Bosch. Retrieved 2008-03-11.
- ↑ Knight, Kevin (December 2013). "UNDERSTANDING MOBILTY AT BOSCH FRANCE WITH VALÉRIE KURZ AND EMILIE BENARD". Expatriates Magazine (3): 10. Retrieved 2012-12-18.
- ↑ "The Bosch Group - Locations". Bosch.com. 2010-03-24. Retrieved 2011-06-19.
- ↑ Bosch says it has contract for diesel-hybrid parts - Automotive News Europe
- ↑ "Terms of Use". BoschTools.com. Retrieved 2009-04-29.
- ↑ http://hoovers.com/free/search/simple/xmillion/index.xhtml?query_string=Bosch+Tools&which=company&page=1&search_x=28&search_y=12
- ↑ "Site where many Bosch Red Dot Awards are listed". En.red-dot.org. Retrieved 2012-06-01.
- ↑ "2011 EID Silver Award for Miter Saw". Appliancedesign.com. 2012-01-25. Retrieved 2012-06-01.
- ↑ Anthenaeum, Chicago. "2012 Good Design Awards". Chicago Anthenaeum. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ↑ sangl, sangl. "IDEA Award Finalists". IDSA. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ↑ Gordon, Paul (2008-09-19). "Bosch Buys Nelson and Sunterra". Pjstar.com. Retrieved 2012-06-01.
- ↑ Chelsie Woods, Security Systems News. "Bosch completes Philips CSI buy." Dec 1, 2002. Retrieved Apr 5, 2012.
- ↑ Andrea Gural, Security Director News. "Ribinski hands over Bosch reins." Oct, 2005. Retrieved Apr 5, 2012.
- ↑ EE Times Asia. "Bosch to acquire Philips CSI business unit." Aug 12, 2002. Retrieved Apr 5, 2012.
- ↑ Matthew Harwood, Security Management. "Infrared Night-Vision Innovator Extreme CCTV to Become Part of Bosch." Dec 20, 2007. Retrieved Apr 5, 2012.
- ↑ Homeland Security News Wire. "Bosch acquires Extreme CCTV." Mar 5, 2008. Retrieved Apr 5, 2012.
- ↑ Robert Bosch Stiftung: Über uns, retrieved on 2008-08-11
- ↑ Joann Muller (2005-11-28). "Parts for the Sensitive Car". Forbes magazine.
- ↑ "Corporate Social Responsibility Report 2010" (PDF). Bosch. Retrieved 28 Jan 2012.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Robert Bosch GmbH. |
- Robert Bosch GmbH official website
- Profile at Yahoo! Finance: Bosch-YF-profile
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

