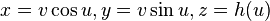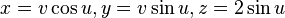Right conoid
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

A right conoid as a ruled surface.
In geometry, a right conoid is a ruled surface generated by a family of straight lines that all intersect perpendicularly a fixed straight line, called the axis of the right conoid.
Using a Cartesian coordinate system in three-dimensional space, if we take the z-axis to be the axis of a right conoid, then the right conoid can be represented by the parametric equations:
where h(u) is some function for representing the height of the moving line.
Examples

Generation of a typical right conoid
A typical example of right conoids is given by the parametric equations:
The image on the right shows how the coplanar lines generate the right conoid.
Other right conoids include:
- Helicoid:
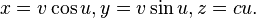
- Whitney umbrella:

- Wallis’s conical edge:
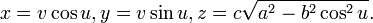
- Plücker’s conoid:

- hyperbolic paraboloid:
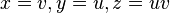 (with x-axis and y-axis as its axes).
(with x-axis and y-axis as its axes).
See also
External links
- Hazewinkel, Michiel, ed. (2001), "Conoid", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4
- Right Conoid from MathWorld.
- Plücker's conoid from MathWorld
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.